Kirkwood (crater)
 Clementine mosaic | |
| Coordinates | 68°48′N 156°06′E / 68.8°N 156.1°ECoordinates: 68°48′N 156°06′E / 68.8°N 156.1°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 68.12 km |
| Depth | Unknown |
| Colongitude | 200° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Daniel Kirkwood |
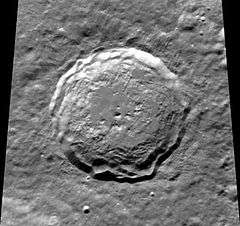
Kirkwood is a well-formed lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, on the northern hemisphere, approximately 68 kilometer in diameter. It lies just to the northeast of the crater Sommerfeld, and Hippocrates is located to the east-northeast. It was named after American astronomer Daniel Kirkwood.[1]
Description
The perimeter of this crater is generally circular, with a few slight outward notches particularly to the southeast. It displays very little appearance of wear, and neither the interior nor the outer rampart are marked by any craters of note.
The inner wall has slumped somewhat, and has formed a few terrace-like structures. The interior ejecta spreads a good way across the inner floor, covering nearly half the diameter. At the midpoint appear several small hills producing a central peak formation.
Satellite craters

By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Kirkwood.
| Feature | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kirkwood T | 69.4° N | 165.2° W | 18.61 km | WGPSN |
| Kirkwood Y | 72.2° N | 157.5° W | 17.21 km | WGPSN |
See also
- 1578 Kirkwood, asteroid
References
- ↑ "Kirkwood (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.