Intensive care unit
_2007-03-03.jpg)
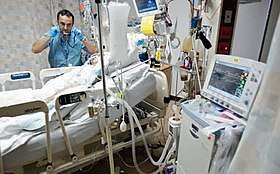
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive treatment medicine.
Intensive care units cater to patients with severe and life-threatening illnesses and injuries, which require constant, close monitoring and support from specialist equipment and medications in order to ensure normal bodily functions. They are staffed by highly trained doctors and nurses who specialise in caring for critically ill patients. ICUs are also distinguished from normal hospital wards by a higher staff-to-patient ratio and access to advanced medical resources and equipment that is not routinely available elsewhere. Common conditions that are treated within ICUs include acute (or adult) respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), trauma, multiple organ failure and sepsis.[1]
Patients may be transferred directly to an intensive care unit from an emergency department if required, or from a ward if they rapidly deteriorate, or immediately after surgery if the surgery is very invasive and the patient is at high risk of complications.[2]
History
In 1854, Florence Nightingale left for the Crimean War, where triage, used to separate seriously wounded soldiers from the less-seriously wounded, was observed. Until recently, it was reported that Nightingale reduced mortality from 40% to 2% on the battlefield. Although this was not the case, her experiences during the war formed the foundation for her later discovery of the importance of sanitary conditions in hospitals, a critical component of intensive care. In 1950, anesthesiologist Peter Safar established the concept of "Advanced Support of Life", keeping patients sedated and ventilated in an intensive care environment. Safar is considered to be the first practitioner of intensive care medicine as a speciality. In response to a polio epidemic (where many patients required constant ventilation and surveillance), Bjørn Aage Ibsen established the first intensive care unit in Copenhagen in 1953.[3][4] The first application of this idea in the United States was in 1955 by Dr. William Mosenthal, a surgeon at the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center.[5] In the 1960s, the importance of cardiac arrhythmias as a source of morbidity and mortality in myocardial infarctions (heart attacks) was recognized. This led to the routine use of cardiac monitoring in ICUs, especially after heart attacks.[6]
Specialities
_to_ensure_a_quick.jpg)

Hospitals may have ICUs that cater to a specific medical speciality or patient, such as those listed below:
- Neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). This specialty unit cares for neonatal patients who have not left the hospital after birth. Common conditions cared for include prematurity and associated complications, congenital disorders such as Congenital diaphragmatic hernia, or complications resulting from the birthing process.
- Pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). Pediatric patients are treated in this intensive care unit for life-threatening medical problems such as asthma, influenza, diabetic ketoacidosis, or traumatic brain injury. Surgical cases may also be transferred to the PICU postoperatively if the patient has a potential for rapid deterioration and requires more frequent monitoring, such as in spinal fusions or surgeries involving the airway such as removal of the tonsils or adenoids. Some facilities also have specialized pediatric cardiac intensive care units, where patients with congenital heart disease are cared for. These units also typically handle cardiac transplantation and postop care of cardiac catheterization patients if those services are offered at the hospital.
- Psychiatric intensive care unit (PICU). Patients who may voluntarily harm themselves are delivered here so they can be monitored more vigorously.
- Coronary care unit (CCU): Also known as Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (CICU) or Cardiovascular Intensive Care Unit (CVICU), this ICU caters to patients specifically with congenital heart defects or life-threatening acute conditions such as cardiac arrest.
- Neurological intensive care unit (NeuroICU). Patients here are treated for aneurysms, brain tumors, stroke, rattlesnake bites and post surgical patients who have undergone various neurological surgeries and require hourly neurological exams. Many nurses who work within these units have neurological intensive care certifications. Once the patients are more stable and off the ventilator, they are transferred to a neurological care unit.
- Trauma intensive care unit (Trauma ICU). These are found only in hospitals certified in Trauma and have a dedicated Trauma Emergency Department equipped with a team of surgeons, nurses, respiratory therapists, and radiological staff.
- Post-anesthesia care unit (PACU): Also known as the post-operative recovery unit, or recovery room, the PACU provides immediate post-op observation and stabilisation of patients following surgical operations and anesthesia. Patients are usually held in such facilities for a limited amount of time, and must meet a set physiological criteria before transfer back to a ward with a qualified nurse escort. Due to high patient flow in recovery units, and owing to the bed management cycle, if a patient breaches a time frame and is too unstable to be transferred back to a ward, they are normally transferred to a high dependency unit (HDU) or post-operative critical care unit (POCCU) for closer observation.
- High dependency unit (HDU): In the United Kingdom and elsewhere (known as step down unit or progressive care unit in North America), most acute hospitals have a transitional high dependency unit (HDU) for patients who require close observation, treatment and nursing care that cannot be provided on a general ward, but whose care is not at a critical enough level to warrant an ICU bed. These units are also called step-down, progressive and intensive recovery units and are utilised until a patient's condition stabilizes enough to qualify them for discharge to a general ward.[7]
- Surgical intensive care unit (SICU): A specialized service in larger hospitals that provides inpatient care for critically ill patients on surgical services. As opposed to other ICUs, the care is managed by surgeons trained in critical-care.
Out of hospital ICU
- Mobile intensive care unit (MICU)
A specialized ambulance with the staff and equipment to provide on-scene Advanced Life Support resuscitation and intensive care during transport. These type of ICUs are generally for people who are being transferred between hospitals and not from home to a hospital. In the Anglo American model of pre-hospital care MICUs are generally paramedic crewed. In the European model Mobile ICU crews are usually a specialized nurse and an emergency medicine physician.
Equipment and systems
Common equipment in an ICU includes mechanical ventilators to assist breathing through an endotracheal tube or a tracheostomy tube; cardiac monitors including those problems; equipment for the constant monitoring of bodily functions; a web of intravenous lines, feeding tubes, nasogastric tubes, suction pumps, drains, and catheters; and a wide array of drugs to treat the primary condition(s) of hospitalization. Medically induced comas, analgesics, and induced sedation are common ICU tools needed and used to reduce pain and prevent secondary infections.
Quality of care
The available data suggests a relation between ICU volume and quality of care for mechanically ventilated patients.[8] After adjustment for severity of illnesses, demographic variables, and characteristics of different ICUs (including staffing by intensivists), higher ICU staffing was significantly associated with lower ICU and hospital mortality rates. A ratio of 2 patients to 1 nurse is recommended for a medical ICU, which contrasts to the ratio of 4:1 or 5:1 typically seen on medical floors. This varies from country to country, though; e.g., in Australia and the United Kingdom most ICUs are staffed on a 2:1 basis (for high-dependency patients who require closer monitoring or more intensive treatment than a hospital ward can offer) or on a 1:1 basis for patients requiring very intensive support and monitoring; for example, a patient on a mechanical ventilator with associated anaesthetics or sedation such as propofol, midazolam and use of strong analgesics such as morphine, fentanyl and/or remifentanil.
In the ICU, international guidelines recommend that every patient gets checked for delirium every day (usually twice or more a day) using a validated clinical tool. The two most widely used are the Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU) and the Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist (ICDSC). There are translations of these tools in over 20 languages and they are used globally in many thousands of ICUs.[9]
Operational logistics
In the United States, up to 20% of hospital beds can be labelled as intensive-care beds; in the United Kingdom, intensive care usually will comprise only up to 2% of total beds. This high disparity is attributed to admission of patients in the UK only when considered the most severely ill.[10]
Intensive care is an expensive healthcare service. A recent study conducted in the United States found, hospital stays that involved ICU services were 2.5 times more costly than other hospital stays.[11]
In the United Kingdom, the average cost of funding an intensive care unit is:[12]
- £838 per bed per day for a neonatal intensive care unit
- £1,702 per bed per day for a pediatric intensive care unit
- £1,328 per bed per day for an adult intensive care unit
Remote collaboration systems
Some hospitals have installed teleconferencing systems that allow doctors and nurses at a central facility (either in the same building, at a central location serving several local hospitals, or in rural locations another more urban facility) to collaborate with on-site staff and speak with patients (a form of telemedicine). This is variously called an eICU, virtual ICU, or tele-ICU. Remote staff typically have access to vital signs from live monitoring equipment, and to electronic health records so they can get a broader view of a patient's medical history. Often bedside and remote staff have met in person and may rotate responsibilities. Such systems allow hospitals to double-check that correct procedures are being followed for the patients most vulnerable to mistakes, and to use access expertise remotely to keep patients that would otherwise have to be transferred to a larger facility, and have demonstrated a significant decrease in mortality.[13][14][15][16]
See also
- ICU quality and management tools
- Intensive Care Foundation, a charity in Australia and New Zealand
- Intensive Care Medicine (journal)
- Geriatric Intensive care unit
References
- ↑
- ↑ Smith, S. E. (2013-03-24). Bronwyn Harris, ed. "What is an ICU". wiseGEEK. Sparks, Nevada: Conjecture Corporation. Retrieved 2012-06-15.
- ↑ Reisner-Sénélar, L. (2009), "Der dänische Anästhesist Björn Ibsen ein Pionier der Langzeitbeatmung über die oberen Luftwege", Doctoral Thesis (in German), Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Johann Wolfgang Goethe University, OCLC 600186486 . Translation of introduction available here .
- ↑ Reisner-Sénélar, L. (2009). "The Danish anaesthesiologist Björn Ibsen a pioneer of long-term ventilation on the upper airways" (PDF).
- ↑ Grossman, D.C. (Spring 2004). "Vital Signs: Remembering Dr. William Mosenthal: A simple idea from a special surgeon". Dartmouth Medicine. Dartmouth College, Geisel School of Medicine. 28 (3). Retrieved 2007-04-10.
- ↑ "História da Terapia Intensiva" [Intensive Care History] (video in English linked to from website). Brazilian Society of Critical Care website. Produced by Tfran Ediçao de Imagens. Uploaded to YouTube by user: Thiago Francisco. 2008-06-06.
- ↑ "Intensive Care Patients Experiences: High Dependency Units" (compiled patient testimonials), healthtalkonline.org, Oxford, England: DIPEx, November 2012
- ↑ Kahn, J.M.; Goss, C.H.; Heagerty, P.J.; Kramer, A.A.; et al. (2006-07-06). "Hospital volume and the outcomes of mechanical ventilation". New England Journal of Medicine. 355 (1): 41–50. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa053993. PMID 16822995.
- ↑ Ely, EW; et al. (2001-12-05). "Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: validity and reliability of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU)". JAMA. 286 (21): 2703–10. doi:10.1001/jama.286.21.2703. PMID 11730446.
- ↑ Bennett, D.; Bion, J. (1999). "Organisation of intensive care". BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 318 (7196): 1468–70. doi:10.1136/bmj.318.7196.1468. PMC 1115845. PMID 10346777.
- ↑ Barrett ML, Smith MW, Elizhauser A, Honigman LS, Pines JM (December 2014). "Utilization of Intensive Care Services, 2011". HCUP Statistical Brief #185. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- ↑ Winterton, R. (2005-06-15), "Written Answers text: Trent Strategic Health Authority", Hansard – House of Commons Debates, Westminister, England: Stationery Office, Parliament, Volume 435, part 87, column 520W, archived from the original on 2011-06-05, retrieved 2009-01-17.
- ↑ "Hospitals Monitor ICU Patients Virtually, From Many Miles Away". WFAE. 2013-05-06. Retrieved 2017-03-16.
- ↑ "Tele-ICU: Efficacy and Cost-Effectiveness of Remotely Managing Critical Care | Perspectives". Perspectives.ahima.org. 2014-06-20. Retrieved 2017-03-16.
- ↑ "Emerging Best Practices for Tele-ICU Care". CHCF.org. Retrieved 2017-03-16.
- ↑ Goran, Susan F. (1 August 2010). "A Second Set of Eyes: An Introduction to Tele-ICU". Crit Care Nurse. 30 (4): 46–55. doi:10.4037/ccn2010283. PMID 20675821 – via ccn.aacnjournals.org.
Further reading
- Lois Reynolds; Tilli Tansey, eds. (2011), History of British Intensive Care, c. 1950-c. 2000, Wellcome Witnesses to Contemporary Medicine, History of Modern Biomedicine Research Group, ISBN 978-0-902238-75-6 , Wikidata Q29581786
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Intensive-care units. |
- "Intensive Care". NHS choices. UK: National Health Service.
- "Critical Care". MedlinePlus. US: National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- Society of Critical Care Medicine
- ICUsteps – Intensive care patient support charity
- Organisation for Critical Care Transportation
- Reynolds, H.N.; Rogove, H.; Bander, J.; McCambridge, M.; et al. (December 2011). "A working lexicon for the tele-intensive care unit: We need to define tele-intensive care unit to grow and understand it". Telemedicine and e-Health. 17 (10): 773–783. doi:10.1089/tmj.2011.0045.
- Olson, Terrah J. Paul; Brasel, Karen J.; Redmann, Andrew J.; Alexander, G. Caleb; Schwarze, Margaret L. (January 2013). "Surgeon-Reported Conflict With Intensivists About Postoperative Goals of Care". JAMA Surgery. 148 (1): 29–35. doi:10.1001/jamasurgery.2013.403. PMC 3624604.
