PKIA
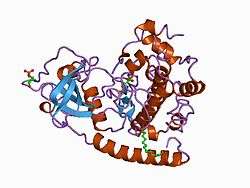
cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PKIA gene.[5][6]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) inhibitor family. This protein was demonstrated to interact with and inhibit the activities of both C alpha and C beta catalytic subunits of the PKA. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been reported.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000171033 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027499 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Olsen SR, Uhler MD (Feb 1992). "Inhibition of protein kinase-A by overexpression of the cloned human protein kinase inhibitor". Mol Endocrinol. 5 (9): 1246–56. doi:10.1210/mend-5-9-1246. PMID 1770951.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: PKIA protein kinase (cAMP-dependent, catalytic) inhibitor alpha".
Further reading
- Olsen SR, Uhler MD (1991). "Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for an inhibitor protein of cAMP-dependent protein kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (17): 11158–62. PMID 1710219.
- Knighton DR, Zheng JH, Ten Eyck LF, et al. (1991). "Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase". Science. 253 (5018): 414–20. doi:10.1126/science.1862343. PMID 1862343.
- Van Patten SM, Heisermann GJ, Cheng HC, Walsh DA (1987). "Tyrosine kinase catalyzed phosphorylation and inactivation of the inhibitor protein of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (7): 3398–403. PMID 2434500.
- Scott JD, Fischer EH, Demaille JG, Krebs EG (1985). "Identification of an inhibitory region of the heat-stable protein inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82 (13): 4379–83. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.13.4379. PMC 390417. PMID 2989819.
- Scott JD, Glaccum MB, Fischer EH, Krebs EG (1986). "Primary-structure requirements for inhibition by the heat-stable inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83 (6): 1613–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.6.1613. PMC 323133. PMID 3456605.
- Wen W, Taylor SS, Meinkoth JL (1995). "The expression and intracellular distribution of the heat-stable protein kinase inhibitor is cell cycle regulated". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (5): 2041–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.5.2041. PMID 7836431.
- Baude EJ, Dignam SS, Olsen SR, et al. (1994). "Glutamic acid 203 of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit participates in the inhibition by two isoforms of the protein kinase inhibitor". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (3): 2316–23. PMID 7905001.
- Baude EJ, Dignam SS, Reimann EM, Uhler MD (1994). "Evidence for the importance of hydrophobic residues in the interactions between the cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit and the protein kinase inhibitors". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (27): 18128–33. PMID 8027074.
- Fritz CC, Green MR (1997). "HIV Rev uses a conserved cellular protein export pathway for the nucleocytoplasmic transport of viral RNAs". Curr. Biol. 6 (7): 848–54. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00608-5. PMID 8805303.
- Zimmermann B, Chiorini JA, Ma Y, et al. (1999). "PrKX is a novel catalytic subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulated by the regulatory subunit type I". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (9): 5370–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.9.5370. PMID 10026146.
- Yu J, Yu L, Chen Z, et al. (2002). "Protein inhibitor of neuronal nitric oxide synthase interacts with protein kinase A inhibitors". Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 99 (2): 145–9. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(02)00104-3. PMID 11978406.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Gassel M, Breitenlechner CB, Rüger P, et al. (2003). "Mutants of protein kinase A that mimic the ATP-binding site of protein kinase B (AKT)". J. Mol. Biol. 329 (5): 1021–34. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00518-7. PMID 12798691.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.