Pigeon toe
| Pigeon toe | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Metatarsus varus, metatarsus adductus, in-toe gait, intoeing, false clubfoot |
| Specialty | Pediatrics, orthopedics |
Pigeon toe, also known as in-toeing, is a condition which causes the toes to point inward when walking. It is most common in infants and children under two years of age[1] and, when not the result of simple muscle weakness,[2] normally arises from underlying conditions, such as a twisted shin bone or an excessive anteversion (femoral head is more than 15° from the angle of torsion) resulting in the twisting of the thigh bone when the front part of a person's foot is turned in.
Causes
The cause of in-toeing can be differentiated based on the location of the disalignment. The variants are:[4][5]
- Curved foot (metatarsus adductus)
- Twisted shin (tibial torsion)
- Twisted thighbone (femoral anteversion)
Metatarsus Adductus
The most common form of being pigeon toed, when the feet bend inward from the middle part of the foot to the toes.
Tibial Torsion
The tibia or lower leg slightly or severely twists inward when walking or standing.
Femoral Anteversion
The femur or thigh bone turns inward when walking.
Diagnosis
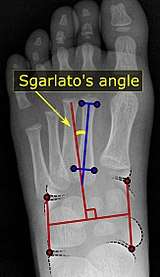
Pigeon toe can be diagnosed by physical examination alone.[7] This can classify the deformity into "flexible", when the foot can be straightened by hand, or otherwise "nonflexible".[7] Still, X-rays are often done in the case of nonflexible pigeon toe.[7] On X-ray, the severity of the condition can be measured with a "metatarsus adductus angle", which is the angle between the directions of the metatarsal bones as compared to the lesser tarsus (the cuneiforms, the cuboid and the navicular bone).[8] Many variants of this measurement exist, but Sgarlato's angle has been found to at least have favorable correlation with other measurements.[9] Sgarlato's angle is defined as the angle between:[6]
- A line through the longitudinal axis of the second metatarsal bone.
- The longitudinal axis of the lesser tarsal bones. For this purpose, one line is drawn between the lateral limits of the 4th tarsometatarsal joint and the calcaneocuboid joint, and another line is drawn between the medial limits of the talonavicular joint and the 1st tarsometatarsal joint. The transverse axis is defined as going through the middle of those lines, and hence the longitudinal axis is perpendicular to this axis.
This angle is normally up to 15°, and an increased angle indicates pigeon toe.[6] Yet, it becomes more difficult to infer the locations of the joints in younger children due to incomplete ossification of the bones, especially when younger than 3-4 years.
Treatment
In those less than eight years old with simple in-toeing and minor symptoms, no specific treatment is needed.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ "Pigeon toe (in-toeing)". University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics. 2005. Retrieved 2008-11-27.
- ↑ Glenn Copeland; Stan Solomon; Mark Myerson (2005). The Good Foot Book. New York: Hunter House. pp. 96–97. ISBN 0-89793-448-2.
- ↑ "pigeon toe" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ "Intoeing". American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Retrieved 6 July 2013.
Reviewed by members of the Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America
- ↑ Clifford R. Wheeless III (ed.). "Internal Tibial Torsion". Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics. Retrieved 6 July 2013.
- 1 2 3 Chen L, Wang C, Wang X, Huang J, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Ma X (2014). "A reappraisal of the relationship between metatarsus adductus and hallux valgus". Chin. Med. J. 127 (11): 2067–72. PMID 24890154.
- 1 2 3 "Metatarsus Adductus". Lucile Packard Children's Hospital. Retrieved 2018-02-03.
- ↑ Dawoodi, Aryan I.S.; Perera, Anthony (2012). "Reliability of metatarsus adductus angle and correlation with hallux valgus". Foot and Ankle Surgery. 18 (3): 180–186. doi:10.1016/j.fas.2011.10.001. ISSN 1268-7731.
- ↑ Michael Crawford, Donald Green. "METATARSUS ADDUCTUS: Radiographic and Pathomechanical Analysis" (PDF). The Podiatry Institute.
- ↑ "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question" (PDF). American Academy of Pediatrics-Section on Orthopaedics and the Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- UK information from Oxford Hospitals NHS Trust
- Metatarsus Adductus on POSNA—The Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America