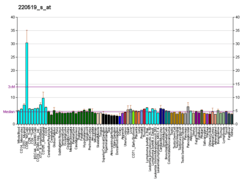
Lens fiber membrane intrinsic protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LIM2 gene.[5][6]
The mammalian lens fiber cell membrane contains 5 major proteins ranging from 70 kD to 19 kD in size. The specific function of these proteins is unknown. Some of them have been shown to be involved in the formation of cataracts, e.g., crystalline-gamma-1 (CRYG1; MIM 123660). The second most abundant intrinsic membrane protein of the lens fiber cell is MP19, so named for major lens protein having a molecular weight of 19.5 kD.
This protein appears to contain 4 transmembrane domains, is a substrate for cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C, and binds with calmodulin. Taken together, these suggest that MP19 functions in some way as a junctional component, possibly involved with lens cell communication. It has been shown to be involved with cataractogenesis.[supplied by OMIM][6]
Further reading
- Louis CF, Hur KC, Galvan AC, et al. (1989). "Identification of an 18,000-dalton protein in mammalian lens fiber cell membranes". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (33): 19967–73. PMID 2584203.
- Church RL, Wang JH (1994). "The human lens fiber-cell intrinsic membrane protein MP19 gene: isolation and sequence analysis". Curr. Eye Res. 12 (12): 1057–65. doi:10.3109/02713689309033503. PMID 8137630.
- Lieuallen K, Christensen M, Brandriff B, et al. (1994). "Assignment of the human lens fiber cell MP19 gene (LIM2) to chromosome 19q13.4, and adjacent to ETFB". Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 20 (1): 67–9. doi:10.1007/BF02257488. PMID 8197479.
- Kerscher S, Church RL, Boyd Y, Lyon MF (1996). "Mapping of four mouse genes encoding eye lens-specific structural, gap junction, and integral membrane proteins: Cryba1 (crystallin beta A3/A1), Crybb2 (crystallin beta B2), Gja8 (MP70), and Lim2 (MP19)". Genomics. 29 (2): 445–50. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.9983. PMID 8666393.
- Gonen T, Grey AC, Jacobs MD, et al. (2002). "MP20, the second most abundant lens membrane protein and member of the tetraspanin superfamily, joins the list of ligands of galectin-3". BMC Cell Biol. 2: 17. doi:10.1186/1471-2121-2-17. PMC 48140. PMID 11532191.
- Pras E, Levy-Nissenbaum E, Bakhan T, et al. (2002). "A Missense Mutation in the LIM2 Gene Is Associated with Autosomal Recessive Presenile Cataract in an Inbred Iraqi Jewish Family". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 70 (5): 1363–7. doi:10.1086/340318. PMC 447612. PMID 11917274.
- Wistow G, Bernstein SL, Ray S, et al. (2002). "Expressed sequence tag analysis of adult human iris for the NEIBank Project: steroid-response factors and similarities with retinal pigment epithelium". Mol. Vis. 8: 185–95. PMID 12107412.
- Wistow G, Bernstein SL, Wyatt MK, et al. (2002). "Expressed sequence tag analysis of adult human lens for the NEIBank Project: over 2000 non-redundant transcripts, novel genes and splice variants". Mol. Vis. 8: 171–84. PMID 12107413.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.