Lake Abijatta
| Lake Abijatta | |
|---|---|
 Lake Abijatta (right) and Lake Shala (left) | |
 | |
| Coordinates | 7°37′N 38°36′E / 7.617°N 38.600°ECoordinates: 7°37′N 38°36′E / 7.617°N 38.600°E |
| Basin countries | Ethiopia |
| Max. length | 17 km (11 mi) |
| Max. width | 15 km (9.3 mi) |
| Surface area | 205 km2 (79 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 14 m (46 ft) |
| Surface elevation | 1,573 m (5,161 ft) |
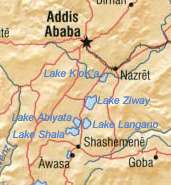
Lake Abijatta is an alkaline lake in Ethiopia. It lies in the Main Ethiopian Rift valley south of Addis Ababa, in the Abijatta-Shalla National Park.
Overview

According to the Statistical Abstract of Ethiopia for 1967/68, the lake is 17 kilometers long and 15 km wide, with a surface area of 205 square kilometers. It has a maximum depth of 14 meters and is at an elevation of 1,573 meters.
Along the northeastern corner of this lake are a number of hot springs, which are important both as a tourist attraction and to the local inhabitants.
Additionally, there is a soda ash operation on the shores of this lake, which produces 20,000 tons of sodium carbonate. Proven reserves at Lake Abijata, as well as the neighboring Shala and Chitu lakes, exceed 460 million tons.[1] Flamingoes are also found at the lake.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Current Exploration and Mining Archived 2007-04-22 at Archive.is, Geological Survey of Ethiopia Web Page (accessed 26 January 2009)