Nara Canal
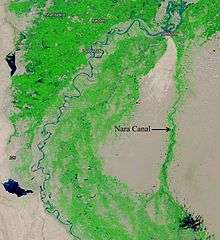
The Nara Canal is a deepened delta channel of Indus River in Sindh province, Pakistan. It was built as an excavated channel off the left bank of the Indus River into the course of the old Nara River.[1][2] The canal runs from above the Sukkur Barrage through the Khairpur, Sanghar, Mirpurkhas and Tharparkar Districts to the Jamrao Canal.[3] Nara is the longest canal in Pakistan, running for about 226 mi (364 km). It has a designed capacity of 13,602 cu ft/s (385.2 m3/s), but actually discharges 14,145 cu ft/s (400.5 m3/s). About 2,000,000 acres (8,100 km2) of land are irrigated by this canal.[4] Within the Khairpur District, the canal and its associated wetlands were made into the Nara Game Reserve in 1972.
The Eastern Nara was an inundation channel/river with its source of supply from the foot of the Punjab Hills. After traversing Bahawalpur, it used to enter into the Nara canal / river / delta channel a few miles downstream of its present head. In those days, the lndus River used to overflow in Bahawalpur and Sind Provinces above Rohri and the spillovers used to enter the Nara River. Bunds were constructed by the Bahawalpur state authorities to protect their lands against Indus floods and spillovers, which reduced the flood intensities into the Nara River. Similarly, due to low flows in the lndus River in certain years, the Nara River did not get much water. Therefore, the Nara supply channel was excavated in 1858-59 to directly supply water from the Indus river. The supply channel was excavated by 2.5 feet in 1884-85 and by a further 3.5 feet in 1893.[5]
Chotiari Dam is located in the catchment area of Nara canal. Nara canal drains in to Shakoor Lake before overflowing into Kori Creek of Great Rann of Kutch. This delta channel or river is known as Puran river or Koree river in its lower reaches.
See also
References
- ↑ "Nāra Canal". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 3 April 2018.
- ↑ Rehman, S.; et al. (2001). Proposed business plan for pilot farmer organizations: extended project on farmer managed irrigated agriculture in LBOD project area of Sindh Province. IWMI. p. 2. ISBN 92-9090-464-X.
- ↑ Bradnock, Robert W. (1993). South Asian handbook. Travelers world guides. 1992. Trade & Travel Publications. p. 1071. ISBN 0-900751-40-1.
- ↑ Khanzada, Mohammed N. (1997). Preliminary Business Plan for Bareji Distributary. Lahore: Pakistan National Program, International Irrigation Management Institute. p. 2. Retrieved 2011-03-27.
- ↑ "Nara River" (PDF). Retrieved 3 April 2018.