Pallas family
The Pallas or Palladian family of asteroids is a grouping of B-type asteroids at very high inclinations in the intermediate asteroid belt (Cellino et al. (2002)). It was first noted by Kiyotsugu Hirayama in 1928.
The namesake of the family is 2 Pallas, an extremely large asteroid with a mean diameter of about 512 km.[1] The remaining bodies are far smaller; the largest is 5222 Ioffe with an estimated diameter of 22 km. This, along with the preponderance of the otherwise rare B spectral type among its members, indicates that this is likely a cratering family composed of ejecta from impacts on Pallas. Another suspected Palladian is 3200 Phaethon, the parent body of the Geminid meteor shower.[2]
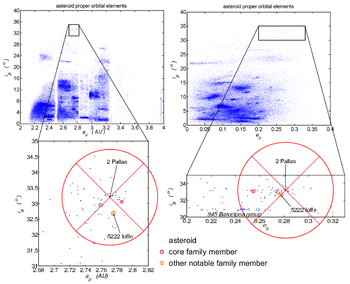
From the diagram, their proper orbital elements lie in the approximate ranges
| ap | ep | ip | |
|---|---|---|---|
| min | 2.71 AU | 0.25 | 32° |
| max | 2.79 AU | 0.31 | 34° |
At the present epoch, the range of osculating orbital elements of the members (by comparison to the MPCORB database ) is about
| a | e | i | |
|---|---|---|---|
| min | 2.71 AU | 0.13 | 30° |
| max | 2.79 AU | 0.37 | 38° |
References
- ↑ Carry, B.; et al. (2009). "Physical properties of (2) Pallas" (PDF). Icarus. 205 (2): 460–472. arXiv:0912.3626. Bibcode:2010Icar..205..460C. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2009.08.007. Retrieved 13 September 2015.
- ↑ "Exploding Clays Drive Geminids Sky Show?", 2010 October 12
- A. Lemaitre & A. Morbidelli, Proper elements for highly inclined asteroidal orbits, Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy, Vol. 60, pp. 29 (1994).
- Y. Kozai Secular perturbations of asteroids and comets In: Dynamics of the solar system; Proceedings of the Symposium, Tokyo, Japan, May 23–26, 1978. Dordrecht, D. Reidel Publishing Co., 1979, p. 231-236; Discussion, p. 236, 237.
- A. Cellino et al. "Spectroscopic Properties of Asteroid Families", in Asteroids III, p. 633-643, University of Arizona Press (2002). (Table on page 636, in particular).
- MPCORB orbit database