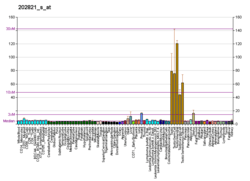
Lipoma-preferred partner is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LPP gene.[5][6]
Function
Lipoma-preferred partner is a subfamily of LIM domain proteins that are characterized by an N-terminal proline rich region and three C-terminal LIM domains. The encoded protein localizes to the cell periphery in focal adhesions and may be involved in cell-cell adhesion and cell motility. This protein also shuttles through the nucleus and may function as a transcriptional co-activator. This gene is located at the junction of certain disease related chromosomal translocations which result in the expression of fusion proteins that may promote tumor growth.[6]
Further reading
- Schoenmakers EF, Wanschura S, Mols R, et al. (1995). "Recurrent rearrangements in the high mobility group protein gene, HMGI-C, in benign mesenchymal tumours". Nat. Genet. 10 (4): 436–44. doi:10.1038/ng0895-436. PMID 7670494.
- Petit MM, Swarts S, Bridge JA, Van de Ven WJ (1998). "Expression of reciprocal fusion transcripts of the HMGIC and LPP genes in parosteal lipoma". Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 106 (1): 18–23. doi:10.1016/S0165-4608(98)00038-7. PMID 9772904.
- Petit MM, Fradelizi J, Golsteyn RM, et al. (2000). "LPP, an Actin Cytoskeleton Protein Related to Zyxin, Harbors a Nuclear Export Signal and Transcriptional Activation Capacity". Mol. Biol. Cell. 11 (1): 117–29. doi:10.1091/mbc.11.1.117. PMC 14761. PMID 10637295.
- Rogalla P, Lemke I, Kazmierczak B, Bullerdiek J (2001). "An identical HMGIC-LPP fusion transcript is consistently expressed in pulmonary chondroid hamartomas with t(3;12)(q27-28;q14-15)". Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 29 (4): 363–6. doi:10.1002/1098-2264(2000)9999:9999<1::AID-GCC1043>3.0.CO;2-N. PMID 11066083.
- Harrington JJ, Sherf B, Rundlett S, et al. (2001). "Creation of genome-wide protein expression libraries using random activation of gene expression". Nat. Biotechnol. 19 (5): 440–5. doi:10.1038/88107. PMID 11329013.
- Dahéron L, Veinstein A, Brizard F, et al. (2001). "Human LPP gene is fused to MLL in a secondary acute leukemia with a t(3;11) (q28;q23)". Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 31 (4): 382–9. doi:10.1002/gcc.1157. PMID 11433529.
- Lemke I, Rogalla P, Bullerdiek J (2002). "A novel LPP fusion gene indicates the crucial role of truncated LPP proteins in lipomas and pulmonary chondroid hamartomas". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 95 (3–4): 153–6. doi:10.1159/000059338. PMID 12063392.
- Petit MM, Meulemans SM, Van de Ven WJ (2003). "The focal adhesion and nuclear targeting capacity of the LIM-containing lipoma-preferred partner (LPP) protein". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (4): 2157–68. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206106200. PMID 12441356.
- Lemke I, Rogalla P, Grundmann F, et al. (2003). "Expression of the HMGA2-LPP fusion transcript in only 1 of 61 karyotypically normal pulmonary chondroid hamartomas". Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 138 (2): 160–4. doi:10.1016/S0165-4608(02)00595-2. PMID 12505264.
- Salomon AR, Ficarro SB, Brill LM, et al. (2003). "Profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation pathways in human cells using mass spectrometry". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (2): 443–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.2436191100. PMC 141014. PMID 12522270.
- Li B, Zhuang L, Reinhard M, Trueb B (2003). "The lipoma preferred partner LPP interacts with alpha-actinin". J. Cell Sci. 116 (Pt 7): 1359–66. doi:10.1242/jcs.00309. PMID 12615977.
- Gorenne I, Nakamoto RK, Phelps CP, et al. (2003). "LPP, a LIM protein highly expressed in smooth muscle". Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. 285 (3): C674–85. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00608.2002. PMID 12760907.
- Brill LM, Salomon AR, Ficarro SB, et al. (2004). "Robust phosphoproteomic profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation sites from human T cells using immobilized metal affinity chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry". Anal. Chem. 76 (10): 2763–72. doi:10.1021/ac035352d. PMID 15144186.
- Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, et al. (2005). "Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells". Nat. Biotechnol. 23 (1): 94–101. doi:10.1038/nbt1046. PMID 15592455.
- Petit MM, Meulemans SM, Alen P, et al. (2006). "The tumor suppressor Scrib interacts with the zyxin-related protein LPP, which shuttles between cell adhesion sites and the nucleus". BMC Cell Biol. 6: 1. doi:10.1186/1471-2121-6-1. PMC 546208. PMID 15649318.
- Zhang Y, Wolf-Yadlin A, Ross PL, et al. (2005). "Time-resolved mass spectrometry of tyrosine phosphorylation sites in the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network reveals dynamic modules". Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 4 (9): 1240–50. doi:10.1074/mcp.M500089-MCP200. PMID 15951569.
- Tao WA, Wollscheid B, O'Brien R, et al. (2005). "Quantitative phosphoproteome analysis using a dendrimer conjugation chemistry and tandem mass spectrometry". Nat. Methods. 2 (8): 591–8. doi:10.1038/nmeth776. PMID 16094384.
- von Ahsen I, Rogalla P, Bullerdiek J (2006). "Expression patterns of the LPP-HMGA2 fusion transcript in pulmonary chondroid hamartomas with t(3;12)(q27 approximately 28;q14 approximately 15)". Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 163 (1): 68–70. doi:10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2005.02.023. PMID 16271958.
- Kubo T, Matsui Y, Goto T, et al. (2006). "Overexpression of HMGA2-LPP fusion transcripts promotes expression of the alpha 2 type XI collagen gene". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 340 (2): 476–81. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.12.042. PMID 16375854.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.