Monocystis
Monocystis is a genus (the type of the family Monocystidae) of acephaline gregarines not having the protoplasm divided into segments by septa and including internal parasites of invertebrates (as M. agilis of the reproductive system of earthworms).[1].
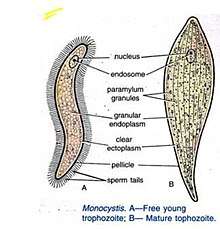
Habit and Habitat
Monocystis lives as an intracellular [Parasite] in its young stage when it lives in the bundle of developing [sperms] and becomes extracellular in its mature stage when it lives in the contents of seminal vesicles of [Earthworms]. Its infection is so wide that practically all mature earthworms are found parasitized by this Parasite[2].
Structure
The adult mature Monocystis is called trophozoite which is a feeding stage. The young trophozoite lives in the sperm morula (sperm morula is a group of developing sperms) of the host; it feeds and grows at the expense of the protoplasm of the developing sperms until all the protoplasm is exhausted. So, it is now seen to be surrounded by the tails of the dead sperms. In this stage, it is sometimes mistaken to be a ciliated organism. But, soon the sperm tails are detached from its body and the trophozoite becomes free[3]
References
- ↑ "Definition of MONOCYSTIS". www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 2018-02-05.
- ↑ "Monocystis: Habitat, Structure and Life Cycle | Protozoa". Biology Discussion. 2016-05-02. Retrieved 2018-02-05.
- ↑ "Monocystis: Habitat, Structure and Life Cycle | Protozoa". Biology Discussion. 2016-05-02. Retrieved 2018-02-05.