PAPOLG
Poly(A) polymerase gamma is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAPOLG gene.[5]
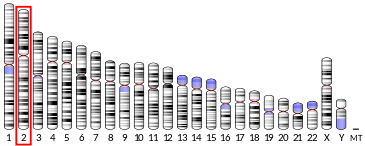
This gene encodes a member of the poly(A) polymerase family which catalyzes template-independent extension of the 3' end of a DNA/RNA strand. This enzyme shares 60% identity to the well characterized poly(A) polymerase II (PAPII) at the amino acid level. These two enzymes have similar organization of structural and functional domains. This enzyme is exclusively localized in the nucleus and exhibits both nonspecific and CPSF (cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor)/AAUAAA-dependent polyadenylation activity. This gene is located on chromosome 2 in contrast to the PAPII gene, which is located on chromosome 14.[5]
References
Further reading
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Topalian SL, Kaneko S, Gonzales MI, et al. (2001). "Identification and functional characterization of neo-poly(A) polymerase, an RNA processing enzyme overexpressed in human tumors". Mol. Cell. Biol. 21 (16): 5614–23. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.16.5614-5623.2001. PMC 87282. PMID 11463842.
- Kyriakopoulou CB, Nordvarg H, Virtanen A (2001). "A novel nuclear human poly(A) polymerase (PAP), PAP gamma". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (36): 33504–11. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104599200. PMID 11431479.
- Perumal K, Sinha K, Henning D, Reddy R (2001). "Purification, characterization, and cloning of the cDNA of human signal recognition particle RNA 3'-adenylating enzyme". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (24): 21791–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101905200. PMID 11287430.
- Weichs an der Glon C, Ashe M, Eggermont J, Proudfoot NJ (1993). "Tat-dependent occlusion of the HIV poly(A) site". EMBO J. 12 (5): 2119–28. PMC 413433. PMID 8491200.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.