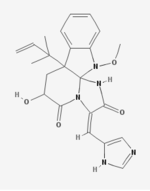
Neoxaline
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Nedoxaline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H25N5O4 | |
| Molar mass | 435.48 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Neoxaline is a bio-active Aspergillus japonicus isolate. It is an antimitotic agent and shows weak inhibitory activity of blood platelet aggregation induced by simulation of the central nervous system.[1][2] It has been synthesized through the "highly stereoselective introduction of a reverse prenyl group to create a quaternary carbon stereocenter using (−)-3a-hydroxyfuroindoline as a building block, construction of the indoline spiroaminal via cautious stepwise oxidations with cyclizations from the indoline, assembly of (Z)-dehydrohistidine, and photoisomerization of unnatural (Z)-neoxaline to the natural (E)-neoxaline." [3]
See also
References
- ↑ Neoxaline an antimiotic agent
- ↑ Hirano, A; Iwai, Y; Masuma, R; Tei, K; Omura, S (1979). "Neoxaline, a new alkaloid produced by Aspergillus japonicus. Production, isolation and properties". J Antibiot (Tokyo). 32 (8): 781–785. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.32.781. PMID 500498.
- ↑ Ideguchi, Tetsuya; Yamada, Takeshi (August 11, 2013). "Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Neoxaline". The American Chemical Society. 135 (34): 12568–12571. doi:10.1021/ja406657v. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.