OSTbeta
Organic solute transporter beta, also known as OST-beta, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the OSTB gene.[5][6]
Function
OST-beta together with OST-alpha is able to transport estrone sulfate, taurocholate, digoxin, and prostaglandin E2 across cell membranes.[6][7] The Ost-alpha / Ost-beta heterodimer, but not the individual subunits, stimulates sodium-independent bile acid uptake.[7] The heterodimer furthermore is essential for intestinal bile acid transport.[8]
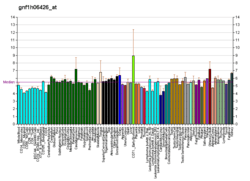
OST-alpha and OST-beta have high expression in the testis, colon, liver, small intestine, kidney, ovary, and adrenal gland.[6]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000186198 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000053862 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: OSTbeta organic solute transporter beta".
- 1 2 3 Seward DJ, Koh AS, Boyer JL, Ballatori N (July 2003). "Functional complementation between a novel mammalian polygenic transport complex and an evolutionarily ancient organic solute transporter, OSTalpha-OSTbeta". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (30): 27473–82. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301106200. PMID 12719432.
- 1 2 Dawson PA, Hubbert M, Haywood J, Craddock AL, Zerangue N, Christian WV, Ballatori N (February 2005). "The Heteromeric Organic Solute Transporter α-β, Ostα-Ostβ, Is an Ileal Basolateral Bile Acid Transporter". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (8): 6960–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M412752200. PMC 1224727. PMID 15563450.
- ↑ Rao A, Haywood J, Craddock AL, Belinsky MG, Kruh GD, Dawson PA (March 2008). "The organic solute transporter α-β, Ostα-Ostβ, is essential for intestinal bile acid transport and homeostasis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 (10): 3891–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0712328105. PMC 2268840. PMID 18292224.
Further reading
- Sun AQ, Balasubramaniyan N, Xu K, et al. (2007). "Protein-protein interactions and membrane localization of the human organic solute transporter". Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 292 (6): G1586–93. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00457.2006. PMID 17332473.
- Boyer JL, Trauner M, Mennone A, et al. (2006). "Upregulation of a basolateral FXR-dependent bile acid efflux transporter OSTalpha-OSTbeta in cholestasis in humans and rodents". Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 290 (6): G1124–30. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00539.2005. PMID 16423920.
- Ballatori N, Christian WV, Lee JY, et al. (2005). "OSTalpha-OSTbeta: a major basolateral bile acid and steroid transporter in human intestinal, renal, and biliary epithelia". Hepatology. 42 (6): 1270–9. doi:10.1002/hep.20961. PMID 16317684.
- Landrier JF, Eloranta JJ, Vavricka SR, Kullak-Ublick GA (2006). "The nuclear receptor for bile acids, FXR, transactivates human organic solute transporter-alpha and -beta genes". Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 290 (3): G476–85. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00430.2005. PMID 16269519.
- Lee H, Zhang Y, Lee FY, et al. (2006). "FXR regulates organic solute transporters alpha and beta in the adrenal gland, kidney, and intestine". J. Lipid Res. 47 (1): 201–14. doi:10.1194/jlr.M500417-JLR200. PMID 16251721.
- Dawson PA, Hubbert M, Haywood J, et al. (2005). "The Heteromeric Organic Solute Transporter α-β, Ostα-Ostβ, Is an Ileal Basolateral Bile Acid Transporter". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (8): 6960–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M412752200. PMC 1224727. PMID 15563450.
- Seward DJ, Koh AS, Boyer JL, Ballatori N (2003). "Functional complementation between a novel mammalian polygenic transport complex and an evolutionarily ancient organic solute transporter, OSTalpha-OSTbeta". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (30): 27473–82. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301106200. PMID 12719432.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.