Kalinin K-1
| Kalinin K-1 | |
|---|---|
| Role | Airliner |
| National origin | Soviet Union |
| Manufacturer | RVZ-6 |
| First flight | 20 April 1925 |
| Status | Retired |
| Number built | 5 |
The Kalinin K-1 (Russian Калинин К-1), also known as RVZ-6, was a Soviet passenger plane that could carry three people.
Development
Konstantin A. Kalinin began work on the K-1 in 1925 at the Kharkov aviation institute. Kalinin's closest collaborators included Dmitri Tomashevich , AN Grazianski and AT Rudenko. The first designs had been drawn by Kalinin as early as 1923, when the Ukrainian airline Ukrovsdukhput had demanded a cheap, robust and easy to maintain aircraft, after the opening of the first regular flight from Moscow to Nizhny Novgorod. The K-1 was a High-wing strutted monoplane with elliptical wooden wing covered with fabric. The fuselage consisted of a tubular steel frame with Aluminium sheet covering to the rear of the cabin and fabric covering the rear fuselage, constructed was carried out by RVZ-6 (RVZ - Remvozdhukozavod - factory) at Kiev. After the first flight, on 20 April 1925,[1] factory testing took place over the Summer, and in September 1925 the K-1 carried out state acceptance trials at Moscow, reaching a speed of 191 km/h (119 mph; 103 kn) with full load at 3,000 m (9,800 ft).[2]
After the K-1 was put into use, the designers came very quickly to the decision, to replace the 170 hp Salmson RB-9 engine with a more powerful and modern engine. Several engines were considered, but Kalinin and his group ultimately opted for a 240 hp BMW IV engine.
The type was mainly used as a airliner, later as an air ambulance and also as an Agricultural aircraft, as it was able to carry 400 kg (880 lb) of chemicals.
Specifications (K-1)
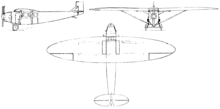
Data from The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995[3]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Capacity: 3 pax / 520 kg (1,150 lb)
- Length: 10.72 m (35 ft 2 in)
- Wingspan: 16.76 m (55 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 40 m2 (430 sq ft)
- Aspect ratio: 7
- Empty weight: 1,452 kg (3,201 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 1,972 kg (4,348 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 170 kg (370 lb) fuel; 20 kg (44 lb) oil
- Powerplant: 1 × Salmson RB-9 9-cylinder water-cooled radial piston engine, 127 kW (170 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed pitch wooden propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 160 km/h (99 mph; 86 kn)
- Cruise speed: 130 km/h (81 mph; 70 kn)
- Stall speed: 70 km/h (43 mph; 38 kn)
- Range: 600 km (373 mi; 324 nmi)
- Endurance: 4 hours
- Service ceiling: 3,000 m (9,800 ft)
- Time to altitude: 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in 12.3 minutes
- Wing loading: 49.3 kg/m2 (10.1 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.061 kW/kg (0.037 hp/lb)
- Take-off distance: 120 m (390 ft)
- Landing distance: 120 m (390 ft) at70 km/h (43 mph; 38 kn)
References
- ↑ Kopenhagen, Wilfried (2007). Lexikon Sowjetluftfahrt (Reprint ed.). Klitzschen: Elbe-Dnjepr-Verl. p. 112. ISBN 978-3-933395-90-0.
- ↑ "unknown". Flieger Revue 10/1972 (10). 1972.
- ↑ Gunston, Bill (1995). The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995. London: Osprey. pp. 132–133. ISBN 1-85532-405-9.