Isotopes of neptunium
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Neptunium (93Np) is usually considered an artificial element, although trace quantities are found in nature, so thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all trace or artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized and identified was 239Np in 1940, produced by bombarding 238U with neutrons to produce 239U, which then underwent beta decay to 239Np.
Trace quantities are found in nature from neutron capture reactions by uranium atoms, a fact not discovered until 1951.
Twenty neptunium radioisotopes have been characterized, with the most stable being 237
Np
with a half-life of 2.14 million years, 236
Np
with a half-life of 154,000 years, and 235
Np
with a half-life of 396.1 days. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 4.5 days, and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 50 minutes. This element also has 4 meta states, with the most stable being 236m
Np
(t1/2 22.5 hours).
The isotopes of neptunium range in atomic weight from 225.0339 u (225
Np
) to 244.068 u (244
Np
). The primary decay mode before the most stable isotope, 237
Np
, is electron capture (with a good deal of alpha emission), and the primary mode after is beta emission. The primary decay products before 237
Np
are isotopes of uranium and protactinium, and the primary products after are isotopes of plutonium. Uranium-237 and neptunium-239 are regarded as the leading hazardous radioisotopes in the first hour-to-week period following nuclear fallout from a nuclear detonation, with Np-239 dominating "the spectrum for several days".[1][2]
Actinides vs fission products
Actinides and fission products by half-life | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinides[3] by decay chain | Half-life range (y) |
Fission products of 235U by yield[4] | ||||||
| 4n | 4n+1 | 4n+2 | 4n+3 | |||||
| 4.5–7% | 0.04–1.25% | <0.001% | ||||||
| 228Ra№ | 4–6 | † | 155Euþ | |||||
| 244Cmƒ | 241Puƒ | 250Cf | 227Ac№ | 10–29 | 90Sr | 85Kr | 113mCdþ | |
| 232Uƒ | 238Puƒ | 243Cmƒ | 29–97 | 137Cs | 151Smþ | 121mSn | ||
| 248Bk[5] | 249Cfƒ | 242mAmƒ | 141–351 |
No fission products | ||||
| 241Amƒ | 251Cfƒ[6] | 430–900 | ||||||
| 226Ra№ | 247Bk | 1.3 k – 1.6 k | ||||||
| 240Pu | 229Th | 246Cmƒ | 243Amƒ | 4.7 k – 7.4 k | ||||
| 245Cmƒ | 250Cm | 8.3 k – 8.5 k | ||||||
| 239Puƒ | 24.1 k | |||||||
| 230Th№ | 231Pa№ | 32 k – 76 k | ||||||
| 236Npƒ | 233Uƒ | 234U№ | 150 k – 250 k | ‡ | 99Tc₡ | 126Sn | ||
| 248Cm | 242Pu | 327 k – 375 k | 79Se₡ | |||||
| 1.53 M | 93Zr | |||||||
| 237Npƒ | 2.1 M – 6.5 M | 135Cs₡ | 107Pd | |||||
| 236U | 247Cmƒ | 15 M – 24 M | 129I₡ | |||||
| 244Pu№ | 80 M |
... nor beyond 15.7 M years[7] | ||||||
| 232Th№ | 238U№ | 235Uƒ№ | 0.7 G – 14.1 G | |||||
|
Legend for superscript symbols | ||||||||
Notable isotopes
Neptunium-235
Neptunium-235 has 142 neutrons and a half-life of 400 days. This isotope of Neptunium either decays by:
- Emitting an alpha particle: the decay energy is 5.2 MeV and the decay product is protactinium-231.
- Electron capture: the decay energy is 0.125 MeV and the decay product is uranium-235
This particular isotope of neptunium has a weight of 235.044 063 3 u.
Neptunium-236
Neptunium-236 has 143 neutrons and a half-life of 154,000 years. It can decay by the following methods:
- Electron capture: the decay energy is 0.93 MeV and the decay product is uranium-236. This usually decays (with a half-life of 23 million years) to thorium-232.
- Beta emission: the decay energy is 0.48 MeV and the decay product is plutonium-236. This usually decays (half-life 2.8 years) to uranium-232, which usually decays (half-life 69 years) to thorium-228 which decays in a few years to lead-208.
- Alpha emission: the decay energy is 5.007 MeV and the decay product is protactinium-232. This decays with a half-life of 1.3 days to uranium-232.
This particular isotope of neptunium has a mass of 236.04657 u. It is a fissile material with a critical mass of 6.79 kg.[8]
236
Np
is produced in small quantities via the (n,2n) and (γ,n) capture reactions of 237
Np
,[9] however it is nearly impossible to separate in any significant quantities from its parent 237
Np
.[10] It is for this reason that, despite its low critical mass and high neutron cross section, it has not been researched as a nuclear fuel in weapons or reactors.
Neptunium-237
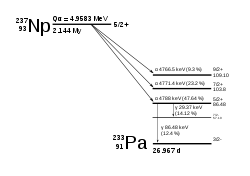
237
Np
decays via the neptunium series, which terminates with thallium-205, which is stable, unlike most other actinides, which decay to stable isotopes of lead.
In 2002, 237
Np
was shown to be capable of sustaining a chain reaction with fast neutrons, as in a nuclear weapon, with a critical mass of around 60 kg.[11] However, it has a low probability of fission on bombardment with thermal neutrons, which makes it unsuitable as a fuel for conventional nuclear power plants (as opposed to accelerator-driven systems, etc.).
237
Np
is the only neptunium isotope produced in significant quantity in the nuclear fuel cycle, both by successive neutron capture by uranium-235 (which fissions most but not all of the time) and uranium-236, or (n,2n) reactions where a fast neutron occasionally knocks a neutron loose from uranium-238 or isotopes of plutonium. Over the long term, 237
Np
also forms in spent nuclear fuel as the decay product of americium-241.
237
Np
was projected to be one of the most mobile nuclides at the Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository.
Use in plutonium-238 production
When exposed to neutron bombardment 237
Np
can capture a neutron and become 238
Pu
, this product being useful as an thermal energy source in a radio-isotope thermoelectric generator for the production of electricity and heat in deep space probes (such as the New Horizons and Voyager probes) and, of recent note, the Mars Science Laboratory (Curiosity rover). These applications are economically practical where photovoltaic power sources are weak or inconsistent due to probes being too far from the sun or rovers facing climate events that may obstruct sunlight for long periods. Space probes and rovers also make use of the heat output of the generator to keep their instruments and internals warm.[12]
List of isotopes
| nuclide symbol |
Z(p) | N(n) | isotopic mass (u) |
half-life | decay mode(s)[13][n 1] |
daughter isotope(s) |
nuclear spin and parity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| excitation energy | |||||||
| 223 Np [14] |
93 | 130 | 2.15(+100-52) µs | α | 219Pa | 9/2− | |
| 225 Np |
93 | 132 | 225.03391(8) | 3# ms [>2 µs] | α | 221Pa | 9/2−# |
| 226 Np |
93 | 133 | 226.03515(10)# | 35(10) ms | α | 222Pa | |
| 227 Np |
93 | 134 | 227.03496(8) | 510(60) ms | α (99.95%) | 223Pa | 5/2−# |
| β+ (.05%) | 227U | ||||||
| 228 Np |
93 | 135 | 228.03618(21)# | 61.4(14) s | β+ (59%) | 228U | |
| α (41%) | 224Pa | ||||||
| β+, SF (.012%) | (various) | ||||||
| 229 Np |
93 | 136 | 229.03626(9) | 4.0(2) min | α (51%) | 225Pa | 5/2+# |
| β+ (49%) | 229U | ||||||
| 230 Np |
93 | 137 | 230.03783(6) | 4.6(3) min | β+ (97%) | 230U | |
| α (3%) | 226Pa | ||||||
| 231 Np |
93 | 138 | 231.03825(5) | 48.8(2) min | β+ (98%) | 231U | (5/2)(+#) |
| α (2%) | 227Pa | ||||||
| 232 Np |
93 | 139 | 232.04011(11)# | 14.7(3) min | β+ (99.99%) | 232U | (4+) |
| α (.003%) | 228Pa | ||||||
| 233 Np |
93 | 140 | 233.04074(5) | 36.2(1) min | β+ (99.99%) | 233U | (5/2+) |
| α (.001%) | 229Pa | ||||||
| 234 Np |
93 | 141 | 234.042895(9) | 4.4(1) d | β+ | 234U | (0+) |
| 235 Np |
93 | 142 | 235.0440633(21) | 396.1(12) d | EC | 235U | 5/2+ |
| α (.0026%) | 231Pa | ||||||
| 236 Np [n 2] |
93 | 143 | 236.04657(5) | 1.54(6)×105 y | EC (87.3%) | 236U | (6−) |
| β− (12.5%) | 236Pu | ||||||
| α (.16%) | 232Pa | ||||||
| 236m Np |
60(50) keV | 22.5(4) h | EC (52%) | 236U | 1 | ||
| β− (48%) | 236Pu | ||||||
| 237 Np [n 2][n 3] |
93 | 144 | 237.0481734(20) | 2.144(7)×106 y | α | 233Pa | 5/2+ |
| SF (2×10−10%) | (various) | ||||||
| CD (4×10−12%) | 207Tl 30Mg | ||||||
| 238 Np |
93 | 145 | 238.0509464(20) | 2.117(2) d | β− | 238Pu | 2+ |
| 238m Np |
2300(200)# keV | 112(39) ns | |||||
| 239 Np |
93 | 146 | 239.0529390(22) | 2.356(3) d | β− | 239Pu | 5/2+ |
| 240 Np |
93 | 147 | 240.056162(16) | 61.9(2) min | β− | 240Pu | (5+) |
| 240m Np |
20(15) keV | 7.22(2) min | β− (99.89%) | 240Pu | 1(+) | ||
| IT (.11%) | 240Np | ||||||
| 241 Np |
93 | 148 | 241.05825(8) | 13.9(2) min | β− | 241Pu | (5/2+) |
| 242 Np |
93 | 149 | 242.06164(21) | 2.2(2) min | β− | 242Pu | (1+) |
| 242m Np |
0(50)# keV | 5.5(1) min | 6+# | ||||
| 243 Np |
93 | 150 | 243.06428(3)# | 1.85(15) min | β− | 243Pu | (5/2−) |
| 244 Np |
93 | 151 | 244.06785(32)# | 2.29(16) min | β− | 244Pu | (7−) |
- ↑ Abbreviations:
CD: Cluster decay
EC: Electron capture
IT: Isomeric transition
SF: Spontaneous fission - 1 2 Fissile nuclide
- ↑ Most common nuclide
Notes
- Values marked # are not purely derived from experimental data, but at least partly from systematic trends. Spins with weak assignment arguments are enclosed in parentheses.
- Uncertainties are given in concise form in parentheses after the corresponding last digits. Uncertainty values denote one standard deviation, except isotopic composition and standard atomic mass from IUPAC, which use expanded uncertainties.
References
- ↑ [Film Badge Dosimetry in Atmospheric Nuclear Tests, By Committee on Film Badge Dosimetry in Atmospheric Nuclear Tests, Commission on Engineering and Technical Systems, Division on Engineering and Physical Sciences, National Research Council. pg24-35]
- ↑ Bounding Analysis of Effects of Fractionation of Radionuclides in Fallout on Estimation of Doses to Atomic Veterans DTRA-TR-07-5. 2007
- ↑ Plus radium (element 88). While actually a sub-actinide, it immediately precedes actinium (89) and follows a three-element gap of instability after polonium (84) where no nuclides have half-lives of at least four years (the longest-lived nuclide in the gap is radon-222 with a half life of less than four days). Radium's longest lived isotope, at 1,600 years, thus merits the element's inclusion here.
- ↑ Specifically from thermal neutron fission of U-235, e.g. in a typical nuclear reactor.
- ↑ Milsted, J.; Friedman, A. M.; Stevens, C. M. (1965). "The alpha half-life of berkelium-247; a new long-lived isomer of berkelium-248". Nuclear Physics. 71 (2): 299. Bibcode:1965NucPh..71..299M. doi:10.1016/0029-5582(65)90719-4.
"The isotopic analyses disclosed a species of mass 248 in constant abundance in three samples analysed over a period of about 10 months. This was ascribed to an isomer of Bk248 with a half-life greater than 9 y. No growth of Cf248 was detected, and a lower limit for the β− half-life can be set at about 104 y. No alpha activity attributable to the new isomer has been detected; the alpha half-life is probably greater than 300 y." - ↑ This is the heaviest nuclide with a half-life of at least four years before the "Sea of Instability".
- ↑ Excluding those "classically stable" nuclides with half-lives significantly in excess of 232Th; e.g., while 113mCd has a half-life of only fourteen years, that of 113Cd is nearly eight quadrillion years.
- ↑ Final Report, Evaluation of nuclear criticality safety data and limits for actinides in transport Archived 2011-05-19 at the Wayback Machine., Republic of France, Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, Département de Prévention et d'étude des Accidents.
- ↑ Analysis of the Reuse of Uranium Recovered from the Reprocessing of Commercial LWR Spent Fuel, United States Department of Energy, Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
- ↑
- Jukka Lehto; Xiaolin Hou (2011). "15.15: Neptunium". Chemistry and Analysis of Radionuclides (1st ed.). John Wiley & Sons. 231. ISBN 3527633022.
- ↑ P. Weiss (26 October 2002). "Neptunium Nukes? Little-studied metal goes critical". Science News. 162 (17): 259. Archived from the original on 15 December 2012. Retrieved 7 November 2013.
- ↑ Witze, Alexandra (2014-11-27). "Nuclear power: Desperately seeking plutonium". Nature. 515 (7528): 484–486. Bibcode:2014Natur.515..484W. doi:10.1038/515484a.
- ↑ "Universal Nuclide Chart". nucleonica. (Registration required (help)).
- ↑ New short-lived isotope 223 Np and the absence of the Z = 92 subshell closure near N = 126 M.d. Sun-Z. Liu-T.h. Huang-W.q. Zhang-J.g. Wang-X.y. Liu-B. Ding-Z.g. Gan-L. Ma-H.b. Yang-Z.y. Zhang-L. Yu-J. Jiang-K.l. Wang-Y.s. Wang-M.l. Liu-Z.h. Li-J. Li-X. Wang-H.y. Lu-C.j. Lin-L.j. Sun-N.r. Ma-C.x. Yuan-W. Zuo-H.s. Xu-X.h. Zhou-G.q. Xiao-C. Qi-F.s. Zhang - Physics Letters B - 2017
- Isotope masses from:
- G. Audi; A. H. Wapstra; C. Thibault; J. Blachot; O. Bersillon (2003). "The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties" (PDF). Nuclear Physics A. 729: 3–128. Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729....3A. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-09-23.
- Isotopic compositions and standard atomic masses from:
- J. R. de Laeter; J. K. Böhlke; P. De Bièvre; H. Hidaka; H. S. Peiser; K. J. R. Rosman; P. D. P. Taylor (2003). "Atomic weights of the elements. Review 2000 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 75 (6): 683–800. doi:10.1351/pac200375060683.
- M. E. Wieser (2006). "Atomic weights of the elements 2005 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 78 (11): 2051–2066. doi:10.1351/pac200678112051. Lay summary.
- Half-life, spin, and isomer data selected from the following sources. See editing notes on this article's talk page.
- G. Audi; A. H. Wapstra; C. Thibault; J. Blachot; O. Bersillon (2003). "The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties" (PDF). Nuclear Physics A. 729: 3–128. Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729....3A. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-09-23.
- National Nuclear Data Center. "NuDat 2.1 database". Brookhaven National Laboratory. Retrieved 23 February 2017.
- N. E. Holden (2004). "Table of the Isotopes". In D. R. Lide. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (85th ed.). CRC Press. Section 11. ISBN 978-0-8493-0485-9.