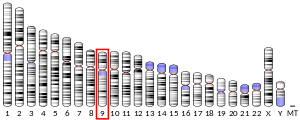
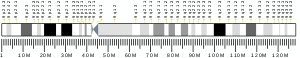
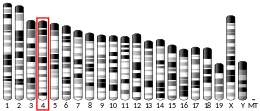
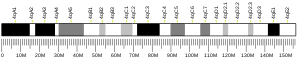
Nucleolar protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NOL6 gene.[5][6][7]
The nucleolus is a dense subnuclear membraneless organelle that assembles around clusters of rRNA genes and functions in ribosome biogenesis. This gene encodes a nucleolar RNA-associated protein that is highly conserved between species. RNase treatment of permeabilized cells indicates that the nucleolar localization is RNA dependent. Further studies suggest that the protein is associated with ribosome biogenesis through an interaction with pre-rRNA primary transcripts. Alternative splicing has been observed at this locus and two splice variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000165271 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028430 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Utama B, Kennedy D, Ru K, Mattick JS (Mar 2002). "Isolation and characterization of a new nucleolar protein, Nrap, that is conserved from yeast to humans". Genes Cells. 7 (2): 115–32. doi:10.1046/j.1356-9597.2001.00507.x. PMID 11895476.
- ↑ Bernstein KA, Gallagher JE, Mitchell BM, Granneman S, Baserga SJ (Dec 2004). "The small-subunit processome is a ribosome assembly intermediate". Eukaryot Cell. 3 (6): 1619–26. doi:10.1128/EC.3.6.1619-1626.2004. PMC 539036. PMID 15590835.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: NOL6 nucleolar protein family 6 (RNA-associated)".
Further reading
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, et al. (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298.
- Scherl A, Couté Y, Déon C, et al. (2003). "Functional proteomic analysis of human nucleolus". Mol. Biol. Cell. 13 (11): 4100–9. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-05-0271. PMC 133617. PMID 12429849.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Humphray SJ, Oliver K, Hunt AR, et al. (2004). "DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 9". Nature. 429 (6990): 369–74. doi:10.1038/nature02465. PMC 2734081. PMID 15164053.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, et al. (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. 433 (7021): 77–83. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413.
- Nousiainen M, Silljé HH, Sauer G, et al. (2006). "Phosphoproteome analysis of the human mitotic spindle". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (14): 5391–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507066103. PMC 1459365. PMID 16565220.