Mandelic acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid | |||
| Other names
2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid Mandelic acid Phenylglycolic acid α-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.825 | ||
| EC Number | 202-007-6 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number | OO6300000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 152.15 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White crystalline powder | ||
| Density | 1.30 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 119 °C (246 °F; 392 K) optically pure: 132 to 135 °C (270 to 275 °F; 405 to 408 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 321.8 °C (611.2 °F; 595.0 K) | ||
| 15.87 g/100 mL | |||
| Solubility | soluble in diethyl ether, ethanol, isopropanol | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.41[2] | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.5204 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
0.1761 kJ/g | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| B05CA06 (WHO) J01XX06 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 162.6 °C (324.7 °F; 435.8 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
mandelonitrile, phenylacetic acid, vanillylmandelic acid | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Mandelic acid is an aromatic alpha hydroxy acid with the molecular formula C6H5CH(OH)CO2H. It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a useful precursor to various drugs. The molecule is chiral. The racemic mixture is known as paramandelic acid.
Isolation, synthesis, occurrence
Mandelic acid was discovered in 1831 by the German pharmacist Ferdinand Ludwig Winckler (1801–1868) while heating amygdalin, an extract of bitter almonds, with diluted hydrochloric acid.[3] The name is derived from the German "Mandel" for "almond". Derivatives of mandelic acid are formed as a result of metabolism of adrenaline and noradrenaline by monoamine oxidase and catechol-O-methyl transferase.
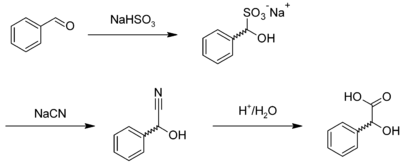
Mandelic acid is usually prepared by the acid-catalysed hydrolysis of mandelonitrile,[4] which is the cyanohydrin of benzaldehyde. Mandelonitrile can also be prepared by reacting benzaldehyde with sodium bisulfite to give the corresponding adduct, forming mandelonitrile with sodium cyanide, which is hydrolyzed:[5]
Alternatively, it can be prepared by base hydrolysis of phenylchloroacetic acid and dibromacetophenone.[6] It also arises by heating phenylglyoxal with alkalis.[7][8]
It arises from the biodegradation of styrene, as detected in urine.[9]
Uses
Mandelic acid has a long history of use in the medical community as an antibacterial, particularly in the treatment of urinary tract infections.[10] It has also been used as an oral antibiotic, and as a component of chemical face peels, along with other alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs).
- The drugs cyclandelate and homatropine are esters of mandelic acid.
- Pemoline is synthesized by the condensation of the ethyl ester of mandelic acid with guanidine.
- Amolanone
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 5599.
- ↑ Bjerrum, J., et al. Stability Constants, Chemical Society, London, 1958.
- ↑ See:
- Winckler, F. L. (1831) "Ueber die Zersetzung des Calomels durch Bittermandelwasser, und einige Beiträge zur genaueren Kenntniss der chemischen Zusammensetzung des Bittermandelwassers" (On the decomposition of calomel [i.e., mercury(I) chloride] by bitter almond water, and some contributions to a more precise knowledge of the chemical composition of bitter almond water), Repertorium für die Pharmacie, 37 : 388–418 ; mandelic acid is named on p. 415.
- Winckler, F. L. (1831) "Ueber die chemische Zusammensetzung des Bittermandelwassers; als Fortsetzung der im 37sten Band S. 388 u.s.w. des Repertoriums enthaltenen Mittheilungen" [On the chemical composition of bitter almond water; as a continuation of the report contained in the 37th volume, pp. 388 ff. of the Repertorium], Repertorium für die Pharmacie, 38 : 169–196. On p. 193, Winckler describes the preparation of mandelic acid from bitter almond water and hydrochloric acid (Salzsäure).
- (Editor) (1832) "Ueber einige Bestandtheile der Bittermandeln" (On some components of bitter almonds), Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie, 4 : 242–247.
- Winckler, F. L. (1836) "Ueber die Mandelsäure und einige Salze derselben" (On mandelic acid and some salts of the same), Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie, 18 (3) : 310–319.
- Hermann Schelenz, Geschichte der Pharmazie [The History of Pharmacy] (Berlin, German: Julius Springer, 1904), p. 675.
- ↑ Edwin Ritzer and Rudolf Sundermann "Hydroxycarboxylic Acids, Aromatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a13_519
- ↑ Corson, B. B.; Dodge, R. A.; Harris, S. A.; Yeaw, J. S. (1941). "Mandelic Acid". Organic Syntheses. ; Collective Volume, 1, p. 336
- ↑ J. G. Aston, J. D. Newkirk, D. M. Jenkins, and Julian Dorsky (1952). "Mandelic Acid". Organic Syntheses. ; Collective Volume, 3, p. 538
- ↑ Pechmann, H. von (1887). "Zur Spaltung der Isonitrosoverbindungen". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 20 (2): 2904–2906. doi:10.1002/cber.188702002156.
- ↑ Pechmann, H. von; Muller, Hermann (1889). "Ueber α-Ketoaldehyde". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 22 (2): 2556–2561. doi:10.1002/cber.188902202145.
- ↑ Engström K, Härkönen H, Kalliokoski P, Rantanen J. "Urinary mandelic acid concentration after occupational exposure to styrene and its use as a biological exposure test" Scand. J. Work Environ. Health. 1976, volume 2, pp. 21-6.
- ↑ Putten, P. L. (1979). "Mandelic acid and urinary tract infections". Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 45 (4): 622. doi:10.1007/BF00403669.


-Mandelic_acid_molecule_ball.png)