List of ships of the Confederate States Navy

This is a list of ships of the Confederate States Navy (CSN), used by the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War between 1861 and 1865. Included are some types of civilian vessels, such as blockade runners, steamboats, and privateers which contributed to the war efforts by the CSN. Also included are special types of floating batteries and harbor defense craft.
CSN Warships
The Secretary of the CS Navy, Stephen Mallory, was very aggressive on a limited budget in a land-focused war, and developed a two-pronged warship strategy of building ironclad warships for coastal and national defense, and commerce raiding cruisers, supplemented with exploratory use of special weapons such as torpedo boats and torpedoes.
Batteries
Based upon the successful employment of ironclad warships, particularly batteries, at the Battle of Kinburn, Britain and France decided to focus on armor plated warships, starting with coastal battery designs. Initial ocean-going ironclad cruisers, such as the French Gloire and the British HMS Warrior were only just emerging in 1859 and 1860, and were beyond the budget and timeline necessary for rapid force deployment that the CS Navy needed for immediate coastal defenses in 1861.
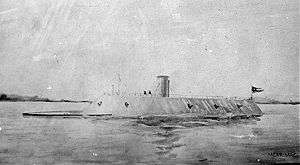
Therefore, the Confederate Congress voted $2 million in May 1861 to buy ironclads from overseas, and in July and August started work on construction and converting wooden ships locally. On 12 October 1861, the Manassas became the first ironclad to enter battle when she fought Union warships on the Mississippi. In February 1862, the even larger Virginia joined the Confederate Navy, having been built at Norfolk. The Confederacy built a number of ships designed as versions of the Virginia, of which several saw action. In the failed attack on Charleston on April 7, 1863 two small ironclads, Palmetto State and Chicora participated in the successful defense of the harbor. For the later attack at Mobile Bay, the Union faced the Tennessee, the Confederacy's most powerful ironclad.
Ironclad steam-powered batteries
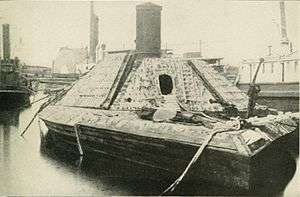
_on_James_River_after_capture_-_NARA_-_527533.jpg)
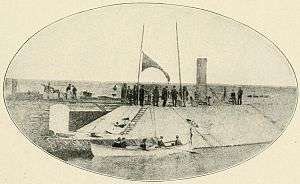

The CS Navy ironclad steamer batteries were all designed for national coastal defense.
- CSS Albemarle, twin-screw steamer, ironclad, sunk: October 28, 1864
- CSS Arkansas, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: August 5, 1862
- CSS Atlanta, triple-screw steamer, ironclad, captured: June 17, 1863
- CSS Baltic, surrendered: May 10, 1865
- CSS Charleston, steamer, ironclad, destroyed: February 18, 1865
- CSS Chicora, steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: February 18, 1865
- CSS Columbia, single screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: April 26, 1865
- CSS Eastport, incomplete, captured: February 8, 1862
- CSS Fredericksburg, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: April 4, 1865
- CSS Georgia, ironclad steam battery, scuttled: December 21, 1864
- CSS Huntsville, ironclad steam battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
- CSS Louisiana, twin screw and double center-wheel steamer, ironclad, destroyed: April 28, 1862
- CSS Manassas, screw steamer, ironclad ram, sunk: April 24, 1862
- CSS Milledgeville, steamer ironclad, burned/sunk: December 21, 1864
- CSS Mississippi, 3-screw steamer, ironclad, burned: April 25, 1862
- CSS Missouri, steam sloop, ironclad, surrendered: June 3, 1865
- CSS Mobile, screw steamer, burned before launching: May 21, 1863
- CSS Muscogee, twin-screw with center-wheel steamer, ironclad, burned: April 17, 1865
- CSS Nashville, side-wheel steamer, ironclad, surrendered: May 10, 1865
- CSS Neuse, twin-screw steamer, ironclad, destroyed: March 14, 1865
- CSS New Orleans, floating steam battery, scuttled: April 7, 1862
- CSS North Carolina, steamer, ironclad, accidentally sank: September 27, 1864
- CSS Palmetto State, sloop, ironclad, destroyed: 18 February 1865
- CSS Raleigh, sloop, ironclad, wrecked: May 7, 1864
- CSS Richmond, screw steamer, ironclad, scuttled: April 3, 1865
- CSS Savannah, steam sloop ironclad, burned: December 21, 1864
- CSS Tennessee, ironclad ram, destroyed before launching: June 5, 1862
- CSS Tennessee, single screw steamer, ironclad, captured: August 5, 1864
- CSS Texas, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, never completed, captured: April 4, 1865
- CSS Tuscaloosa, ironclad steam battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
- CSS Virginia, screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: May 11, 1862
- CSS Virginia II, ironclad, destroyed: April 4, 1865
- CSS Wilmington, twin-screw steamer, ironclad, destroyed before completion: January 1865
Ironclad floating batteries
CS Navy ironclad floating batteries lacked steam engines for propulsion and were towed into firing positions.
- CSS Arctic, ironclad floating battery, scuttled: 24 December 1864[1]
- CSS Phoenix, ironclad floating battery, destroyed: 1865
- CSS Georgia, ironclad floating battery, scuttled: December 21, 1864
Wooden floating batteries

CS Navy wooden floating batteries were towed into firing positions, and as in the case at Charleston Harbor, used for makeshift defense.
- Floating Battery of Charleston Harbor
- CSS Memphis, floating battery
Cruisers
CS Navy cruisers were ocean-going ships designed primarily for the Confederate Navy's strategy of guerre de course. Confederate States Navy cruisers were typically lightly armed, with a couple of large guns or a pivot gun, and often very fast. The Navy planned to add ironclad cruisers to their fleet, successfully procuring one, but too late to be of benefit for the war.
Wooden Cruisers
- CSS Alabama, screw steamer, sloop-of-war, built in Birkenhead, England by John Laird Sons and Company, sunk: June 19, 1864
- CSS Alexandra, screw steamer, bark-rigged, built in Liverpool, England, seized before delivery: April 5, 1863
- CSS America, racing yacht, scuttled: 1862
- CSS Archer, schooner, captured: June 28, 1863
- CSS Caleb Cushing, revenue cutter, burned: June 28, 1863
- CSS Chickamauga, screw steamer, burned
- CSS Clarence, brig, burned: June 12, 1863
- CSS Florida, screw steamer, sloop, captured: October 7, 1864
- CSS Georgia, screw steamer, iron, sold: June 1, 1864
- CSS Georgiana, steamer, destroyed: After leaving port on March 20, 1863 the steamer is destroyed on March 22, 1863
- CSS Lapwing, bark, burned: June 20, 1863
- CSS Nashville, side-wheel steamer, brig rigged, sold and used as privateer Rattlesnake and sunk, February 28, 1862
- CSS Rappahannock, screw steamer, sloop-of-war, turned over at war's end
- CSS Shenandoah, screw steamer, full rigged, iron-framed, turned over to British Government
- CSS Sumter, screw steamer, sloop, sold: December 19, 1862
- CSS Tacony, bark, burned: June 25, 1863
- CSS Tallahassee, twin-screw steamer, sloop, seized: April 9, 1865 by British Government
- CSS Tuscaloosa, bark, seized: December 29, 1863
- CSS United States, frigate, sail, harbor defense use only, scuttled
Ironclad cruisers
But the CS Navy attempts to procure ironclad cruisers from overseas were frustrated as European nations confiscated ships being built for the Confederacy. Only the Stonewall was completed and successfully delivered, and she arrived in American waters just in time for the end of the war.
- CSS North Carolina I, seized October 1863 and commissioned as HMS Scorpion
- CSS Mississippi II, seized October 1863 and commissioned as HMS Wivern
- CSS Stonewall, twin-screw steamer, brig rigged, ironclad, surrendered in Cuba at end of war, returned to US, sold to Japan and renamed Kotetsu
- CSS Cheops, sister to Stonewall, built in France and sold to Prussia, October 29, 1865, and named SMS Prinz Adalbert
- "Ironclad Frigate No. 61", arranged by Captain James H. North, CSN, sold to Denmark, commissioned as Danmark
- CSS Georgia screw corvette 2017 tons [1,150 tons BOM].[2] Sold to Peru after the French government stopped its sale to the Confederacy. Taken into service as BAP Unión 1864. Scuttled January 1881 to avoid capture.[3][4]
- CSS Texas, screw corvette and sister-ship of BAP Union. Sold to Peru after the French government stopped its sale to the Confederacy. Taken into service as BAP America.
Lost during the Arica tsunami on 13 August 1868.
.jpg) HMS Scorpion
HMS Scorpion HMS Wivern
HMS Wivern CSS Stonewall 1865
CSS Stonewall 1865 SMS PrinzAdalbert 1864
SMS PrinzAdalbert 1864.jpg) KMD Danmark
KMD Danmark
 BAP Unión 1880
BAP Unión 1880 The scuttled BAP Unión 1881
The scuttled BAP Unión 1881 The BAP corvette America wrecked by the 1868 tsunami at Arica
The BAP corvette America wrecked by the 1868 tsunami at Arica
Gunboats

- CSS Appomattox, tugboat, burned: February 10, 1862
- CSS Bartow, schooner
- CS Bayou City, surrendered to U.S. Navy 1865; sold 1866
- CSS Beaufort, screw steamer, captured by U.S. Navy April 3, 1865
- CSS Bienville, side-wheel steamer, destroyed incomplete April 1862
- CSS Black Warrior, schooner, burned February 10, 1862
- CSS Bombshell, steamer, captured: May 5, 1864
- CSS Calhoun, sidewheel gunboat, captured: January 23, 1862
- CSS Carondelet, sidewheel steamer, destroyed April 1862
- CSS Chattahoochee, twin-screw steamer, scuttled: December, 1864
- CSS Clifton, side-wheel gunboat, Texas Marine Department, scuttled March 1864
- CSS Curlew, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: February 7, 1862
- CSS De Soto, side-wheel steamer, captured: September 30, 1862
- CSS Defiance, river steamer, destroyed: April 28, 1862
- CSS Diana, steamer, which twice changed hands, managed to survive the Civil War and was presumably decommissioned.
- CSS Drewry, steamer, tender, destroyed: January 24, 1865
- CSS Ellis, steamer, tugboat, captured: February 10, 1862
- CSS Equator, steamer, burned: 1865
- CSS Fanny, screw steamer, iron hull, burned: February 10, 1862
- CSS Fashion, schooner
- CSS Forrest, steamer, tugboat, burned: February 10, 1862
- CSS Fulton
- CSS Gaines, side-wheel steamer
- CSS General Quitman, steamer, destroyed: April 24, 1862
- CSS General Polk, steamer, destroyed: June 26, 1862
- CSS George Page, side-wheel river steamer, burned
- CSS Germantown sloop-of-war, sunk as blockship May 10, 1862
- CSS Governor Moore, side-wheel steamer, schooner rigged, destroyed: April 23, 1862
- CSS Hampton, screw steamer, burned: April 4, 1865
- CSS Harmony, steamer, tug
- CSS Helen, side-wheel steamer; Charleston harbor gunboat: sank March 10, 1864
- CSS Henry Dodge, cutter, schooner rigged
- CSS Huntress, side-wheel steamer
- CSS Isondiga, steamer, burned: December 21, 1864
- CSS Ivy, side-wheel river steamer, burned: 1863
- CSS J. A. Cotton, a side-wheel river steamer, burned: January 14, 1863 (See: Bayou Teche)(See: USS Colonel Kinsman (1862)). Sometimes called an ironclad since she had a small amount of railroad iron tacked onto her side.
- CSS Jackson, side-wheel river steamer, tug, sunk
- CSS Jamestown, side-wheel steamer, sunk: May, 1862
- CSS Junaluska, steamer, tug, dismantled: 1862
- CSS Kate Bruce, schooner, scuttled
- CSS Lady Davis, steamer tug, iron, machinery mounted in CSS Palmetto
- CSS Launch No. 3, steamer, captured: April, 1862
- CSS Launch No. 2, steamer, destroyed: April 24, 1862
- CSS Livingston, side-wheel steamer, destroyed: June 26, 1862
- CSS Macon, steamer
- CSS Matilda, bark
- CSS Maurepas, side-wheel steamer, sunk: June, 1862
- CSS McRae, screw steamer, sloop rigged, sunk: April 28, 1862
- CSS Morgan, side-wheel steamer, surrender: 1865
- CSS Morgan, cutter
- CSS Morning Light, sail, burned: January 23, 1863
- CSS Nansemond, twin-screw gunboat, burned: April 3, 1865
- CSS Neptune, steamer, sunk: January 1, 1863
- CSS Nina, steamer
- CSS Oregon, steamer, scuttled: Apr, 1862
- CSS Pamlico, side-wheel river steamer, burned: 1862
- CSS Patrick Henry, side-wheel steamer, CSNA school ship, burned: April 4, 1865
- CSS Pedee, screw steamer, sunk: 1865
- CSS Pickens, cutter, schooner rigged
- CSS Plymouth, sloop-of-war, burned: 1862
- CSS Polk, side-wheel river steamer, burned
- CSS Pontchartrain, side-wheel river steamer, burned: 1863
- CSS Raleigh, steamer
- CSS Rappahannock, formerly St. Nicholas until seized and purchased in 1861, side-wheel steamer, burned: April, 1862
- CSS Rescue, cutter, schooner rigged
- CSS Resolute, burned: April 24, 1862
- CSS Roanoke, screw steamer, destroyed: April 4, 1865
- CSS Queen of the West,
- CSS Sampson, side-wheel river steamer
- CSS Savannah, steamer, foundered: August 18, 1863
- CSS Schultz, formerly A.H. Schultz, until seized and purchased in 1861, side-wheel steamer, used as a flag of truce vessel, sunk: February 17, 1865
- CSS Sea Bird, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: February 10, 1862
- CSS Selma, side-wheel river steamer, captured: August 5, 1864
- CSS Spray, steam tug, sunk
- CSS St. Mary, side-wheel river steamer, burned
- CSS Stono, burned: 1865
- CSS Talomico, side-wheel steamer, sunk: 1863
- CSS Teaser, tug, captured: 1862
- CSS Tiger
- CSS Torpedo, screw steamer, tug/tender, iron, burned: April 4, 1865
- CSS Tropic
- CSS Tuscarora, side-wheel steamer, burned
- CSS Velocity
- CSS Washington, schooner
- CSS Water Witch, side-wheel steamer, burned: December 19, 1864
- CSS Winslow, side-wheel river steamer, wrecked
- CSS Yadkin, steamer, burned: 1865
Torpedo boats

- CSS David, semi-submersible torpedo boat
- CSS David, larger version of David, captured incomplete: February, 1865
- CSS Midge, steam torpedo boat, captured: February, 1865
- CSS Saint Patrick, semi-submersible torpedo boat or submarine
- CSS Squire
- CSS Squib, spar torpedo boat
- CSS Hornet, spar torpedo boat
- CSS Scorpion, spar torpedo boat
- CSS Wasp, spar torpedo boat
CSN Support ships
Government blockade runners

- CSS Advance, side-wheel steamer, captured: September 10, 1864
- CSS Florida, screw steamer
- CSS Harriet Lane, side-wheel steamer
- CSS Kate Dale
- CSS Lady Stirling, side-wheel steamer, captured: October 28, 1864
- CSS Owl
- CSS Rob Roy
- CSS Robert E. Lee
- CSS William G. Hewes, (later SS Ella and Annie), captured: November 9, 1863
Government steamers
- CSS Admiral, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
- CSS Atlanta
- CSS Appomattox, screw steamer, burned: February 10, 1862
- CSS Beaufort
- CSS Beauregard, side-wheel coastal steamer, captured: December, 1864
- CSS Capitol, side-wheel river steamer burned: June 28, 1862
- CSS Campion, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
- CSS Curlew
- CSS Ellis
- CSS Fanny
- CSS George Page
- CSS Governor Moore
- CSS Grampus, stern-wheel river steamer, scuttled: April 7, 1862
- CSS Grand Duke
- CSS Ida, side-wheel coastal steamer, captured/burned: December 10, 1864
- CSS Jamestown
- CSS Nashville, 1861
- CSS Ohio Belle, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
- CSS Patrick Henry
- CSS Prince, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: April 7, 1862
- CSS Raleigh, 1861
- CSS Red Rover, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
- CSS Sea Bird
- CSS Selma
- CSS Tennessee, side-wheel steamer, captured: January, 1862
- CSS Winchester, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
Government Transports

- CSS Bombshell
- CSS City of Vicksburg, side-wheel steamer transport, damaged when rammed on February 3, 1863 then destroyed: February/March 1863
- CSS Cotton Plant
- CSS Darlington
- CSS Mars, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
- CSS The Planter, side-wheel steamer, captured by its slave pilot Robert Smalls, May 13, 1862
- CSS Sumter
- CSS Yazoo, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: April 7, 1862
Cutters
- CSS Duane, revenue cutter, schooner rigged
- CSS Lewis Cass, revenue cutter, schooner rigged
- CSS Manassas, revenue cutter, schooner rigged, dismantled
- CSS Robert McClelland, revenue cutter, schooner rigged
Hospital ships
- CSS Kanawha Valley, stern-wheel river steamer, burned: April 7, 1862
Tenders and tugs
- CSS Alert, lighthouse tender, schooner rigged
- CSS Beaufort, tugboat
- CSS Caswell, side-wheel steamer tender, burned
- CSS Firefly, side-wheel steamer tender, burned: December 21, 1864
- CSS Indian Chief, receiving ship, burned
- CSS Resolute, side-wheel steamer, tugboat, captured: December 12, 1864
- CSS Retribution, steam tugboat, sold: March 8, 1863
- CSS Satellite, tugboat, destroyed: August, 1863
- CSS Shrapnel, tender, burned: April 4, 1865
- CSS St. Philip, receiving ship, sunk
- CSS Uncle Ben, steam tugboat, machinery mounted into CSS North Carolina II
Civilian Auxiliary
Privateers
- A. C. Gunnison, privateer steam tug
- Beauregard, privateer cutter, schooner rigged, captured: November 12, 1861
- Dixie, privateer schooner, captured on April 15, 1862, but had itself captured the USA Schooner Mary Alice on July 25, 1861, the USA Barque Glenn on July 31st of 1861.
- Gibralter, privateer schooner
- Gordon, privateer, which captured the USA Brigandine William McGilvery on July 25, 1861, the USA Schooner Protector on July 28, 1861.
- Governor A. Mouton, privateer steamer, captured: May 11, 1862
- Isabella, privateer screw steamer
- J. C. Calhoun, privateer side-wheel steamer, which captured the Barque Ocean Eagle on May 16, 1861, the ship Milan in May, 1861, the Schooner Etta in May, 1861, the Brigandine Panama on May 29, 1861, the Schooner Mermaid on May 24, 1861 and the Schooner John Adams on May 24, 1861, all within its first month of operation in 1861, and which was burned: 1862
- J. M. Chapman, privateer schooner, captured: March 15, 1863
- J. O. Nixon, privateer schooner
- Jefferson Davis, privateer brig, ran aground: mid-August, 1861
- 'Judah, privateer schooner, destroyed: September 14, 1861
- Lorton, privateer schooner
- Mariner, privateer screw steamer, which captured the USA Schooner Nathaniel Chase on July 25, 1861.
- Music, privateer steamer
- Petrel, privateer, goes to sea on July 1, 1861 but sunk on July 28, 1861 by the Union U.S. Navy's USS St. Lawrence (1848).
- Sallie, privateer schooner
- Savannah, privateer schooner, captured: June 3, 1861
- Sealine, privateer brig
- Theodora, privateer side-wheel steamer
- V. H. Ivy, privateer steamer
- York, privateer pilot boat, schooner rigged, which was burned on August 9, 1861, after capturing the USA Brigandine B.T. Martin about July 28, 1861 and the Schooner George G. Baker on August 9, 1861, on the day of its demise, and then the Union quickly recaptured the George G. Baker.
Privateer Submersible Torpedo Boats
- Bayou St. John submarine
- H. L. Hunley, hand-cranked, sunk: February 17, 1864. Named in honor of its designer, Confederate marine engineer Horace Lawson Hunley.
- Pioneer
Civilian Steamers
- Dick Keys, captured: May 7, 1861
- Lewis, captured: May 7, 1861
- Swan, of Savannah
Civilian Transports
- Berwick Bay, steamer, captured February 3, 1863
- O.W. Baker, steamer, captured February 3, 1863
- Moro, steamer, captured February 3, 1863
- Era No. 5, shallow-draft steamer, captured: February 14, 1863
Civilian Blockade Runners
- Caroline, (aka USS Arizona)
- Bat, side-wheel steamship, captured: October 10, 1864
- Colonel Lamb, side-wheel steamer
- Constance Decimer (aka Constance), side-wheel steamer
- Flamingo, side-wheel steamer
- Lelia, paddle-steamer
- Mary Bowers, side-wheel steamer
- Memphis, (later USS Memphis)
- Monticello, Cuban blockade runner
- Norseman
- Ruby, side-wheel steamer
- San Quintin, Cuban blockade runner
- Stonewall Jackson, (ex-Leopard), side-wheel steamer
Foreign Blockade Runners
- Denbigh side-wheel steamer, schooner rigged
CS Army
CSA cotton-clads

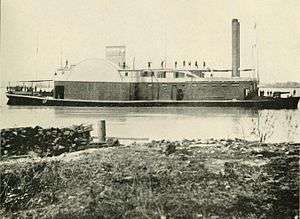

_watercolor.jpg)

Used for river defense, CS Army cottonclads were typically more lightly armored and reinforced than a regular ironclad, such as the General Sterling Price, which was converted by placing a 4-inch oak sheath with a 1-inch iron covering on her bow, and by installing double pine bulkheads filled with compressed cotton bales. Many of the cottonclads were outfitted with rams.
River Defense Fleet cotton-clads:
- CSS Colonel Lovell, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, sunk: June 6, 1862
- CSS General Beauregard, steamer, cotton-clad ram, sunk: June 6, 1862
- CSS General Bragg, steamer, cotton-clad ram, captured: June 6, 1862
- CSS Breckinridge, stern-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, burned: Apr, 1862
- CSS Defiance, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, burned: 1862
- CSS General Earl Van Dorn, steamer, cotton-clad ram, burned
- CSS General M. Jeff Thompson, steamer, cotton-clad ram, sunk: June 6, 1862
- CSS General Sterling Price, steamer, cotton-clad ram, sunk: June 6, 1862; raised into Union service
- CSS General Sumter, steamer, cotton-clad ram, captured: June 6, 1862
- CSS Governor Moore, steamer, schooner rigged, cotton-clad ram, destroyed: April 24, 1862
- CSS Little Rebel, steamer, cotton-clad ram, captured: June 6, 1862
- CSS Resolute, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram
- CSS Stonewall Jackson, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, burned: April 24, 1862
- CSS Warrior, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, destroyed: April, 1862
Other CS Army cotton-clads:
- CSS Grand Duke, steamer, cotton-clad, burned: 1863
- CSS Josiah A. Bell, steamer, cotton-clad, operated by Texas Marine Department
- CSS Queen of the West, river steamer, cotton-clad and ironclad ram, exploded: April 14, 1863
- CSS Uncle Ben, steamer, cotton-clad, operated by Texas Marine Department
- CSS Webb, river steamer, cotton-clad ram, transferred to CS Navy early 1865, burned: April, 1865
Other CSA Boats
- CSA Bayou City, CS Army gunboat, side-wheel steamer
- CSA General Lee, CS Army transport, which was captured by the Union on August 10, 1862 while the transport was on the Savannah River in Georgia
- CSA John Simonds, CS Army support ship, side-wheel steamer, sunk: April 7, 1862
- CSA Louisville, CS Army cargo steamer, captured: July 13, 1863
- CSA Planter, CS Army transport, side-wheel steamer, surrendered: May 13, 1862
- CSA Neptune, CS Army tugboat, sank: January 1, 1863
Other
Prizes
- Alvarado - prize bark, captured: by privateer Jefferson Davis, July 21, 1861
- Enchantress - prize schooner, captured: by privateer Jefferson Davis July 6, 1861
Undetermined
- CSS Segar
- CSS Smith
- CSS W. R. Miles
See also
Notes
- ↑ Naval History and Heritage Command: Ship Histories: Confederate Ships: Arctic
- ↑ Page 77, Clowes, William Laird, Four Modern Naval Campaigns, pub Unit Library, 1902, reprinted Cormarket Press, ISBN 0-7191-2020-9
- ↑ More old Peruvian ships, page 1, American and French made ships
See also Spanish Wikipedia article on BAP Union. - ↑
References
- Coski, John M. Capital Navy: The Men, Ships and Operations of the James River Squadron, Campbell, CA: Savas Woodbury Publishers, 1996, ISBN 1-882810-03-1
- Gardiner Steam, Steel and Shellfire
- Lambert A., Iron Hulls and Armour Plate
- Scharf, J. Thomas. History of the Confederate States Navy: From its Organization to the Surrender of its Last Vessel. New York: Rogers and Sherwood, 1887; repr. The Fairfax Press, 1977.