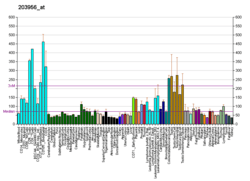
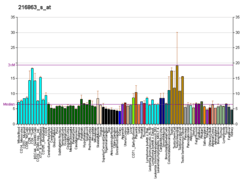
MORC family CW-type zinc finger protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MORC2 gene.[5][6]
Further reading
- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Suyama M, et al. (1999). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 5 (6): 355–64. doi:10.1093/dnares/5.6.355. PMID 10048485.
- Dunham I, Shimizu N, Roe BA, et al. (1999). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 22". Nature. 402 (6761): 489–95. doi:10.1038/990031. PMID 10591208.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Collins JE, Wright CL, Edwards CA, et al. (2005). "A genome annotation-driven approach to cloning the human ORFeome". Genome Biol. 5 (10): R84. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r84. PMC 545604. PMID 15461802.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Nousiainen M, Silljé HH, Sauer G, et al. (2006). "Phosphoproteome analysis of the human mitotic spindle". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (14): 5391–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507066103. PMC 1459365. PMID 16565220.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, et al. (2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nat. Biotechnol. 24 (10): 1285–92. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.