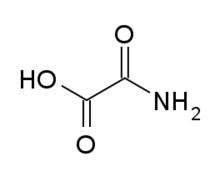
Oxamic acid
 | |
 Ball And Stick Model Of Oxamic Acid | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Oxamic acid[1] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Amino(oxo)acetic acid[1] | |
| Other names
2-Amino-2-oxoacetic acid Aminooxoacetic acid Oxalamic acid Oxamidic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H3NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 89.05 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 209 °C[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Oxamic acid is the organic compound with the formula H2NC(O)CO2H. It is a white, water-soluble solid. It is the monoamide of oxalic acid.[3] Oxamic acid inhibits Lactate dehydrogenase A.[4]
References
- 1 2 Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 415. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 3.430. ISBN 1439855110.
- ↑ "OXAMIC ACID". Pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-12-14.
- ↑ Miskimins, W. Keith; Ahn, Hyun Joo; Kim, Ji Yeon; Ryu, Sun; Jung, Yuh-Seog; Choi, Joon Young (2014). "Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effect of Phenformin and Oxamate". PLoS ONE. 9 (1): e85576. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085576. PMC 3897486. PMID 24465604.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.