Lartigue Monorail

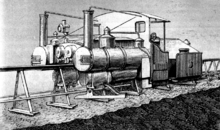
The Lartigue Monorail system was developed by the French engineer Charles Lartigue (1834–1907). He developed a horse drawn monorail system invented by Henry Robinson Palmer in 1821 further.[1]
The most famous Lartigue railway was the Listowel and Ballybunion Railway in Ireland.
Another line, 17 km (11 mi) long, was built in 1895 between Feurs and Panissières, in the French département of Loire.
Lartigue had seen camels in Algeria carrying heavy loads balanced in panniers on their backs. This inspired him to design a new type of railway. Instead of the conventional two parallel rails on the ground, it had a single rail sitting above the sand and held at waist height on A-shaped trestles. The carriages sat astride the trestles like panniers.
By 1881 Lartigue had built a 90 km (56 mi) monorail to transport esparto grass across the Algerian desert, with mules pulling trains of panniers that straddled the elevated rail.
However the Lartigue system as built was not truly a monorail, since it was necessary to add two further rails, one on each side, lower down the A frames. These did not carry any weight, but unpowered stabilising wheels fitted to all the engines and wagons contacted these extra rails to prevent the vehicles from overbalancing.
Listowel and Ballybunion Railway


This was a 14.4 km (8.9 mi) monorail built on the Lartigue principle in County Kerry in Ireland. It linked Listowel and Ballybunion, and opened on 29 February 1888.[2] The track was prefabricated and easily erected, and the capital cost was only £30,000, far lower than a conventional railway. However, the system had significant operating drawbacks.
The locomotives were of the 0-6-0 type (strictly speaking, 0-3-0), constructed by the Hunslet Engine Company. They were specially built with two boilers to balance on the track, and consequently two fireboxes, one of which had to be stoked by the driver. They were also fitted with powered tenders for auxiliary use on hills. The tender wheels were driven by two cylinders via spur gears. Two small chimneys were fitted to each tender to discharge the exhaust steam from these cylinders. A smaller engine, nicknamed the "coffee pot", was used in the construction of the railway, having been used previously on a demonstration line at Tothill Fields in London. It can be seen on an early photo of 1888.
Loads had to be evenly balanced. If a farmer wanted to send a cow to market, he would have to send two calves to balance it, which would travel back on opposite sides of the same freight wagon, thereby balancing each other.[3]
Another problem with using the Lartigue system in populated areas was that, due to the track's design, it was not possible to build level crossings. In order for a road to cross the track, a kind of double-sided drawbridge had to be constructed, which required an attendant to operate it. Where farmers' tracks crossed the line there were level crossings based on the principle of a turntable. These were locked and the farmer in question provided with a key. Once unlocked, the track could be swivelled to one side to allow the crossing to be used. Both the swivelling and drawbridge type crossings were automatically linked to signals, which stopped any approaching trains; road traffic was always given priority under this system.
Passengers could not pass from one side of a carriage to another while in motion. A kind of footbridge was built into one end of some of the passenger coaches, while at least one such bridge was carried on a separate wagon. This allowed passengers to cross from one side of the line to the other when the train stopped at a station.
Conventional railway points could not be used, so a similar function was fulfilled by a large number of curved movable pieces of track which, when rotated one way, would connect the main and one direction; when turned end-for-end, the curve went in the opposite direction, and so connected the main and a different track. These could not be called turntables since they could only be moved when there was no rolling stock on them.
The line closed in 1924 after the track was damaged during the Irish Civil War, and everything was scrapped, except a short section of the track.
Accidents
On 29 September 1889, a passenger train was derailed near Galey bridge, probably as a result of sabotage to the line. Several bolts were found to have been removed from the track and discarded some distance away. Fortunately no-one was injured.[4]
On 28 November 1907, a double-headed train on a busy race day collided with some sleepers on a trestle and derailed.[5]
Restoration

In 2003 the Lartigue Monorailway Restoration Committee, a voluntary organisation from Listowel, opened a 1-kilometre (0.62 mi) section of Lartigue monorail on the trackbed of the former North Kerry line in Listowel. The line is worked by a Diesel locomotive built to resemble the original 0-3-0 steam engines. The locomotive and its train of replica coaches were built by Alan Keef Ltd.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ "The Lartigue Railway". Australian Town and Country Journal. NSW. 19 March 1887. p. 32. Retrieved 23 February 2013 – via National Library of Australia.
- ↑ Guerin, Michael (1988). The Lartigue: Listowel and Ballybunion Railway. Listowel: Lartigue Centenary Committee. ISBN 0-9513549-0-6.
- ↑ Sekon, G. A. (November 1924). The Railway Magazine. London. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ http://www.railwaysarchive.co.uk/documents/BoT_GaleyBridge1889.pdf
- ↑ "RAILWAY DISASTER". The Freeman's Journal. LVIII (3592). Sydney. 28 November 1907. p. 8. Retrieved 31 January 2017 – via National Library of Australia.
- ↑ "Listowel and Ballybunion Railway".
Further reading
- Newham, A.T. (1998) [1989]. The Listowel and Ballybunion Railway (LP33 ed.). Oakwood Press. ISBN 0-85361-093-2.
- The Graphic (January): 61. 1887. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lartigue Monorail. |