ISEE-2
 ISEE-2 | |
| Names |
ISEE-2 ISEE-B |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Study of the Earth's magnetic field and the solar wind |
| Operator | ESA / NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1977-102A |
| SATCAT no. | 10423 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Dornier-System GmbH |
| Launch mass | 340 kg (750 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 13:53, October 22, 1977 |
| Rocket | Delta-2914 |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral LC-17B |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | Re-entry |
| Decay date | September 26, 1987 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Eccentricity | 0.91 |
| Perigee | 1.04 Earth radii |
| Apogee | 23 Earth radii |
| Inclination | 28.76° |
| Period | 3556.8 |
| Epoch | October 22, 1977 |
The International Sun-Earth Explorer 2 (ISEE-2 a.k.a. ISEE-B)[1] was a space probe used to study magnetic fields near the Earth. ISEE-1 and ISEE-2 were launched on October 22, 1977, and they re-entered on September 26, 1987.[2][2] The instruments on board ISEE-2 were designed to measure electric and magnetic field properties.
ISEE-2 had a thruster to adjust the spacing between the two spacecraft, depending on desired goal.[3] Early results from duo stated that by having two spacecraft, the "spatial and temporal variations in the magnetosphere and solar wind" could be detected.[4]
Mission
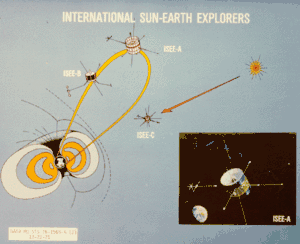
The space probe was part of a program consisting of three spacecraft: a mother/daughter pair (ISEE-1 and ISEE-2) and the ISEE-3 spacecraft (later renamed to International Cometary Explorer). The program was a cooperative mission between NASA and ESRO (later ESA) designed to study the interaction between the Earth's magnetic field and the solar wind. At least 32 institutions were involved, and the focus was on understanding magnetic fields.[5] ISEE-1 (a.k.a. Explorer 56) and ISEE-3 were built by NASA, while ISEE-2 was built by ESA. All three had complimentary instruments supported by the same group of over 100 scientists.[5]
ISEE-3 was launched the following year, later renamed ICE, and was noted for being contacted in the 2010s from Earth
Technical
See also
- ISEE-1
- International Cometary Explorer (ISEE-3, launched the following year)
- 1977 in spaceflight
- List of heliophysics missions
- European Space Research Organisation
- Van Allen Probes (Double spacecraft mission of the 2010s)