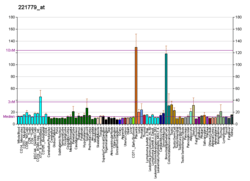
MICALL1
References
Further reading
- Dunham I, Shimizu N, Roe BA, et al. (1999). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 22". Nature. 402 (6761): 489–95. doi:10.1038/990031. PMID 10591208.
- Hirosawa M, Nagase T, Murahashi Y, et al. (2001). "Identification of novel transcribed sequences on human chromosome 22 by expressed sequence tag mapping". DNA Res. 8 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1093/dnares/8.1.1. PMID 11258795.
- Marzesco AM, Dunia I, Pandjaitan R, et al. (2002). "The small GTPase Rab13 regulates assembly of functional tight junctions in epithelial cells". Mol. Biol. Cell. 13 (6): 1819–31. doi:10.1091/mbc.02-02-0029. PMC 117606. PMID 12058051.
- Terman JR, Mao T, Pasterkamp RJ, et al. (2002). "MICALs, a family of conserved flavoprotein oxidoreductases, function in plexin-mediated axonal repulsion". Cell. 109 (7): 887–900. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00794-8. PMID 12110185.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Weide T, Teuber J, Bayer M, Barnekow A (2003). "MICAL-1 isoforms, novel rab1 interacting proteins". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 306 (1): 79–86. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00918-5. PMID 12788069.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Jin J, Smith FD, Stark C, et al. (2004). "Proteomic, functional, and domain-based analysis of in vivo 14-3-3 binding proteins involved in cytoskeletal regulation and cellular organization". Curr. Biol. 14 (16): 1436–50. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.07.051. PMID 15324660.
- Collins JE, Wright CL, Edwards CA, et al. (2005). "A genome annotation-driven approach to cloning the human ORFeome". Genome Biol. 5 (10): R84. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r84. PMC 545604. PMID 15461802.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.