Hyperbolic orthogonality
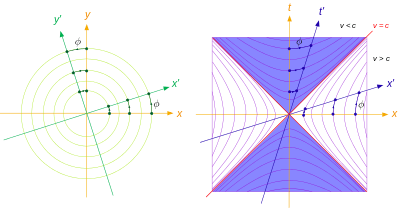
In plane geometry, two lines are hyperbolic orthogonal when they are reflections of each other over the asymptote of a given hyperbola. Two particular hyperbolas are frequently used in the plane:
- (A) xy = 1 with y = 0 as asymptote.
- When reflected in the x-axis, a line y = mx becomes y = −mx.
- In this case the lines are hyperbolic orthogonal if their slopes are additive inverses.
- (B) x2 − y2 = 1 with y = x as asymptote.
- For lines y = mx with −1 < m < 1, when x = 1/m, then y = 1.
- The point (1/m , 1) on the line is reflected across y = x to (1, 1/m).
- Therefore the reflected line has slope 1/m and the slopes of hyperbolic orthogonal lines are reciprocals of each other.
The relation of hyperbolic orthogonality actually applies to classes of parallel lines in the plane, where any particular line can represent the class. Thus, for a given hyperbola and asymptote A, a pair of lines (a,b) are hyperbolic orthogonal if there is a pair (c,d) such that , and c is the reflection of d across A.
The property of the radius being orthogonal to the tangent at the curve, is extended from the circle to the hyperbola by the hyperbolic orthogonal concept.[1][2]
Since Hermann Minkowski's foundation for spacetime study in 1908, the concept of points in a spacetime plane being hyperbolic-orthogonal to a timeline (tangent to a world line) has been used to define simultaneity of events relative to the timeline. In Minkowski's development the hyperbola of type (B) above is in use.[3] Two vectors are normal (meaning hyperbolic orthogonal) when
When c = 1 and the y's and z's are zero, x ≠ 0, t1 ≠ 0, then .
A bilinear form is used to describe orthogonality in analytic geometry, with two elements orthogonal when their bilinear form vanishes. In the plane of complex numbers , the bilinear form is , while in the plane of hyperbolic numbers the bilinear form is
- The vectors z1 and z2 in the complex number plane, and w1 and w2 in the hyperbolic number plane are said to be respectively Euclidean orthogonal or hyperbolic orthogonal if their respective inner products [bilinear forms] are zero.[4]
Given a hyperbola with asymptote A, its reflection in A produces the conjugate hyperbola. Any diameter of the original hyperbola is reflected to a conjugate diameter. The directions indicated by conjugate diameters are taken for space and time axes in relativity. As E. T. Whittaker wrote in 1910, "[the] hyperbola is unaltered when any pair of conjugate diameters are taken as new axes, and a new unit of length is taken proportional to the length of either of these diameters."[5] On this principle of relativity, he then wrote the Lorentz transformation in the modern form using rapidity.
Edwin Bidwell Wilson and Gilbert N. Lewis developed the concept within synthetic geometry in 1912. They note "in our plane no pair of perpendicular [hyperbolic-orthogonal] lines is better suited to serve as coordinate axes than any other pair"[1]
The notion of hyperbolic orthogonality arose in analytic geometry in consideration of conjugate diameters of ellipses and hyperbolas.[6] if g and g′ represent the slopes of the conjugate diameters, then in the case of an ellipse and in the case of a hyperbola. When a = b the ellipse is a circle and the conjugate diameters are perpendicular while the hyperbola is rectangular and the conjugate diameters are hyperbolic-orthogonal.
In the terminology of projective geometry, the operation of taking the hyperbolic orthogonal line is a involution. Suppose the slope of a vertical line is denoted ∞ so that all lines have a slope in the projectively extended real line. Then whichever hyperbola (A) or (B) is used, the operation is an example of a hyperbolic involution where the asymptote is invariant.
References
- 1 2 Edwin B. Wilson & Gilbert N. Lewis (1912) "The Space-time Manifold of Relativity. The Non-Euclidean Geometry of Mechanics and Electromagnetics" Proceedings of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences 48:387-507, esp. 415
- ↑ Bjørn Felsager (2004), Through the Looking Glass - A glimpse of Euclid’s twin geometry, the Minkowski geometry, ICME-10 Copenhagen; pages 6 & 7.
- ↑ Minkowski, Hermann (1909), "Raum und Zeit", Physikalische Zeitschrift, 10: 75–88
- Various English translations on Wikisource: Space and Time
- ↑ Sobczyk, G.(1995) Hyperbolic Number Plane, also published in College Mathematics Journal 26:268–80.
- ↑ E. T. Whittaker (1910) A History of the theories of aether and electricity Dublin: Longmans, Green and Co. (see page 441)
- ↑ Barry Spain (1957) Analytical Conics, ellipse §33, page 38 and hyperbola §41, page 49, from Hathi Trust
- G. D. Birkhoff (1923) Relativity and Modern Physics, pages 62,3, Harvard University Press.
- Francesco Catoni, Dino Boccaletti, & Roberto Cannata (2008) Mathematics of Minkowski Space, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel. See page 38, Pseudo-orthogonality.
- Robert Goldblatt (1987) Orthogonality and Spacetime Geometry, chapter 1: A Trip on Einstein's Train, Universitext Springer-Verlag ISBN 0-387-96519-X MR 0888161
- J.A. Wheeler; C. Misner; K.S. Thorne (1973). Gravitation. W.H. Freeman & Co. p. 58. ISBN 0-7167-0344-0.