Partial/total eclipses on the Moon
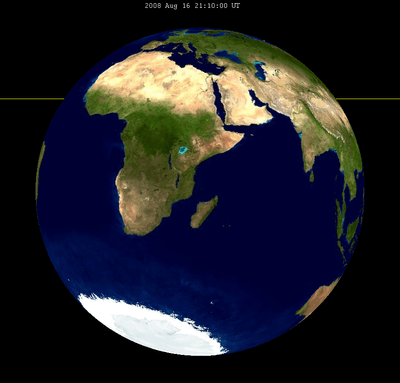
Partial/total Solar eclipses on the Moon are caused when the Earth passes in front of the Sun, blocking a part its light in one part and the whole light in the other. Viewers on Earth will see a partial lunar eclipse.[1]
During its eclipses, the Earth will be in new phase, completely dark, except for moonshine and sunlight refracted through the earth's atmosphere, visible as a ring of light.[2]
The next partial-total solar eclipse on the Moon will be partial-total on August 7, 2017 with the southern portion of the Southern Hemisphere seeing totality.
Description
Seen on Earth as a partial lunar eclipse, unlike the Earth where a total eclipse only occurs in a small spot while the remainder of a solar eclipse are total, on the Moon, a part is shown as partial and a part is shown is total as the center of the Earth's shadow's coverage totality is more larger than the Moon on Earth. In some eclipses, about 15-20% of a surface of the moon covered by the center of the Earth's shadow sees totality where the Earth eclipses the sun, some eclipses has about 75-80% of the surface covered by the center of the Earth's shadow while the remainder visilbly as partial, some has 50/50 covered by the center of the Earth's shadow and visibly as partial.
Length
The shortest can be for around 2 hours and the longest can be up to 5–6 hours.[1]
See also
- Solar eclipses on the Moon
- Partial eclipse - Partial eclipses that are seen on Earth that its light are partly blocked by the Moon for an hour or more in one spot
- Partial lunar eclipse - Some of its lunar eclipses that are seen on Earth
- Partial eclipses on the Moon - one part of the Moon is visible as partial and the other being not visible
References
- 1 2 "Туманность Андромеды (Lunar eclipses)". xn--31-7lc.xn--p1ai. Retrieved 2017-08-03.
- ↑ The Earth will be in new phase, completely dark, except for moonshine and sunlight refracted through the earth's atmosphere, visible as a ring of light.