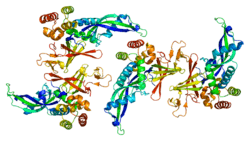POLR2G
DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLR2G gene.[5][6]
This gene encodes the seventh largest subunit of RNA polymerase II, the polymerase responsible for synthesizing messenger RNA in eukaryotes. In yeast, the association of this subunit with the polymerase under suboptimal growth conditions indicates it may play a role in regulating polymerase function.[7]
Interactions
POLR2G has been shown to interact with TAF15,[8] POLR2C,[9] POLR2H[9] and POLR2E.[9]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000168002 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000071662 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Khazak V, Sadhale PP, Woychik NA, Brent R, Golemis EA (December 1995). "Human RNA polymerase II subunit hsRPB7 functions in yeast and influences stress survival and cell morphology". Mol Biol Cell. 6 (7): 759–75. doi:10.1091/mbc.6.7.759. PMC 301239. PMID 7579693.
- ↑ Schoen TJ, Chandrasekharappa SC, Guru SC, Mazuruk K, Chader GJ, Rodriguez IR (August 1997). "Human gene for the RNA polymerase II seventh subunit (hsRPB7): structure, expression and chromosomal localization". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1353 (1): 39–49. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(97)00041-9. PMID 9256063.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: POLR2G polymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide G".
- ↑ Bertolotti, A; Melot T; Acker J; Vigneron M; Delattre O; Tora L (March 1998). "EWS, but not EWS-FLI-1, is associated with both TFIID and RNA polymerase II: interactions between two members of the TET family, EWS and hTAFII68, and subunits of TFIID and RNA polymerase II complexes". Mol. Cell. Biol. UNITED STATES. 18 (3): 1489–97. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.3.1489. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 108863. PMID 9488465.
- 1 2 3 Acker, J; de Graaff M; Cheynel I; Khazak V; Kedinger C; Vigneron M (July 1997). "Interactions between the human RNA polymerase II subunits". J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 272 (27): 16815–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.27.16815. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9201987.
Further reading
- Jeang KT (1998). "Tat, Tat-associated kinase, and transcription". J. Biomed. Sci. 5 (1): 24–7. doi:10.1007/BF02253352. PMID 9570510.
- Yankulov K, Bentley D (1998). "Transcriptional control: Tat cofactors and transcriptional elongation". Curr. Biol. 8 (13): R447–9. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(98)70289-1. PMID 9651670.
- Romano G, Kasten M, De Falco G, et al. (2000). "Regulatory functions of Cdk9 and of cyclin T1 in HIV tat transactivation pathway gene expression". J. Cell. Biochem. 75 (3): 357–68. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19991201)75:3<357::AID-JCB1>3.0.CO;2-K. PMID 10536359.
- Marcello A, Zoppé M, Giacca M (2002). "Multiple modes of transcriptional regulation by the HIV-1 Tat transactivator". IUBMB Life. 51 (3): 175–81. doi:10.1080/152165401753544241. PMID 11547919.
- Stevens M, De Clercq E, Balzarini J (2007). "The regulation of HIV-1 transcription: molecular targets for chemotherapeutic intervention". Med Res Rev. 26 (5): 595–625. doi:10.1002/med.20081. PMID 16838299.
- Harrich D, McMillan N, Munoz L, et al. (2007). "Will diverse Tat interactions lead to novel antiretroviral drug targets?". Current drug targets. 7 (12): 1595–606. doi:10.2174/138945006779025338. PMID 17168834.
- Kato H, Sumimoto H, Pognonec P, et al. (1992). "HIV-1 Tat acts as a processivity factor in vitro in conjunction with cellular elongation factors". Genes Dev. 6 (4): 655–66. doi:10.1101/gad.6.4.655. PMID 1559613.
- Southgate C, Zapp ML, Green MR (1990). "Activation of transcription by HIV-1 Tat protein tethered to nascent RNA through another protein". Nature. 345 (6276): 640–2. Bibcode:1990Natur.345..640S. doi:10.1038/345640a0. PMID 2190099.
- Wu-Baer F, Sigman D, Gaynor RB (1995). "Specific binding of RNA polymerase II to the human immunodeficiency virus trans-activating region RNA is regulated by cellular cofactors and Tat". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (16): 7153–7. Bibcode:1995PNAS...92.7153W. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.16.7153. PMC 41297. PMID 7638159.
- Herrmann CH, Rice AP (1995). "Lentivirus Tat proteins specifically associate with a cellular protein kinase, TAK, that hyperphosphorylates the carboxyl-terminal domain of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II: candidate for a Tat cofactor". J. Virol. 69 (3): 1612–20. PMC 188757. PMID 7853496.
- Keen NJ, Gait MJ, Karn J (1996). "Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 Tat is an integral component of the activated transcription-elongation complex". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (6): 2505–10. Bibcode:1996PNAS...93.2505K. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.6.2505. PMC 39827. PMID 8637904.
- Yang X, Herrmann CH, Rice AP (1996). "The human immunodeficiency virus Tat proteins specifically associate with TAK in vivo and require the carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II for function". J. Virol. 70 (7): 4576–84. PMC 190394. PMID 8676484.
- Agostini I, Navarro JM, Rey F, et al. (1996). "The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr transactivator: cooperation with promoter-bound activator domains and binding to TFIIB". J. Mol. Biol. 261 (5): 599–606. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0485. PMID 8800208.
- Zhou Q, Sharp PA (1996). "Tat-SF1: cofactor for stimulation of transcriptional elongation by HIV-1 Tat". Science. 274 (5287): 605–10. Bibcode:1996Sci...274..605Z. doi:10.1126/science.274.5287.605. PMID 8849451.
- Okamoto H, Sheline CT, Corden JL, et al. (1996). "Trans-activation by human immunodeficiency virus Tat protein requires the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (21): 11575–9. Bibcode:1996PNAS...9311575O. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.21.11575. PMC 38099. PMID 8876177.
- Chun RF, Jeang KT (1996). "Requirements for RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain for activated transcription of human retroviruses human T-cell lymphotropic virus I and HIV-1". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (44): 27888–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.44.27888. PMID 8910388.
- Parada CA, Roeder RG (1996). "Enhanced processivity of RNA polymerase II triggered by Tat-induced phosphorylation of its carboxy-terminal domain". Nature. 384 (6607): 375–8. Bibcode:1996Natur.384..375P. doi:10.1038/384375a0. PMID 8934526.
- García-Martínez LF, Ivanov D, Gaynor RB (1997). "Association of Tat with purified HIV-1 and HIV-2 transcription preinitiation complexes". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (11): 6951–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.11.6951. PMID 9054383.
- Cujec TP, Cho H, Maldonado E, et al. (1997). "The human immunodeficiency virus transactivator Tat interacts with the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (4): 1817–23. PMC 232028. PMID 9121429.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.