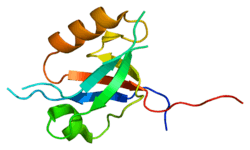MPDZ
Multiple PDZ domain protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MPDZ gene.[5]
Interactions
MPDZ has been shown to interact with:
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000107186 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028402 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: MPDZ multiple PDZ domain protein".
- ↑ Becamel C, Figge A, Poliak S, Dumuis A, Peles E, Bockaert J, Lubbert H, Ullmer C (April 2001). "Interaction of serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2C receptors with PDZ10 of the multi-PDZ domain protein MUPP1". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (16): 12974–82. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008089200. PMID 11150294.
- ↑ Ullmer C, Schmuck K, Figge A, Lübbert H (March 1998). "Cloning and characterization of MUPP1, a novel PDZ domain protein". FEBS Lett. 424 (1–2): 63–8. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00141-0. PMID 9537516.
- ↑ Mancini A, Koch A, Stefan M, Niemann H, Tamura T (September 2000). "The direct association of the multiple PDZ domain containing proteins (MUPP-1) with the human c-Kit C-terminus is regulated by tyrosine kinase activity". FEBS Lett. 482 (1–2): 54–8. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(00)02036-6. PMID 11018522.
- ↑ Kimber WA, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Cheung PC, Deak M, Marsden LJ, Kieloch A, Watt S, Javier RT, Gray A, Downes CP, Lucocq JM, Alessi DR (February 2002). "Evidence that the tandem-pleckstrin-homology-domain-containing protein TAPP1 interacts with Ptd(3,4)P2 and the multi-PDZ-domain-containing protein MUPP1 in vivo". Biochem. J. 361 (Pt 3): 525–36. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3610525. PMC 1222335. PMID 11802782.
Further reading
- Ullmer C, Schmuck K, Figge A, Lübbert H (1998). "Cloning and characterization of MUPP1, a novel PDZ domain protein". FEBS Lett. 424 (1–2): 63–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00141-0. PMID 9537516.
- Barritt DS, Pearn MT, Zisch AH, Lee SS, Javier RT, Pasquale EB, Stallcup WB (2000). "The multi-PDZ domain protein MUPP1 is a cytoplasmic ligand for the membrane-spanning proteoglycan NG2". J. Cell. Biochem. 79 (2): 213–24. doi:10.1002/1097-4644(20001101)79:2<213::AID-JCB50>3.0.CO;2-G. PMC 3501957. PMID 10967549.
- Lee SS, Glaunsinger B, Mantovani F, Banks L, Javier RT (2000). "Multi-PDZ Domain Protein MUPP1 Is a Cellular Target for both Adenovirus E4-ORF1 and High-Risk Papillomavirus Type 18 E6 Oncoproteins". J. Virol. 74 (20): 9680–93. doi:10.1128/JVI.74.20.9680-9693.2000. PMC 112400. PMID 11000240.
- Mancini A, Koch A, Stefan M, Niemann H, Tamura T (2000). "The direct association of the multiple PDZ domain containing proteins (MUPP-1) with the human c-Kit C-terminus is regulated by tyrosine kinase activity". FEBS Lett. 482 (1–2): 54–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02036-6. PMID 11018522.
- Becamel C, Figge A, Poliak S, Dumuis A, Peles E, Bockaert J, Lubbert H, Ullmer C (2001). "Interaction of serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2C receptors with PDZ10 of the multi-PDZ domain protein MUPP1". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (16): 12974–82. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008089200. PMID 11150294.
- Vassilev A, Kaneko KJ, Shu H, Zhao Y, DePamphilis ML (2001). "TEAD/TEF transcription factors utilize the activation domain of YAP65, a Src/Yes-associated protein localized in the cytoplasm". Genes Dev. 15 (10): 1229–41. doi:10.1101/gad.888601. PMC 313800. PMID 11358867.
- Hamazaki Y, Itoh M, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2002). "Multi-PDZ domain protein 1 (MUPP1) is concentrated at tight junctions through its possible interaction with claudin-1 and junctional adhesion molecule". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (1): 455–61. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109005200. PMID 11689568.
- Kimber WA, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Cheung PC, Deak M, Marsden LJ, Kieloch A, Watt S, Javier RT, Gray A, Downes CP, Lucocq JM, Alessi DR (2002). "Evidence that the tandem-pleckstrin-homology-domain-containing protein TAPP1 interacts with Ptd(3,4)P2 and the multi-PDZ-domain-containing protein MUPP1 in vivo". Biochem. J. 361 (Pt 3): 525–36. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3610525. PMC 1222335. PMID 11802782.
- Poliak S, Matlis S, Ullmer C, Scherer SS, Peles E (2002). "Distinct claudins and associated PDZ proteins form different autotypic tight junctions in myelinating Schwann cells". J. Cell Biol. 159 (2): 361–72. doi:10.1083/jcb.200207050. PMC 2173042. PMID 12403818.
- Griffon N, Jeanneteau F, Prieur F, Diaz J, Sokoloff P (2003). "CLIC6, a member of the intracellular chloride channel family, interacts with dopamine D(2)-like receptors". Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 117 (1): 47–57. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(03)00283-3. PMID 14499480.
- Krapivinsky G, Medina I, Krapivinsky L, Gapon S, Clapham DE (2004). "SynGAP-MUPP1-CaMKII synaptic complexes regulate p38 MAP kinase activity and NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic AMPA receptor potentiation". Neuron. 43 (4): 563–74. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.08.003. PMID 15312654.
- van de Pavert SA, Kantardzhieva A, Malysheva A, Meuleman J, Versteeg I, Levelt C, Klooster J, Geiger S, Seeliger MW, Rashbass P, Le Bivic A, Wijnholds J (2005). "Crumbs homologue 1 is required for maintenance of photoreceptor cell polarization and adhesion during light exposure". J. Cell Sci. 117 (Pt 18): 4169–77. doi:10.1242/jcs.01301. PMID 15316081.
- Coyne CB, Voelker T, Pichla SL, Bergelson JM (2005). "The coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor interacts with the multi-PDZ domain protein-1 (MUPP-1) within the tight junction". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (46): 48079–84. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409061200. PMID 15364909.
- Okuhira K, Fitzgerald ML, Sarracino DA, Manning JJ, Bell SA, Goss JL, Freeman MW (2006). "Purification of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 and associated binding proteins reveals the importance of beta1-syntrophin in cholesterol efflux". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (47): 39653–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.M510187200. PMID 16192269.
- Heydecke D, Meyer D, Ackermann F, Wilhelm B, Gudermann T, Boekhoff I (2006). "The multi PDZ domain protein MUPP1 as a putative scaffolding protein for organizing signaling complexes in the acrosome of mammalian spermatozoa". J. Androl. 27 (3): 390–404. doi:10.2164/jandrol.05166. PMID 16452527.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Szafranski K, Schindler S, Taudien S, Hiller M, Huse K, Jahn N, Schreiber S, Backofen R, Platzer M (2007). "Violating the splicing rules: TG dinucleotides function as alternative 3' splice sites in U2-dependent introns". Genome Biology. 8 (8): R154. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-8-r154. PMC 2374985. PMID 17672918.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.