Lactacystin
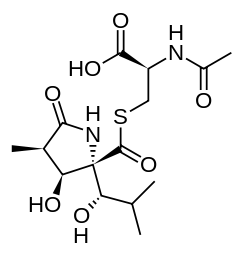 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(acetylamino)-3-[({3-hydroxy-2-[1-hydroxy-2-methylpropyl]-4-methyl-5-oxopyrrolidin-2-yl}carbonyl)sulfanyl]propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Lactacystin |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24N2O7S | |
| Molar mass | 376.42 g·mol−1 |
| log P | 0.086 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.106 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 10.891 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lactacystin is an organic compound naturally synthesized by bacteria of the genus Streptomyces first described in 1991.[1] The first total synthesis of lactacystin was developed by Elias Corey and Gregory Reichard in 1992.[2] Lactacystin binds and inhibits specific catalytic subunits of the proteasome,[3] a protein complex responsible for the bulk of proteolysis in the cell, as well as proteolytic activation of certain protein substrates. It was the first non-peptidic proteasome inhibitor discovered and is widely used as a research tool in biochemistry and cell biology. It covalently modifies the amino-terminal threonine of specific catalytic subunits of the proteasome, a discovery helped to establish the proteasome as a mechanistically novel class of protease: an amino-terminal threonine protease. The molecule is most commonly used as in biochemistry and cell biology laboratories as a selective inhibitor of the proteasome.[3][4] The molecule is a lactam, or cyclic amide. A number of syntheses of this molecule have been published and there are more than 1,500 citations for lactacystin in PubMed as of 2013.
See also
References
- ↑ Omura S, Fujimoto T, Otoguro K, Matsuzaki K, Moriguchi R, Tanaka H, Sasaki Y. (1991). Lactacystin, a novel microbial metabolite, induces neuritogenesis of neuroblastoma cells: S. Omura, et al. J. Antibiot. 44(1):113-6.
- ↑ "Total Synthesis of Lactacystin" Corey, E. J.; Reichard, G. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10677.
- 1 2 Fenteany G, Standaert RF, Lane WS, Choi S, Corey EJ, Schreiber SL (1995). "Inhibition of proteasome activities and subunit-specific amino-terminal threonine modification by lactacystin". Science. 268 (5211): 726–31. doi:10.1126/science.7732382. PMID 7732382.
- ↑ Orlowski RZ. (1999). The role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6: 303-313.