NAB2
NGFI-A-binding protein 2 also known as EGR-1-binding protein 2 or melanoma-associated delayed early response protein (MADER) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NAB2 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
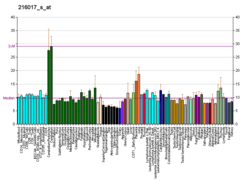
This gene encodes a member of the family of NGFI-A binding (NAB) proteins, which function in the nucleus to repress or activate transcription induced by some members of the EGR (early growth response) family of transactivators. NAB proteins can homo- or hetero-multimerize with other EGR or NAB proteins through a conserved N-terminal domain, and repress transcription through two partially redundant C-terminal domains. Transcriptional repression by the encoded protein is mediated in part by interactions with the nucleosome remodeling and deactylase (NuRD) complex. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, but their biological validity has not been determined.[7]
Pathology
Recurrent somatic fusions of the two genes, NGFI-A–binding protein 2 (NAB2) and STAT6, located at chromosomal region 12q13, have been identified in solitary fibrous tumors.[8]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000166886 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025402 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Svaren J, Sevetson BR, Apel ED, Zimonjic DB, Popescu NC, Milbrandt J (Aug 1996). "NAB2, a corepressor of NGFI-A (Egr-1) and Krox20, is induced by proliferative and differentiative stimuli". Mol Cell Biol. 16 (7): 3545–53. PMC 231349. PMID 8668170.
- ↑ Kirsch KH, Korradi Y, Johnson JP (Jul 1996). "Mader: a novel nuclear protein over expressed in human melanomas". Oncogene. 12 (5): 963–71. PMID 8649813.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: NAB2 NGFI-A binding protein 2 (EGR1 binding protein 2)".
- ↑ Kabbinavar, F. F.; Hambleton, J; Mass, R. D.; Hurwitz, H. I.; Bergsland, E; Sarkar, S (2005). "Combined analysis of efficacy: The addition of bevacizumab to fluorouracil/leucovorin improves survival for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 23 (16): 3706–12. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.00.232. PMID 15867200.
Further reading
- Svaren J, Apel ED, Simburger KS, et al. (1997). "The Nab2 and Stat6 genes share a common transcription termination region". Genomics. 41 (1): 33–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4609. PMID 9126479.
- Qu Z, Wolfraim LA, Svaren J, et al. (1998). "The transcriptional corepressor NAB2 inhibits NGF-induced differentiation of PC12 cells". J. Cell Biol. 142 (4): 1075–82. doi:10.1083/jcb.142.4.1075. PMC 2132876. PMID 9722618.
- Svaren J, Sevetson BR, Golda T, et al. (1998). "Novel mutants of NAB corepressors enhance activation by Egr transactivators". EMBO J. 17 (20): 6010–9. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.20.6010. PMC 1170927. PMID 9774344.
- Abdulkadir SA, Qu Z, Garabedian E, et al. (2001). "Impaired prostate tumorigenesis in Egr1-deficient mice". Nat. Med. 7 (1): 101–7. doi:10.1038/83231. PMID 11135623.
- Abdulkadir SA, Carbone JM, Naughton CK, et al. (2001). "Frequent and early loss of the EGR1 corepressor NAB2 in human prostate carcinoma". Hum. Pathol. 32 (9): 935–9. doi:10.1053/hupa.2001.27102. PMID 11567222.
- Venken K, Di Maria E, Bellone E, et al. (2003). "Search for mutations in the EGR2 corepressor proteins, NAB1 and NAB2, in human peripheral neuropathies". Neurogenetics. 4 (1): 37–41. doi:10.1007/s10048-001-0124-2. PMID 12030330.
- Lucerna M, Mechtcheriakova D, Kadl A, et al. (2003). "NAB2, a corepressor of EGR-1, inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated gene induction and angiogenic responses of endothelial cells". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (13): 11433–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204937200. PMID 12427750.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Kumbrink J, Gerlinger M, Johnson JP (2005). "Egr-1 induces the expression of its corepressor nab2 by activation of the nab2 promoter thereby establishing a negative feedback loop". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (52): 42785–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511079200. PMID 16260776.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Srinivasan R, Mager GM, Ward RM, et al. (2006). "NAB2 represses transcription by interacting with the CHD4 subunit of the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase (NuRD) complex". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (22): 15129–37. doi:10.1074/jbc.M600775200. PMID 16574654.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.