MTHFD2
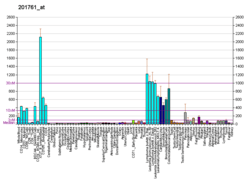
Bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTHFD2 gene.[5][6][7]
This gene encodes a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial bifunctional enzyme with methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase and methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase activities. The enzyme functions as a homodimer and is unique in its absolute requirement for magnesium and inorganic phosphate. Formation of the enzyme-magnesium complex allows binding of NAD. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcripts encoding different isoforms. This gene has a pseudogene on chromosome 7.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000065911 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000005667 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Peri KG, Belanger C, Mackenzie RE (Dec 1989). "Nucleotide sequence of the human NAD-dependent methylene tetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase-cyclohydrolase". Nucleic Acids Res. 17 (21): 8853. doi:10.1093/nar/17.21.8853. PMC 335047. PMID 2587219.
- ↑ Yang XM, MacKenzie RE (Nov 1993). "NAD-dependent methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase-methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase is the mammalian homolog of the mitochondrial enzyme encoded by the yeast MIS1 gene". Biochemistry. 32 (41): 11118–23. doi:10.1021/bi00092a022. PMID 8218174.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: MTHFD2 methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 2, methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase".
Further reading
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Kokame K, Kato H, Miyata T (1997). "Homocysteine-respondent genes in vascular endothelial cells identified by differential display analysis. GRP78/BiP and novel genes". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (47): 29659–65. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.47.29659. PMID 8939898.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Pawelek PD, MacKenzie RE (1998). "Methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase is rate limiting for the enzymatic conversion of 10-formyltetrahydrofolate to 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate in bifunctional dehydrogenase-cyclohydrolase enzymes". Biochemistry. 37 (4): 1109–15. doi:10.1021/bi971906t. PMID 9454603.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Hillier LW, Graves TA, Fulton RS, et al. (2005). "Generation and annotation of the DNA sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4". Nature. 434 (7034): 724–31. doi:10.1038/nature03466. PMID 15815621.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: Large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein–protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.