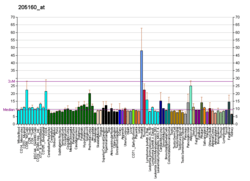
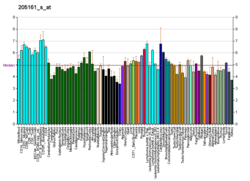
PEX11A
Peroxisomal membrane protein 11A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX11A gene.[5][6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000166821 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030545 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Schrader M, Reuber BE, Morrell JC, Jimenez-Sanchez G, Obie C, Stroh TA, Valle D, Schroer TA, Gould SJ (Dec 1998). "Expression of PEX11beta mediates peroxisome proliferation in the absence of extracellular stimuli". J Biol Chem. 273 (45): 29607–14. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.45.29607. PMID 9792670.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: PEX11A peroxisomal biogenesis factor 11A".
Further reading
- Abe I, Okumoto K, Tamura S, Fujiki Y (1998). "Clofibrate-inducible, 28-kDa peroxisomal integral membrane protein is encoded by PEX11". FEBS Lett. 431 (3): 468–72. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00815-1. PMID 9714566.
- South ST, Gould SJ (1999). "Peroxisome Synthesis in the Absence of Preexisting Peroxisomes". J. Cell Biol. 144 (2): 255–66. doi:10.1083/jcb.144.2.255. PMC 2132891. PMID 9922452.
- Sacksteder KA, Jones JM, South ST, et al. (2000). "Pex19 Binds Multiple Peroxisomal Membrane Proteins, Is Predominantly Cytoplasmic, and Is Required for Peroxisome Membrane Synthesis". J. Cell Biol. 148 (5): 931–44. doi:10.1083/jcb.148.5.931. PMC 2174547. PMID 10704444.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Shimizu M, Akter MH, Emi Y, et al. (2007). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor subtypes differentially cooperate with other transcription factors in selective transactivation of the perilipin/PEX11 alpha gene pair". J. Biochem. 139 (3): 563–73. doi:10.1093/jb/mvj053. PMID 16567422.
- Orth T, Reumann S, Zhang X, et al. (2007). "The PEROXIN11 Protein Family Controls Peroxisome Proliferation in Arabidopsis". Plant Cell. 19 (1): 333–50. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.045831. PMC 1820951. PMID 17220199.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.