Joice Heth
| Joice Heth | |
|---|---|
| Born | c. 1756 |
| Died |
February 19, 1836 (aged 79–80) New York City, New York, United States |
| Occupation | Slave, circus performer |
Joice Heth (c. 1756 – February 19, 1836)[1] was an African-American slave who was exhibited by P.T. Barnum with the false claim that she was the 161-year-old nursing mammy of George Washington.
Biography
Little is known of Heth's early years. In 1835, she was held as a slave by John S. Bowling and exhibited in Louisville, Kentucky.[2] In June 1835, she was sold to promoters R.W. Lindsay and Coley Bartram.[2] Lindsay introduced her as having been the childhood nurse of George Washington, but, lacking success, he sold her in her old age to P.T. Barnum.[2][3] Posters advertising her shows in 1835 included the lines, "Joice Heth is unquestionably the most astonishing and interesting curiosity in the World! She was the slave of Augustine Washington, (the father of Gen. Washington) and was the first person who put clothes on the unconscious infant, who, in after days, led our heroic fathers on to glory, to victory, and freedom. To use her own language when speaking of the illustrious Father of this Country, 'she raised him'. Joice Heth was born in the year 1674, and has, consequently, now arrived at the astonishing age of 161 years".[4]
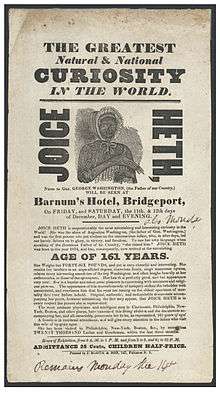
She was toward the end of her life, blind and almost completely paralyzed (she could talk, and had some ability to move her right arm)[5] when Barnum started to exhibit her on August 10, 1835, at Niblo's Garden in New York City.[3][6] As a 7-month traveling exhibit for Barnum, Heth told stories about "little George" and sang a hymn.[7] Eric Lott claims that Heth earned the impresario $1,500 a week, a princely sum in that era.[8] Barnum's career as a showman took off.[9] Her case was discussed extensively in the press. As doubt had been expressed about her age Barnum announced that upon her death she would be publicly autopsied. She died the next year.[1][6] Barnum stated that Joice's remains were "buried respectably" in his home town of Bethel, Connecticut.[10]
Public autopsy
Joice Heth died in New York City on February 19, 1836, aged around 79. To gratify public interest, Barnum set up a public autopsy.[11] Barnum engaged the service of a surgeon, Dr. David L. Rogers, who performed the autopsy on February 25, 1836, in front of fifteen hundred spectators in New York's City Saloon, with Barnum charging fifty cents admission.[2] When Rogers declared the age claim a fraud, Barnum insisted that the autopsy victim was another person, and that Heth was alive, on a tour to Europe. Later, Barnum admitted the hoax.[3]
See also
Notes
- 1 2 "Joice Heth", Hoaxes.org
- 1 2 3 4 "Heth, Joice (17??–19 Feb. 1836)". American National Biography (Oxford University Press. Retrieved March 12, 2015. (subscription required)
- 1 2 3 Washington, Harriet A. (2006). Medical Apartheid. New York: Doubleday. p. 86ff. ISBN 0-385-50993-6.
- ↑ Joice Heth Poster, 1835.
- ↑ Benton (1891).
- 1 2 Freed, "Joice Heth"
- ↑ Freed cites this to Phineas T. Barnum, Barnum's Own Story, ed. Waldo R. Browne (Massachusetts: Peter Smith, 1972), p. 49.
- ↑ Lott 1993.
- ↑ "P.T. Barnum", Britannica Eleventh Edition mentions the claim to have been nurse of George Washington and lists his exhibiting her as the first significant event in Barnum's career.
- ↑ The Life of P.T. Barnum: Written By Himself. Originally published 1855. Reprint ed., Champaign: University of Illinois Press, 2000. ISBN 0-252-06902-1.
- ↑ Reiss, Benjamin (2001). The Showman and the Slave: Race, Death and Memory in Barnum's America. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-674-00636-2.
References

- Joel Benton. Life of Phineas T. Barnum at Project Gutenberg, Edgewood Publishing, 1891; accessed December 3, 2007. The most detailed of these accounts, including information about Barnum's purchase of Heth, a detailed description of her appearance, how Barnum exhibited her, etc.
- Lott, Eric (1993). Love and Theft: Blackface Minstrelsy and the American Working Class. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 76–78. ISBN 0-19-507832-2.
- Boese, Alex. "Joice Heth". Hoaxes.org. Archived from the original on April 5, 2017. Retrieved December 10, 2017.
- Freed, Robin. "Joice Heth". MA candidate, University of Virginia American Studies Department. Archived from the original on May 18, 2002. Retrieved April 8, 2007.
- Washington, Harriet A. (2007). Medical Apartheid:The Dark History of Medical Experimentation on African Americans from Colonial Times to the Present. New York: Doubleday Press. pp. 86–90. ISBN 0-19-507832-2.
External links
- The Life of Joice Heth, the Nurse of Gen. George Washington, (the Father of Our Country) New York: The Author, 1835.