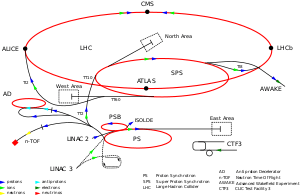
CERN Hadron Linacs
 | |
| List of current particle accelerators at CERN | |
|---|---|
| Linac 2 | Accelerates protons |
| Linac 3 | Accelerates ions |
| Linac 4 | Accelerates negative hydrogen ions |
| AD | Decelerates antiprotons |
| LHC | Collides protons or heavy ions |
| LEIR | Accelerates ions |
| PSB | Accelerates protons or ions |
| PS | Accelerates protons or ions |
| SPS | Accelerates protons or ions |

The CERN hadron Linacs are linear accelerators that accelerate beams of hadrons from a standstill to be used by the larger circular accelerators at the facility.
 Linac 1, operating from 1958 until 1992
Linac 1, operating from 1958 until 1992 Linac 2, currently used to accelerate protons
Linac 2, currently used to accelerate protons Linac 3, currently used to accelerate ions
Linac 3, currently used to accelerate ions Linac 4, planned to replace Linac 2 by 2020, will accelerate negative hydrogen ions
Linac 4, planned to replace Linac 2 by 2020, will accelerate negative hydrogen ions
Linac 1
Linac 1 was CERN's first linear accelerator, built to inject 50 MeV protons into the Proton Synchrotron (PS). Conceived in the early 1950s, its principle design was based on a similar accelerator at AERE in England.[1] The first beams were accelerated in 1958, at currents of 5 mA and a pulse length of 20 μs, which was the world record at that time.[1] The accelerator was fully operational by September 1959, when the design energy of 50 MeV was first reached.[1][2]
From then on, Linac 1 experienced a phase of rapid development and constant improve of the output parameters. This culminated in 1978, when a maximal proton current of 70 mA at pulse lengths of 100 μs could be reached.[1] From 1972 on, Linac 1 didn't deliver the protons directly to the PS anymore, but to the Proton Synchrotron Booster (PSB). The PSB had been built to allow for higher energies of the protons beams already before they enter the PS.
After Linac 2 had taken over the task of accelerating protons in 1978, Linac 1 continued to be used as a reliable testbed for new developments. This included the testing and implementation of a Radio-frequency quadrupole as the initial accelerator, which replaced the original Cockcroft-Walton generator in 1984. Furthermore, ways to create and accelerate deuterons, α-particles and H− atoms were developed. The latter were used as test beams for LEAR.[1] From late 1986 on, Linac 1 was also used to accelerate oxygen and sulphur ions.[3][4]
Linac 1 ceased to be used in experiments in 1992.[5]
Linac 2
In 1963, it was decided to build a new linear accelerator, since Linac 1 was unable to keep up with the technical advances of the other machines within CERN's accelerator complex. Linac 2 replaced Linac 1 as CERN's primary source of proton beams in 1978. It kept the same beam energy, but allowed for more intense beams with beam currents of up to 150 mA and a longer pulse duration of 200 μs.[6] Originally, it had been discussed to further upgrade Linac 1 instead of building a completely new linear accelerator. However, it quickly became clear that the costs of such an update would almost be as expensive as the new Linac 2. Another fact in favor of this new construction was the possibility to ensure a smooth transition from one Linac to the other without any downtime in between.
Construction of Linac 2 started in December 1973, with an estimated budget of 21.3 million CHF, and was completed in 1978.[7]
Throughout its lifetime, Linac 2 went through several updates to keep up with the advances of CERN's accelerator system. The most important upgrade was the replacement of the old Cockcroft-Walton generator with a Radio-frequency quadrupole in 1993. This raised the output current to 180 mA.[8]
Linac 3
Linac 3 was constructed inside the former tunnel of Linac 1 and got commissioned in the summer of 1994. It had been specially constructed to accelerate heavy ions, after tests with Linac 1 and an increasing demand from the scientific community suggested to build a new Linac dedicated specifically to this task.[3] The accelerated particles are mainly lead ions, which are provided to the PSB, LHC and fixed target experiments at the SPS and LEIR. For LEIR's commissioning, also oxygen ions were accelerated.[9]
After preparations from 2013 on, Linac 3 was adapted to accelerate argon ions in 2015. These were used by the NA61/SHINE experiment.[10][11]
Similarly, Linac 3 accelerated xenon ions in 2017 for NA61's fixed-target physics programme. On October 12, 2017, these were delivered to the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) for a unique run of data taking: For the first time, xenon ions were accelerated and collided in the LHC. For six hours, LHC's four experiments could take data of the colliding xenon ions.[12]
Linac 3 is expected to stay in use at least until 2022.[13]
Linac 4
Linac 4 is a future linear accelerator currently being commissioned, designed to replace Linac 2 in 2020. Unlike its predecessors, Linac 4 will accelerate negative hydrogen ions to an energy of 160 MeV. The ions are then injected to the PSB where both electrons are then stripped from each of the hydrogen ions and thus only the nucleus containing one proton remains. By using hydrogen ions instead of protons, the beam loss at the injection is reduced and simplified and this also allows more particles to accumulate in the synchrotron.[14]
Linac 4 will increase the energy by a factor of three over its predecessor, Linac 2, and achieve an energy of 160 MeV. This energy increase, when combined with the increased accumulation of particles, will enable the beam intensity to double when later delivered to LHC. This is part of the planned luminosity increase of the LHC which is scheduled for 2021.[15]
External links
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 History, Developments and Recent Performance of the CERN Linac 1 [Retrieved 2018-07-18]
- ↑ CERN Homepage: Linear accelerator 1 [Retrieved 2018-07-20]
- 1 2 D. J. Warner: New and Proposed Linacs at CERN: The LEP (e+/e-) Injector and the SPS Heavy Ion (Pb) Injector [Retrieved 2018-07-24]
- ↑ B.H.Wolf et al. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A Volume 258, Issue 1, 15 July 1987, Pages 1-8 doi:10.1016/0168-9002(87)90074-X Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved [Retrieved 2011-11-29]
- ↑ CERN Document Server: first tank of Linac 1 [Retrieved 2011-11-28]
- ↑ E. Boltezer et al.: The New CERN 50-MeV LINAC (1979) [Retrieved 2018-07-10]
- ↑ Project study for a new 50 MeV linear accelerator for the C. P. S (1973) [Retrieved 2018-07-18]
- ↑ Linac4 Technical Design Report [Retrieved 2018-07-18]
- ↑ L. Dumas et al.: Operation of the GTS-LHC Source for the Hadron Injector at CERN [Retrieved 2018-07-20]
- ↑ D Küchler et al.: Never Run Your ECR Ion Source with Argon in Afterglow for 6 Months! [Retrieved 2018-07-20]
- ↑ SHINE Homepage: NA61/SHINE Sheds Light on Strong Interactions [Retrieved 2018-07-20]
- ↑ CERN Homepage: LHC report: xenon in action [Retrieved 2018-07-20]
- ↑ CERN Homepage:Linear accelerator 3 [Retrieved 2018-07-20]
- ↑ CERN Homepage: Linear accelerator 4 [Retrieved 2018-07-20]
- ↑ "CERN unveils new linear accelerator". symmetry magazine. Retrieved 2017-09-05.