Moodle
 | |
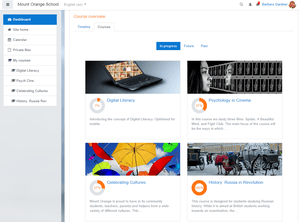 Screenshot of a student's dashboard page, taken from the demonstration site school.demo.moodle.net | |
| Original author(s) | Martin Dougiamas |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) |
Martin Dougiamas Moodle HQ Moodle Community |
| Stable release | |
| Repository |
|
| Written in | PHP |
| Type | Course management system |
| License | GPLv3+[4] |
| Website |
moodle |
Moodle is a free and open-source learning management system (LMS) written in PHP and distributed under the GNU General Public License.[5][6] Developed on pedagogical principles,[7][8] Moodle is used for blended learning, distance education, flipped classroom and other e-learning projects in schools, universities, workplaces and other sectors.[9][10][11]
With customizable management features, it is used to create private websites with online courses for educators and trainers to achieve learning goals.[12][13] Moodle (acronym for modular object-oriented dynamic learning environment) allows for extending and tailoring learning environments using community sourced plugins.[14]
Overview
Moodle was originally developed by Martin Dougiamas to help educators create online courses with a focus on interaction and collaborative construction of content, and it is in continual evolution. The first version of Moodle was released on 20 August 2002.[15] Nowadays the Moodle Project is led and coordinated by Moodle HQ, an Australian company of 50 developers which is financially supported by a network of eighty-four Moodle Partner service companies worldwide. Moodle's development has also been assisted by the work of open-source programmers.[16]
Moodle as a learning platform can enhance existing learning environments.[17] As an E-learning tool, Moodle has a wide range of standard and innovative features[18] such as calendar and Gradebook.[19] Moodle is a leading virtual learning environment[20][21][22] and can be used in many types of environments such as education, training and development[23] and in business settings.[24]
Plugins
Plugins are a flexible tool set, allowing Moodle users to extend the features of the site. There are hundreds of plugins for Moodle, extending the features of Moodle's core functionality.[25] Each plugin is maintained in the Moodle plugins directory. As of June 2017, there are 1,342 plugins available for Moodle with over 405,200 recent downloads.[26]
Themes
Graphical themes for Moodle can be installed to change the look and functionality of a Moodle
Mobile
Many Moodle themes, based on responsive web design, allow Moodle to be used on mobile devices. Also, a Moodle mobile app is available in Google Play, App Store (iOS), and the Windows Phone Store.
E-learning standards support
Moodle has adopted the following e-learning standards:
- Sharable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM) is a collection of E-learning standards and specifications that define communications between client side content and a server side learning management system, as well as how externally authored content should be packaged in order to integrate with the LMS effectively. There are two versions: SCORM 1.2 and SCORM 2004. Moodle is SCORM 1.2 compliant, and passes all the tests in the ADL Conformance test suite 1.2.7 for SCORM 1.2. SCORM 2004 is not supported in Moodle, however Rustici Software have a Moodle plugin which can turn any Moodle site into a fully compliant SCORM 2004 LMS.[27]
- The AICC HACP standard for CMI was developed by the Aviation Industry Computer-Based Training Committee (AICC) and is used to call externally authored content and assessment packages. AICC content packages are supported in Moodle 2.1 and later versions.
- IMS Common Cartridge packages can also be imported into Moodle. In addition, Moodle Book activities can be exported as IMS Content Packages.
- Learning Tools Interoperability (LTI) is a standard way of integrating rich learning applications (often remotely hosted and provided through third-party services) with educational platforms. Moodle uses the External Tool activity to act as an 'LTI consumer' as standard, and will act as an 'LTI provider' using a plugin.
Deployment
Users can download and install Moodle on a Web server, such as Apache HTTP Server, and a number of database management systems, such as PostgreSQL, are supported. Pre-built combinations of Moodle with a Web server and database are available for Microsoft Windows and Macintosh. Other automated installation approaches exist, such as installing a Debian package, deploying a ready-to-use TurnKey Moodle appliance, using the Bitnami installer, or using a "one-click install" service such as Installatron.
Certified Moodle Partners provide other Moodle services, including hosting, training, customization and content development.[28] This network of providers support development of the Moodle project through royalties.[29]
Interoperability
Moodle runs without modification on Unix, Linux, FreeBSD, Windows, OS X, NetWare and any other systems that support PHP and a database, including webhost providers.
Moodle also has import features for use with other specific systems, such as importing quizzes or entire courses from Blackboard or WebCT. As of February 2010, Moodle will not import Blackboard courses, apparently due to changes in php code-releases.[30]
In March 2012 Blackboard acquired two companies based on Moodle's software including Baltimore-based Moodlerooms Inc. and NetSpot of Adelaide, Australia.[31] In August 2015, Blackboard acquired Colombia-based Nivel7, possibly the largest Moodle services provider in Latin America.[32] The Red Hat site, Opensource.com, reports that Moodle will always be an open source project, with clear delineation between Blackboard and Moodle.[33]
For many schools, colleges and universities, SIMS integration is key to ensure a seamless data flow from the Management Information System through to the Learning Platform and back again. Many Learning Platforms do not enable write-back functionality, however this is often a key requirement from schools needing to write data onto their MIS and back again.
Background
Origins
Martin Dougiamas, who has graduate degrees in computer science and education, wrote the first version of Moodle. Dougiamas started a Ph.D. to examine "the use of open source software to support a social constructionist epistemology of teaching and learning within Internet-based communities of reflective inquiry." Although how exactly social constructionism makes Moodle different from other eLearning platforms is difficult to show, it has been cited as an important factor by Moodle adopters.[34][35] Other Moodle adopters, such as the Open University in the UK, have pointed out that Learning Management Systems can equally be seen as "relatively pedagogy-neutral".[36]
Pedagogical approach
The stated philosophy of Moodle includes a constructivist and social constructionist approach to education, emphasizing that learners (and not just teachers) can contribute to the educational experience.[37] Using these pedagogical principles, Moodle provides an environment for learning communities.[38]
Origin of name
The acronym Moodle stands for modular object-oriented dynamic learning environment. (In the early years the "m" stood for "Martin's", named after Martin Dougiamas, the original developer). As well as being an acronym, the name was chosen because of the dictionary definition of Moodle[39] and to correspond to an available domain name.[40]
Development
Moodle has continued to evolve since 1999 (since 2001 with the current architecture). It has been translated into over 100 different languages and is accessible in many countries worldwide.[41] Institutions can add as many Moodle servers as needed without having to pay license fees. The Open University of the UK currently uses a Moodle installation for their 200,000 users[42] while the UK government uses a Moodle installation for their Civil Service Learning platform serving half a million employees.[43]
Releases
| Branch | Original release date |
Version | Version release date |
Support Model | New Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 20 August 2002 | 1.0.9 | 30 May 2003 | EOL | |
| 1.1 | 29 August 2003 | 1.1.1 | 11 September 2003 | EOL | |
| 1.2 | 20 March 2004 | 1.2.1 | 25 March 2004 | EOL | |
| 1.3 | 25 May 2004 | 1.3.5 | 9 September 2004 | EOL | |
| 1.4 | 31 August 2004 | 1.4.5 | 7 May 2005 | EOL | |
| 1.5 | 5 June 2005 | 1.5.4 | 21 May 2006 | EOL | |
| 1.6 | 20 May 2006 | 1.6.9 | 28 January 2009 | EOL | |
| 1.7 | 7 November 2006 | 1.7.7 | 28 January 2009 | EOL | |
| 1.8 | 30 March 2007 | 1.8.14 | 3 December 2010 | EOL | |
| 1.9 | 3 March 2008 | 1.9.19 | 9 July 2012 | EOL (Maintained from March 2008 to June 2012. Third-party extended support until December 2013)[44] | New gradebook, bulk user actions, tagging |
| 2.0 | 24 November 2010 | 2.0.10 | 9 July 2012 | EOL (Maintained from November 2010 to June 2012) | Integration with plagiarism prevention tools |
| 2.1 | 1 June 2011 | 2.1.10 | 14 January 2013 | EOL (Maintained from June 2011 to December 2012) | |
| 2.2 | 5 December 2011 | 2.2.11 | 8 July 2013 | EOL (Maintained from December 2011 to June 2013) | Advanced grading methods including Rubrics |
| 2.3 | 25 June 2012 | 2.3.10 | 11 November 2013 | EOL (Maintained from June 2012 to December 2013) | Drag and drop files |
| 2.4 | 3 December 2012 | 2.4.7 | 11 November 2013 | EOL (Maintained from December 2012 to June 2014) | |
| 2.5 | 14 May 2013 | 2.5.9 | 10 November 2014 | EOL (Maintained from May 2013 to November 2014) | Badges |
| 2.6 | 18 November 2013 | 2.6.11 | 11 May 2015 | EOL (Maintained from December 2013 to May 2015) | Annotate uploaded PDF, bulk course creation, multiple calendars |
| 2.7 | 12 May 2014 | 2.7.20
(LTS) |
8 May 2017 | EOL (Maintained from May 2014 to May 2017) | Atto HTML Editor, responsive design, log in with email address |
| 2.8 | 10 November 2014 | 2.8.12 | 9 May 2016 | EOL (Maintained from November 2014 to May 2016) | Text autosave, like rating |
| 2.9 | 11 May 2015 | 2.9.10 | 14 November 2016 | EOL (Maintained from May 2015 to November 2016) | Dashboard, view all grades |
| 3.0 | 16 November 2015 | 3.0.10 | 8 May 2017 | EOL (Maintained from November 2015 to May 2017) | 4 new quiz types |
| 3.1 | 23 May 2016 | 3.1.13 (LTS) | 9 July 2018 | Sustained (Maintained from May 2016 to May 2019; receives only security updates) | xmlreader required. Competencies, assignment grading, download selected assignment, recycle bin, pinned forum discussions, workshop enhancements, publish as LTI tool, tag course activities, easier section editing, search metalinked courses, competency frameworks, learning plan templates, global search, assignment file conversion using Universal Office Converter (unoconv), search file system repository, lesson default settings, tag collections. |
| 3.2 | 5 December 2016 | 3.2.9 | 17 May 2018 | EOL (Maintained from December 2016 to May 2018) | PHP 5.6.5 as the minimum version. New Boost theme, media player improvements, interactive report charts, discussion locking, assignment overrides, workshop portfolio export, select for students in Choice, negative scores for rubrics, user tours, competency frameworks import and export, new media player plugins, LTS 2 compliance, course end dates, user-friendly messaging and alerts, grading improvements, auto-login, sign-up improvements and SSO, new notification preferences. |
| 3.3 | 15 May 2017 | 3.3.7 | 9 July 2018 | Sustained (Maintained from May 2017 to November 2018; receives only security updates) | openssl and fileinfo required. Better Office integration, improved dashboard, FontAwesome for Moodle icons and general use, Emoji support, set a 'grade by' reminder, specify assignment file types, collapse comments in assignments, better activity completion management, drag and drop media, 'stealth' activities available but not shown, more tag areas. |
| 3.4 | 13 November 2017 | 3.4.4 | 9 July 2018 | Sustained (Maintained from November 2017 to May 2019, receives only security updates) | PHP 7.0.0 as the minimum version, intl required. Better calendar management, category calendar events, drag and drop calendar events, private file storage display, improved global search, easier activity navigation, more efficient user management, teachers can now override activity completion status, helpful filetype selector, tag database entries, Inspire Analytics in core, new filters for user tours, HTTPS conversion tool, OAuth2 services trusted email verification, manage all tokens, clearer site registration. |
| 3.5 | 17 May 2018 | 3.5.1 (LTS) | 9 July 2018 | Active (Maintained from May 2018 to May 2021) | Moodle 3.5 focuses on GDPR compliance, enhanced usability and accessibility. Includes privacy and policy area in Profile, course images on the dashboard, clearer icons and accessible fonts, direct record sound and video, choice results display, more efficient user management, award badges based on other badges awarded, filter questions by tag, quiz essay question type, GDRP features, simple global search (without external engine), LTI Advantage 1.1 support, more badge criteria, cohort themes, new capabilities. |
Legend: Old version Older version, still supported Latest version | |||||
Moodle conferences
A MoodleMoot is a conference for Moodle community members, held to learn about Moodle, share experiences of the learning platform, discuss research in related educational technologies and contribute ideas to future Moodle development. Held around the world, MoodleMoots are organised by universities or other large organisations using Moodle, Moodle Partners, Moodle associations or Moodle HQ.
Adoption
In the higher education market in the United States, Moodle was for a time the second largest provider with 23% market share in 2013 (following Blackboard (41%), Desire2Learn (11%), and Instructure).[45] However, by 2017 Moodle had dropped to the third largest provider, due in part to increased adoption of Instructure's Canvas platform.[46] In March 2016 Blackboard became an official Moodle partner.[47]
See also
References
- ↑ http s://docs.moodle.org/dev/Releases
- ↑ https://github.com/moodle/moodle/releases
- ↑ https://blog.ripstech.com/2018/moodle-remote-code-execution/
- ↑ "Moodle License".
- ↑ "TFD Encyclopedia - Moodle".
- ↑ The Encyclopedia of Distance Learning, Vol1.
- ↑ "Pedagogy - MoodleDocs".
- ↑ "Moodle: Using Learning Communities to Create an Open Source Course Management System". 8 September 2014.
- ↑ Costello, Eamon (1 November 2013). "Opening up to open source: looking at how Moodle was adopted in higher education". 28 (3): 187–200. doi:10.1080/02680513.2013.856289 – via Taylor and Francis+NEJM.
- ↑ Krassa, Anna (4 October 2013). Gamified Moodle Course in a Corporate Environment (PDF). 2nd Moodle Research Conference (MRC2013). Sousse, Tunisia. p. 84-93. ISBN 978-618-80889-0-0.
- ↑ Horvat, Ana; Dobrota, M.; Krsmanovic, M.; & Cudanov, M. (2015). "Student perception of Moodle learning management system: a satisfaction and significance analysis". Interactive Learning Environments. 23 (4): 515-527. doi:10.1080/10494820.2013.788033.
- ↑ Gavin W. Porter (7 June 2013). "Free choice of learning management systems: Do student habits override inherent system quality?". Interactive Tech & Smart Ed. 10 (2): 84–94. doi:10.1108/ITSE-07-2012-0019 – via emeraldinsight.com (Atypon).
- ↑ http://www.cats-pyjamas.net/wp-content/uploads/2010/05/MoodleToolGuideforTeachers_May2010_JS.pdf
- ↑ http://www.ascilite.org.au/conferences/wellington12/2012/images/custom/mcneil,_margot_-_a_pedagogical.pdf
- ↑ "Releases - MoodleDocs". docs.moodle.org. Retrieved 2018-04-18.
- ↑ "How Moodle is driven by user and community feedback".
- ↑ "Technology that puts the classroom in students' laptops". Adam Stanley, The Globe and Mail.
- ↑ Jordan, Sally. "E-assessment: Past, present and future". 9 (1): 87–106. doi:10.11120/ndir.2013.00009.
- ↑ "Online Grading to Make Teaching Life Easier with Moodle". 19 November 2014.
- ↑ "Open Universities VLE / LMS".
- ↑ "2014 Survey of Technology Enhanced Learning for higher education in the UK". UCISA Richard Walker, Julie Voce, Joe Nicholls, Elaine Swift, Jebar Ahmed, Sarah Horrigan and Phil Vincent.
- ↑ "The Top 8 Open Source Learning Management Systems - eLearning Industry". 31 December 2015.
- ↑ "E-learning". http://www.cpce-polyu.edu.hk/itu/new/: Information Technology Unit (itu). Retrieved 2011-03-01.
Moodle is a well-known e-learning platform in tertiary institutions. Many universities and colleges use Moodle as the online learning system in their daily teaching and learning. Moodle is a free open source software it means developer can make modification based on their needs. CPCE decides to use Moodle as a e-learning platform for HKCC and SPEED from 2009/10 academic year onwards.
- ↑ "Knowledge Centre".
- ↑ "Moodle Plugins Directory".
- ↑ "Moodle plugins directory". moodle.org. Retrieved 2017-06-01.
- ↑ "SCORM Cloud Moodle Integration". scorm.com.
- ↑ "List of Moodle Partners". Moodle.
- ↑ "How do the Moodle Partners work?". Moodle.
- ↑ "Blackboard migration". moodle.org.
- ↑ "Blackboard makes Moodle acquisitions". bizjournals.com.
- ↑ "Blackboard acquires Nivel7". Blackboard. August 13, 2015.
- ↑ "Moodle will always be an open source project". opensource.com.
- ↑ Weller, M. (2006). "VLE 2.0 and future directions in learning environments". Proceedings of the first LAMS Conference, Sydney.
- ↑ McMulli & Munroe (2004). "VMoodle at DCU".
- ↑ Sclater, Neil (2008). "A Large-scale Open Source eLearning Systems at the Open University". Educase.
- ↑ "Philosophy - MoodleDocs".
- ↑ "Open-Source Learning Management System". Moodlerooms.
- ↑ "Moodle definition". All Words.
- ↑ "The chicken or the egg". Moodle.org Lounge.
- ↑ "Language packs - MoodleDocs".
- ↑ Kehrer, Anika. "Simply the Best: Case Study for Moodle at Open... » Linux Magazine".
- ↑ "Civil Service Learning - LEO".
- ↑ Marsden, Dan (2 April 2012). "Moodle 1.9 Long Term support". Moodle. Retrieved 27 May 2013.
- ↑ A Profile of the LMS Market (page 23) (PDF), CampusComputing, 2013 .
- ↑ "LMS Data--Spring 2017 Updates". Edutechnica. Client Stat. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- ↑ "Blackboard Is Now An Official Moodle Partner". Moodle News. 2016-03-14. Retrieved 2018-04-18.