Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy
| Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy | |
|---|---|
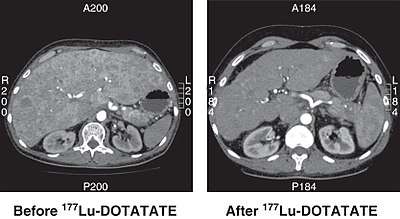 CT scan of non-functioning pancreatic NET before and 6 months after successful treatment with four cycles of 177Lu-DOTATATE. | |
| Specialty | oncology |
Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is a type of unsealed source radiotherapy, using a radiopharmaceutical which targets peptide receptors to deliver localised treatment, typically for neuroendocrine tumours (NETs).[1]
Mechanism
A key advantage of PRRT over other methods of radiotherapy is the ability to target delivery of therapeutic radionuclides directly to the tumour or target site. This works because some tumours have an abundance (overexpression) of peptide receptors, compared to normal tissue. A radioactive substance can be combined with a relevant peptide (or its analogue) so that it preferentially binds to the tumour.[2][3] With a gamma emitter as the radionuclide, the technique can be used for imaging with a gamma camera or PET scanner to locate tumours. When paired with alpha or beta emitters, therapy can be achieved, as in PRRT.[4]
The current generation of PRRT targets somatostatin receptors, with a range of analogue materials such as octreotide and other DOTA compounds. These are combined with indium-111, lutetium-177 or yttrium-90 for treatment.[5] 111In is primarily used for imaging alone, however in addition to its gamma emmission there are also auger electrons emitted, which can have a therapeutic effect in high doses.[6]

PRRT radiopharmaceuticals are constructed with three components; the radionuclide, chelator, and somatostatin analogue (peptide). The radionuclide delivers the actual therapeutic effect, (or photons for imaging). The chelator is the essential link between the radionuclide and peptide. For 177Lu and 90Y this is typically DOTA (tetracarboxylic acid, and its variants) and DTPA (pentetic acid) for 111In.[7] Other chelators known as NOTA (triazacyclononane triacetic acid) and HYNIC (hydrazinonicotinamide) have also been experimented with, albeit more for imaging applications.[8][9] The somatostatin analogue affects biodistribution of the radionuclide, and therefore how effectively any treatment effect can be targeted. Changes affect which somatostatin receptor is most strongly targeted. For example, DOTA-lanreotide (DOTALAN) has a lower affinity for receptor 2 and a higher affinity for receptor 5 compared to DOTA-octreotide (DOTATOC).[6][10]
Applications
The body of research on the effectiveness of current PRRT is promising, but limited. Complete or partial treatment response has been seen in 20-30% of patients in trials treated with 177Lu-DOTATATE or 90Y-DOTATOC, the most widely used PRRT drugs.[1][11][12][13] When it comes to comparing these two PRRT, Y-labeled and Lu-labeled PRRTs, it appears that Y-labeled is more effective for larger tumors, while Lu-labeled is better for smaller and primary tumors. The lack of ɤ-emission with Y-labeled PPRTs is also an important difference between Lu peptides and Y peptide. In particular, with Y-labeled PRRT it becomes difficult to set up a dose of radiations specific to the patient's needs. [14] In most cases PRRT is used for cancers of the gastroenteropancreatic and bronchial tracts, and in some cases phaeochromocytoma, paraganglioma, neuroblastoma or medullary thyroid carcinoma.[1] Various approaches to approve effectiveness and limit side effects are being investigated, including radiosensitising drugs, fractionation regimes and new radionuclides.[15] Alpha emitters, which have much shorter ranges in tissue (limiting the effect on nearby healthy tissue), such as bismuth-213 or actinium-225 labeled DOTATOC are of particular interest.[16]
Dosimetry
Therapeutic PRRT treatments typically involve several gigabecquerels (GBq) of activity.[17] Several radiopharmaceuticals allow simultaneous imaging and therapy, enabling precise dosimetric estimates to be made. For example, the bremsstrahlung emission from 90Y and gamma emissions from 177Lu can be detected by a gamma camera. In other cases, imaging can be performed by labelling a suitable radionuclide to the same peptide as used for therapy.[18] Radionuclides that can be used for imaging include gallium-68, technetium-99m and fluorine-18.[17]
Currently used peptides can result in high kidney doses, as the radiopharmaceutical is retained for relatively long periods. Renal protection is therefore used in some cases, taking the form of alternative substances that reduce the uptake of the kidneys.[5][17][19]
Availability
PRRT is not yet widely available, with various radiopharmaceuticals at different stages of clinical trials. The cost of small volume production of the relevant radionuclides is high.[20] The cost of Lutathera, a commercial 177Lu-DOTATATE product, has been quoted by the manufacturer as £71,500 (€80,000 or $94,000 in July 2018) for 4 administrations of 7.4 GBq.[21]
United States
177Lu-DOTATATE (international nonproprietary name: lutetium (177lu) oxodotreotide) was approved by the FDA in early 2018, for treatment of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs).[22][23]
Europe
Marketing authorisation for 177Lu-DOTATATE was granted by the European Medicines Agency on 26 September 2017.[24] 90Y-DOTATOC (international nonproprietary name: yttrium (90Y) edotreotide) is designated as an orphan drug but has not yet received marketing authorisation.[25]
United Kingdom
In guidance published in August 2018, Lutetium (177Lu) oxodotreotide was recommended by NICE for treating unresectable or metastatic neuroendocrine tumours.[26]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Zaknun, John J.; Bodei, L.; Mueller-Brand, J.; Pavel, M. E.; Baum, R. P.; Hörsch, D.; O’Dorisio, M. S.; O’Dorisiol, T. M.; Howe, J. R.; Cremonesi, M.; Kwekkeboom, D. J. (7 February 2013). "The joint IAEA, EANM, and SNMMI practical guidance on peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRNT) in neuroendocrine tumours". European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 40 (5): 800–816. doi:10.1007/s00259-012-2330-6. PMC 3622744.
- ↑ "Fact Sheet: What Is Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT)?". SNMMI. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ↑ Reubi, Jean Claude (August 2003). "Peptide Receptors as Molecular Targets for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy". Endocrine Reviews. 24 (4): 389–427. doi:10.1210/er.2002-0007. PMID 12920149.
- ↑ Dash, Ashutosh; Chakraborty, Sudipta; Pillai, Maroor Raghavan Ambikalmajan; Knapp, Furn F. (Russ) (March 2015). "Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy: An Overview". Cancer Biotherapy & Radiopharmaceuticals. 30 (2): 47–71. doi:10.1089/cbr.2014.1741. PMID 25710506.
- 1 2 van Essen, Martijn; Krenning, Eric P.; Kam, Boen L. R.; de Jong, Marion; Valkema, Roelf; Kwekkeboom, Dik J. (2 June 2009). "Peptide-receptor radionuclide therapy for endocrine tumors". Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 5 (7): 382–393. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2009.105. PMID 19488074.
- 1 2 Speer, Tod W. (2012). Targeted Radionuclide Therapy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 40. ISBN 9781451153262.
- ↑ Bombardieri, Emilio; Seregni, Ettore; Evangelista, Laura; Chiesa, Carlo; Chiti, Arturo (2018). Clinical Applications of Nuclear Medicine Targeted Therapy. Springer. p. 213. ISBN 9783319630670.
- ↑ SAW, MAUNG MAUNG; Peitl, Petra; Velikyan, Irina (June 2012). "Medicinal Radiopharmaceutical Chemistry of Metal Radiopharmaceuticals". COSMOS. 08 (01): 11–81. doi:10.1142/S0219607712300044.
- ↑ Fani, Melpomeni; Peitl, Petra; Velikyan, Irina (15 March 2017). "Current Status of Radiopharmaceuticals for the Theranostics of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms". Pharmaceuticals. 10 (4): 30. doi:10.3390/ph10010030. PMC 5374434.
- ↑ Stigbrand, Torgny; Carlsson, Jorgen; Adams, Gregory P. (2008). Targeted Radionuclide Tumor Therapy: Biological Aspects. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 122. ISBN 9781402086960.
- ↑ Kjaer, A; Knigge, U (June 2015). "Use of radioactive substances in diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine tumors". Scandinavian journal of gastroenterology. 50 (6): 740–7. doi:10.3109/00365521.2015.1033454. PMC 4487540.
- ↑ Cives, Mauro; Strosberg, Jonathan (20 February 2017). "Radionuclide Therapy for Neuroendocrine Tumors". Current Oncology Reports. 19 (2). doi:10.1007/s11912-017-0567-8. PMID 28220446.
- ↑ Bison, Sander M.; Konijnenberg, Mark W.; Melis, Marleen; Pool, Stefan E.; Bernsen, Monique R.; Teunissen, Jaap J. M.; Kwekkeboom, Dik J.; de Jong, Marion (5 March 2014). "Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy using radiolabeled somatostatin analogs: focus on future developments". Clinical and Translational Imaging. 2 (1): 55–66. doi:10.1007/s40336-014-0054-2. PMC 3991004.
- ↑ Dash, Ashutosh; Chakraborty, Sudipta; Pillai, Maroor Raghavan Ambikalmajan; Knapp, Furn F. (Russ) (March 2015). "Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy: An Overview". Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals. 30 (2): 47–71. doi:10.1089/cbr.2014.1741. ISSN 1084-9785.
- ↑ Sabet, Amir; Biersack, Hans-Jürgen; Ezziddin, Samer (January 2016). "Advances in Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy". Seminars in Nuclear Medicine. 46 (1): 40–46. doi:10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2015.09.005. PMID 26687856.
- ↑ Lee, Sze Ting; Kulkarni, Harshad R.; Singh, Aviral; Baum, Richard P. (2017). "Theranostics of Neuroendocrine Tumors". Visceral Medicine. 33 (5): 358–366. doi:10.1159/000480383. PMC 5697502.
- 1 2 3 IAEA (2013). Practical guidance on peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRNT) for neuroendocrine tumors. IAEA Human Health Series No. 20. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency. ISBN 978-92-0-129210-0.
- ↑ Cremonesi, M; Botta, F; Di Dia, A; Ferrari, M; Bodei, L; De Cicco, C; Rossi, A; Bartolomei, M; Mei, R; Severi, S; Salvatori, M; Pedroli, G; Paganelli, G (February 2010). "Dosimetry for treatment with radiolabelled somatostatin analogues. A review". The quarterly journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 54 (1): 37–51. PMID 20168285.
- ↑ Rolleman, Edgar J.; Melis, Marleen; Valkema, Roelf; Boerman, Otto C.; Krenning, Eric P.; de Jong, Marion (14 November 2009). "Kidney protection during peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with somatostatin analogues". European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 37 (5): 1018–1031. doi:10.1007/s00259-009-1282-y. PMID 19915842.
- ↑ Dash, Ashutosh; Pillai, Maroor Raghavan Ambikalmajan; Knapp, Furn F. (17 February 2015). "Production of 177Lu for Targeted Radionuclide Therapy: Available Options". Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 49 (2): 85–107. doi:10.1007/s13139-014-0315-z. PMC 4463871.
- ↑ "Information about lutetium (177Lu) oxodotreotide". NICE. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. 29 August 2018. Retrieved 3 September 2018.
- ↑ "Lutetium Lu 177 Dotatate Approved by FDA". Cancer Discovery. 8 (4): OF2–OF2. April 2018. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2018-021.
- ↑ Office of the Commissioner (26 January 2018). "FDA approves new treatment for certain digestive tract cancers". Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
- ↑ "Lutathera". European Medicines Agency. Retrieved 24 May 2018.
- ↑ "Yttrium (90Y) edotreotide". European Medicines Agency. Retrieved 24 May 2018.
- ↑ "Lutetium (177Lu) oxodotreotide for treating unresectable or metastatic neuroendocrine tumours [TA539]". National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. 29 August 2018. Retrieved 3 September 2018.