Jin (Korean state)
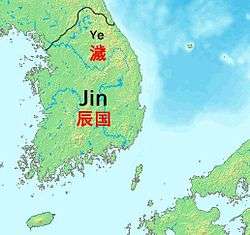
The state of Jin (Korean pronunciation: [tɕin]) was a confederacy of statelets which occupied some portion of the southern Korean peninsula during the 2nd and 3rd centuries BCE, bordering the Korean kingdom Gojoseon to the north. Its capital was somewhere south of the Han River. It preceded the Samhan confederacies, each of which claimed to be successors of the Jin state.[5]
Name
"Jin" is the Revised Romanization of Korean 진, originally written 辰 in Korean Chinese characters (hanja). This character's Old Chinese pronunciation has been reconstructed as /*[d]ər/[6] and originally referred to the 5th earthly branch of the Chinese and Korean zodiacs, a division of the orbit of Jupiter identified with the dragon. This was associated with a bearing of 120° (between ESE and SE) but also with the two-hour period between 7 and 9 am, leading it to be associated with dawn and the direction east.
A variant romanization is Chin.
History
It is not clear as to how well defined of an organized state Jin was. It seems likely that it was a federation of small states much like the subsequent Samhan. For the state to be able to contend with Wiman Joseon and send embassies to the court of Han Dynasty China, there was probably some level of stable central authority. Korean historian Ki-baek Lee (1984, p. 24) also suggests that the kingdom's attempt to open direct contacts "suggests a strong desire on the part of Chin [Jin] to enjoy the benefits of Chinese metal culture." However, for the most part Wiman Joseon prevented direct contact between Jin and China.[7]
King Jun of Gojoseon is reported to have fled to Jin after Wiman seized his throne and established Wiman Joseon. Some believe that Chinese mentions of Gaeguk or Gaemaguk (蓋馬國, Kingdom of armored horses) refers to Jin. Goguryeo is said to have conquered "Gaemaguk" in 26 AD, but this may refer to a different tribe in northern Korea.
Records are somewhat contradictory on Jin's demise: it either became the later Jinhan, or diverged into the Samhan as a whole. Archeological records of Jin have been found centered in territory that later became Mahan.[5]
Archeology
Archaeologically, Jin is commonly identified with the Korean bronze dagger culture, which succeeded the Liaoning bronze dagger culture in the late first millennium BCE.[5] The most abundant finds from this culture have been in southwestern Korea's Chungcheong and Jeolla regions. This suggests that Jin was based in the same area, which roughly coincides with the fragmentary historical evidence. Artifacts of the culture are similar to Baiyue and are found throughout southern Korea and were also exported to the Yayoi people of Kyūshū, Japan.[8]
Legacy
Jin was succeeded by the Samhan: Mahan, Jinhan and Byeonhan. Chinese historical text, Records of the Three Kingdoms says that Jinhan is the successor of Jin state, [9] while Book of the Later Han writes that Mahan, Jinhan and Byeonhan were all the past Jin state and there were 78 states.[10]
The name of Jin continued to be used in the name of the Jinhan confederacy and in the name "Byeonjin," an alternate term for Byeonhan. In addition, for some time the leader of Mahan continued to call himself the "Jin king," asserting nominal overlordship over all of the Samhan tribes.
See also
References
Citations
- ↑ Ohno, Susumu (1970). The Origin of the Japanese Language. Journal of Japanese studies
- ↑ Paek, Nak-chun (1987). The history of Protestant missions in Korea, 1832-1910. Yonsei University Press
- ↑ Min-Sohn, Ho (2001). The Korean Language. Cambridge University Press. p. 28
- ↑ Whitman, John (2012). "Northeast Asian Linguistic Ecology and the Advent of Rice Agriculture in Korea and Japan". Rice. 4 (3–4): 149–158. doi:10.1007/s12284-011-9080-0.
- 1 2 3 Lee Injae, Owen Miller, Park Jinhoon, Yi Hyun-Hae, 〈Korean History in Maps〉, 2014, pp.18-20
- ↑ Baxter-Sagart.
- ↑ Book of Han, "傳子至孫右渠 … 眞番 辰國 欲上書見天子 又雍閼弗通", vol.〈朝鮮〉
- ↑ Kenneth B. Lee, 〈Korea and East Asia: The Story of a Phoenix〉, Greenwood Publishing, 1997, pp.23-25
- ↑ "辰韓者古之辰國也". 〈韓〉,《三國志》
- ↑ "韓有三種 一曰馬韓 二曰辰韓 三曰弁辰 … 凡七十八國 … 皆古之辰國也"〈韓〉,《後漢書》
Bibliography
- Lee, C.-k. (1996). The bronze dagger culture of Liaoning province and the Korean peninsula. Korea Journal 36(4), 17-27.
- Lee, K.-b. (1984). A new history of Korea. Tr. by E.W. Wagner & E.J. Schulz, based on the 1979 rev. ed. Seoul: Ilchogak. ISBN 89-337-0204-0.