Micromonospora
| Micromonospora | |
|---|---|
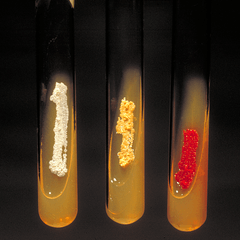 | |
| Micromonospora spp. (red colonies). | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Actinobacteria |
| Order: | Actinomycetales |
| Family: | Micromonosporaceae |
| Genus: | Micromonospora Ørskov 1923 |
| Type species | |
| Micromonospora chalcea (Foulerton 1905) Ørskov 1923 | |
| Species | |
|
See text. | |
Micromonospora is a genus of bacteria of the family Micromonosporaceae. They are gram-positive, spore-forming, generally aerobic, and form a branched mycelium; they occur as saprotrophic forms in soil and water. Various species are sources of aminoglycoside antibiotics, which spellings often ends with -micin, unlike most other aminoglycoside names that end with -mycin to highlight the very different species from which they originate (e.g. neomycin and streptomycin, produced by Streptomyces spp.).
Species
- Micromonospora aurantiaca
- Micromonospora auratinigra
- Micromonospora avicenniae
- Micromonospora carbonacea
- Micromonospora chaiyaphumensis
- Micromonospora chalcea
- Micromonospora chersina
- Micromonospora chokoriensis
- Micromonospora citrea
- Micromonospora coerulea
- Micromonospora coriariae
- Micromonospora costi[1]
- Micromonospora coxensis
- Micromonospora cremea
- Micromonospora eburnea
- Micromonospora echinaurantiaca
- Micromonospora echinofusca
- Micromonospora echinospora—produces highly toxic DNA splicing calicheamicins
- Micromonospora endolithica
- Micromonospora equina
- Micromonospora fluostatini[1]
- Micromonospora fulviviridis
- Micromonospora gallica
- Micromonospora haikouensis
- Micromonospora halophytica
- Micromonospora halotolerans
- Micromonospora harpali[1]
- Micromonospora humi
- Micromonospora inositola—produces the antibiotic sisomicin
- Micromonospora inyonensis—produces the antibiotics mutamicin and netilmicin
- Micromonospora kangleipakensis
- Micromonospora krabiensis
- Micromonospora lupini
- Micromonospora luteifusca[1]
- Micromonospora mangrovi[1]
- Micromonospora marina
- Micromonospora maritima
- Micromonospora matsumotoense
- Micromonospora mirobrigensis
- Micromonospora narathiwatensis
- Micromonospora nickelidurans[1]
- Micromonospora nigra
- Micromonospora noduli[1]
- Micromonospora olivasterospora
- Micromonospora oryzae[1]
- Micromonospora ovatispora[1]
- Micromonospora pallida
- Micromonospora palomenae[1]
- Micromonospora parathelypteridis[1]
- Micromonospora pattaloongensis
- Micromonospora peucetia
- Micromonospora pisi
- Micromonospora polyrhachis
- Micromonospora profundi[1]
- Micromonospora purpureochromogenes—produces the antibiotic gentamicin
- Micromonospora rhizosphaerae
- Micromonospora rifamycinica
- Micromonospora rosaria
- Micromonospora saelicesensis
- Micromonospora sagamiensis
- Micromonospora schwarzwaldensis
- Micromonospora sediminicola
- Micromonospora sediminis[1]
- Micromonospora siamensis
- Micromonospora soli[1]
- Micromonospora sonneratiae
- Micromonospora taraxaci[1]
- Micromonospora terminaliae[1]
- Micromonospora tulbaghiae
- Micromonospora ureilytica[1]
- Micromonospora vinacea[1]
- Micromonospora violae[1]
- Micromonospora viridifaciens
- Micromonospora vulcania[1]
- Micromonospora wenchangensis
- Micromonospora yangpuensis
- Micromonospora zamorensis
- Micromonospora zhanjiangensis[1]
References
- Kroppenstedt RM, Mayilraj S, Wink JM (Jun 2005). "Eight new species of the genus Micromonospora, Micromonospora citrea sp. nov., Micromonospora echinaurantiaca sp. nov., Micromonospora echinofusca sp. nov., Micromonospora fulviviridis sp. nov., Micromonospora inyonensis sp. nov., Micromonospora peucetia sp. nov., Micromonospora sagamiensis sp. nov., and Micromonospora viridifaciens sp. nov". Syst Appl Microbiol. 28 (4): 328–39. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2004.12.011. PMID 15997706.
- Christine CC, Sanders E (1973). "Sisomicin: Evaluation In Vitro and Comparison with Gentamicin and Tobramycin". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 3 (1): 24–8. doi:10.1128/aac.3.1.24. PMC 444355. PMID 4790572.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.