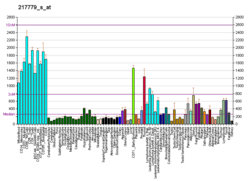
PNRC2
Proline-rich nuclear receptor coactivator 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PNRC2 gene.[5][6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000189266 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028675 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Zhou D, Chen S (Sep 2001). "PNRC2 is a 16 kDa coactivator that interacts with nuclear receptors through an SH3-binding motif". Nucleic Acids Res. 29 (19): 3939–48. doi:10.1093/nar/29.19.3939. PMC 60244. PMID 11574675.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: PNRC2 proline-rich nuclear receptor coactivator 2".
Further reading
- Zhou D, Quach KM, Yang C, et al. (2000). "PNRC: a proline-rich nuclear receptor coregulatory protein that modulates transcriptional activation of multiple nuclear receptors including orphan receptors SF1 (steroidogenic factor 1) and ERRalpha1 (estrogen related receptor alpha-1)". Mol. Endocrinol. 14 (7): 986–98. doi:10.1210/me.14.7.986. PMID 10894149.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, et al. (2001). "Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells". Genome Res. 10 (10): 1546–60. doi:10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Hentschke M, Borgmeyer U (2004). "Identification of PNRC2 and TLE1 as activation function-1 cofactors of the orphan nuclear receptor ERRgamma". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 312 (4): 975–82. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.025. PMID 14651967.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE, et al. (2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature. 441 (7091): 315–21. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
External links
- PNRC2 protein, human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- NURSA C185
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.