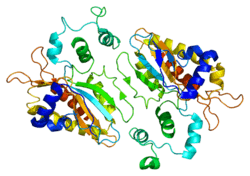ITPKA
Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ITPKA gene.[5][6][7]
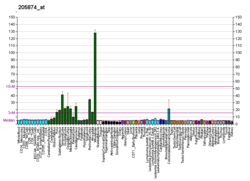
Regulates inositol phosphate metabolism by phosphorylation of second messenger inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to Ins(1,3,4,5)P4. The activity of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase is responsible for regulating the levels of a large number of inositol polyphosphates that are important in cellular signaling. Both calcium/calmodulin and protein phosphorylation mechanisms control its activity. It is also a substrate for the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, calcium/calmodulin- dependent protein kinase II, and protein kinase C in vitro. ITPKA and ITPKB are 68% identical in the C-terminus region.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000137825 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027296 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Erneux C, Roeckel N, Takazawa K, Mailleux P, Vassart G, Mattei MG (Dec 1992). "Localization of the genes for human inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase A (ITPKA) and B (ITPKB) to chromosome regions 15q14-q21 and 1q41-q43, respectively, by in situ hybridization". Genomics. 14 (2): 546–7. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(05)80265-4. PMID 1330886.
- ↑ Takazawa K, Perret J, Dumont JE, Erneux C (Feb 1991). "Human brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase cDNA sequence". Nucleic Acids Res. 18 (23): 7141. doi:10.1093/nar/18.23.7141. PMC 332787. PMID 2175886.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: ITPKA inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase A".
Further reading
- Takazawa K, Perret J, Dumont JE, Erneux C (1991). "Molecular cloning and expression of a new putative inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase isoenzyme". Biochem. J. 278 ( Pt 3) (Pt 3): 883–6. PMC 1151429. PMID 1654894.
- Takazawa K, Erneux C (1992). "Identification of residues essential for catalysis and binding of calmodulin in rat brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase". Biochem. J. 280 ( Pt 1) (Pt 1): 125–9. PMC 1130609. PMID 1660262.
- Takazawa K, Perret J, Dumont JE, Erneux C (1991). "Molecular cloning and expression of a human brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 174 (2): 529–35. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(91)91449-M. PMID 1847047.
- Lin AN, Barnes S, Wallace RW (1990). "Phosphorylation by protein kinase C inactivates an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase purified from human platelets". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 170 (3): 1371–6. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(90)90546-Y. PMID 2167676.
- Takazawa K, Vandekerckhove J, Dumont JE, Erneux C (1991). "Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a rat brain cDNA encoding a Ca2+/calmodulin-sensitive inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase". Biochem. J. 272 (1): 107–12. PMC 1149663. PMID 2176078.
- Ryu SH, Lee SY, Lee KY, Rhee SG (1987). "Catalytic properties of inositol trisphosphate kinase: activation by Ca2+ and calmodulin". FASEB J. 1 (5): 388–93. PMID 2824270.
- Communi D, Vanweyenberg V, Erneux C (1997). "D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase A is activated by receptor activation through a calcium:calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II phosphorylation mechanism". EMBO J. 16 (8): 1943–52. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.8.1943. PMC 1169797. PMID 9155020.
- Woodring PJ, Garrison JC (1997). "Expression, purification, and regulation of two isoforms of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (48): 30447–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.48.30447. PMID 9374536.
- Schell MJ, Erneux C, Irvine RF (2001). "Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase A associates with F-actin and dendritic spines via its N terminus". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (40): 37537–46. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104101200. PMID 11468283.
- Mishra J, Bhalla US (2003). "Simulations of inositol phosphate metabolism and its interaction with InsP(3)-mediated calcium release". Biophys. J. 83 (3): 1298–316. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(02)73901-5. PMC 1302229. PMID 12202356.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Dewaste V, Moreau C, De Smedt F, et al. (2003). "The three isoenzymes of human inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase show specific intracellular localization but comparable Ca2+ responses on transfection in COS-7 cells". Biochem. J. 374 (Pt 1): 41–9. doi:10.1042/BJ20021963. PMC 1223573. PMID 12747803.
- González B, Schell MJ, Letcher AJ, et al. (2004). "Structure of a human inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase: substrate binding reveals why it is not a phosphoinositide 3-kinase". Mol. Cell. 15 (5): 689–701. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.08.004. PMID 15350214.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Kato H, Uzawa K, Onda T, et al. (2006). "Down-regulation of 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase A protein expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma". Int. J. Oncol. 28 (4): 873–81. doi:10.3892/ijo.28.4.873. PMID 16525636.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.