Neutron Time Of Flight
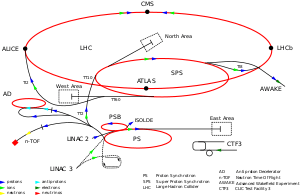 | |
| List of current particle accelerators at CERN | |
|---|---|
| Linac 2 | Accelerates protons |
| Linac 3 | Accelerates ions |
| Linac 4 | Accelerates negative hydrogen ions |
| AD | Decelerates antiprotons |
| LHC | Collides protons or heavy ions |
| LEIR | Accelerates ions |
| PSB | Accelerates protons or ions |
| PS | Accelerates protons or ions |
| SPS | Accelerates protons or ions |
This article is about one specific instrument. For generic information about the spectroscopic method, see Time of flight. For time-of-flight instruments in neutron scattering, see Neutron time-of-flight scattering.
The Neutron Time Of Flight (n-TOF) facility is a neutron spectrometer at CERN. It consists of a pulsed source, a flight path of 200 m length, and a detector systems. Neutron energies are deduced from the time of flight between source and detector; hence the name of the facility. The neutrons are produced by neutron spallation; by directing a pulsed beam of protons from the Proton Synchrotron (PS) towards a lead target about 300 neutrons expelled for each impact of a proton. The neutrons are slowed down after being emitted, first by the lead target and afterwards by a slab containing water. This results in a wide range of neutron energies since some neutrons will slow down more than others when passing through the targets. Finally, the neutrons are ejected through the 200m long flight path before they arrive at an experimental area.[1]
External links
- ↑ "nTOF | CERN". home.cern. Retrieved 2017-09-05.