High-performance sailing
High-performance sailing is achieved with low forward surface resistance—encountered by catamarans, sailing hydrofoils, iceboats or land sailing craft—as the sailing craft obtains motive power with its sails or aerofoils at speeds that are often faster than the wind.[1][2]
High-performance sailing craft
High-performance watercraft that can exceed the velocity of the true wind include catamarans and foiling vessels. Ice boats and land-sailing craft are often able to do so. There are also rotor-driven craft, such as the "land yacht", Blackbird, which are outside the scope of this article.
Watercraft
In 2013, a new class of catamaran was announced for the America's Cup which can achieve well in excess of double the speed of the wind.[3] The catamarans used for the 2013 America's Cup were expected to sail upwind at 1.2 times the speed of the true wind, and downwind at 1.6 times the speed of the true wind.[4][5][6] They proved to be faster, averaging about 1.8 times the speed of the wind with peaks slightly over 2.0.[7]
The Extreme 40 catamaran can sail at 35 knots (65 km/h; 40 mph) in 20–25-knot (37–46 km/h; 23–29 mph) winds.[8] The high-performance International C-Class Catamaran can sail at twice the speed of the wind.[9]
In 2009, the world speed sailing record on water was set by a hydrofoil trimaran sailing at 1.71 times the speed of the wind.[10][11] In late 2012, the Vestas Sailrocket 2 skippered by Paul Larsen achieved a new outright world speed record of 65.45 knots on water, at around 2.5 times the speed of the wind.[12]
Iceboats
Iceboats can typically sail at five times the speed of the wind.[13]
Land sailing craft
By sailing downwind at 135° off the wind, a sand yacht can sail much faster than the wind.[14] The velocity made good downwind is often over twice as fast compared to the same land yacht sailing directly downwind.[14] In 2009, the world land speed record for a wind-powered vehicle was set by the sand yacht Greenbird sailing at about three times the speed of the wind[15] with a recorded top speed of 202.9 kilometres per hour (126.1 mph).[16]
Surface resistance
If hull speed is not a limiting factor, and if the strength of the wind is sufficient to overcome the surface resistance, then the speed of the boat as a multiple of the wind speed depends only on how close it can sail to the wind. For example, assuming that surface resistance is negligible (as for an iceboat), if a boat sails at 90° to the true wind, but at 45° to the apparent wind, then it must be sailing at the same speed as the true wind. That is, if the wind speed is V, then the boat's speed is also V. Elementary trigonometry and elementary vector operations can be used to show that, if a boat sails perpendicular to the true wind, but at angle alpha (α) to the apparent wind, and the wind speed is V, then the boat's speed must be V×cotangent(α). The table below shows the values of this function, as a multiple of windspeed. The actual speed of a sailing vessel depends on the wind speed, how close to the wind it is sailing, the resistance of the surface (water or ice), and leeway (downwind drift).
Points of sail
The points of sail at which sailing craft can achieve highest speeds span between a beam reach (90° to the true wind) and a broad reach (about 135° away from the true wind). Normal cruising boats yachts can sail at about 45° off the apparent wind (50° to 60° off the true wind). High performance racing yachts at about 27° (35° off the true wind).[17] High-performance multihulls can sail at 20° off the apparent wind.[18] Iceboats can sail even closer to the apparent wind. According to the data provided on p. 406 of the cited book High Performance Sailing, a fast keelboat such as a Soling can sail at 30° off the apparent wind, an 18ft Skiff at 20°, and an iceboat at 7°.[19]
Beam reach
For example, a boat can sail a course that is perpendicular to the true wind (that is, at 90° with respect to the true wind). As it accelerates, the wind as seen from the boat increases and the wind appears to shift forward.[20] This is the same effect that causes rain to appear to fall at an angle when seen from a moving car, and is analogous to the astronomical phenomenon of aberration of light.
As the wind increases in speed and shifts forward (because of the acceleration of the boat), the sails have to be trimmed in order to maintain performance. This causes the boat to further accelerate, thus causing a further increase in windspeed and a further forward windshift.
Eventually, the sails cannot be trimmed any further and an equilibrium is reached. Although the boat is sailing perpendicular to the true wind, its sails are set for close hauled sailing.[21]
| Alpha (α) | Multiple of windspeed |
|---|---|
| 45° | 1.00 |
| 40° | 1.19 |
| 35° | 1.43 |
| 30° | 1.73 |
| 25° | 2.14 |
| 20° | 2.75 |
| 15° | 3.73 |
| 10° | 5.67 |
Hull speed is not a limiting factor for an iceboat nor for high-performance multihulls. So a boat capable of sailing at 10° off the apparent wind (which is the case for many iceboats) that sails at 90° to the true wind is sailing nearly 6 times faster than the wind.[22] It can sail slightly faster, as a multiple of the windspeed, if it sails at a greater angle off the true wind.[23]
Broad reach
As stated in the introduction of the book High Performance Sailing,[24] in the section Tacking Downwind, "... any boat which runs 'square' must necessarily sail downwind at some speed less than the wind's speed whereas any boat which tacks downwind has no theoretical limit to its speed. Ice yachts, for example, can tack downwind at average speeds many times the wind speed."
The same book states, in section 24.2, "In a True Wind of 15 knots (28 km/h; 17 mph), the Soling crew will sail the close reach and reaching legs in Apparent Winds little stronger than True Wind. ... The 18-foot Skiff crew sails the cross wind legs in much stronger Apparent Winds which approach 30 knots (56 km/h; 35 mph). Even on the broad reaching legs they must still sail in a strong Apparent Wind which blows from ahead, so they still need to use strong-wind 'going-to-windward' handling techniques even though they are sailing downwind." Figure 24.2 of this book provides vector graphics that show how the 18-foot (5.5 m) Skiff can sail downwind faster than the speed of the wind.
From the detailed data provided for the 2009 record set by a sand yacht, it can be seen that the record was achieved when the yacht's course was about 120° off the true wind.[25] That is, the yacht was moving faster than the wind although the true wind was behind it. This is possible because the speed of the yacht results in a large forward wind shift, so that the yacht is close hauled with respect to the apparent wind.[26]
Suppose that a boat is at a standstill, then starts to sail on a course that is 135° off the true wind (the value 135° is chosen for this explanation in order to simplify certain calculations). The boat accelerates, so the apparent wind is less than the true wind and shifts forward of the true wind. If the boat can reach a speed equal to about 71% of the true windspeed, then the apparent wind is perpendicular to the boat's course and its speed is about 71% of the true windspeed. If that reduced apparent windspeed still generates sufficient force to overcome the resistance of the surface, then the boat continues to accelerate.
That is, the situation is the same as the one explained above, because the boat is still accelerating after having reached a course perpendicular to the apparent wind. In practice, most boats sailing on the water cannot overcome the resistance of the water in order to reach speeds equal to the speed of the wind. However, iceboats can do so, because the resistance of the surface is very small. Thus, an iceboat that starts sailing on a broad reach continues to accelerate until it is close-hauled with respect to the apparent wind.[27]
The table[28] and diagram below illustrate this situation. The vector labelled "boat speed" represents the relative wind resulting from the boat's progress through the water, that is, the wind that is induced by the boat's motion: its speed is the same as the speed of the boat and its direction is directly opposite to the direction of the boat's motion. Both boat speed and apparent wind speed are shown as a fraction (or multiple) of true wind speed, which is represented by the vertical vector at the left of the diagram.
| Boat speed | Alpha (α) | Apparent wind speed |
|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 131° | 0.93 |
| 0.30 | 120° | 0.82 |
| 0.50 | 106° | 0.74 |
| 0.71 | 90° | 0.71 |
| 1.00 | 68° | 0.77 |
| 1.41 | 45° | 1.00 |
| 2.00 | 29° | 1.47 |
| 3.00 | 17° | 2.40 |
| 4.00 | 12° | 3.37 |
| 5.00 | 9° | 4.35 |
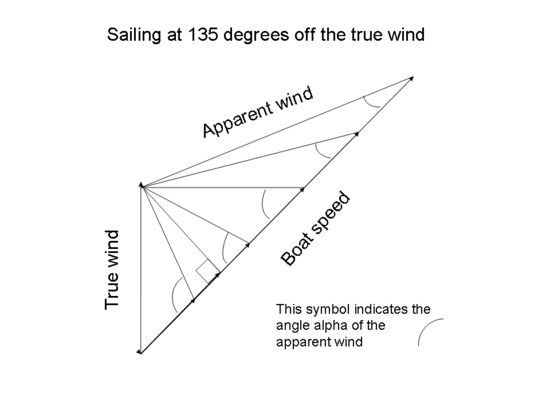
Note that, if a boat can accelerate until it is sailing at 45° off the apparent wind when sailing 135° off the true wind, then its speed is 1.41 times the speed of the true wind. Thus its velocity made good downwind is equal to the velocity of the true wind. If it can accelerate until it is sailing closer than 45° to the apparent wind, then its velocity made good downwind is greater than the velocity of the true wind: see section Velocity made good below.
Vector diagrams and formulas
As explained in the article on apparent wind, a boat's forward motion creates a corresponding head wind of the same strength in the opposite direction. That head wind must be combined with the true wind to find the apparent wind.[29]
The drawing below shows the vector operations and resulting calculations for sailing upwind. Alpha (α) is the angle of the apparent wind. Beta (β) is the course of the boat with respect to the true wind. The true wind is assumed to be equal to 1 in order to simplify the formulas. Note that the true wind is added using vector addition to the head wind created by the boat's speed.
The drawing below shows the vector operations and resulting calculations for sailing downwind. Alpha (α) is the angle of the sails to the apparent wind. Beta (β) is the course of the boat with respect to the true wind. The true wind is assumed to be equal to 1 in order to simplify the formulas. Note that the true wind is added to the head wind created by the boat's speed.
The drawing below shows apparent wind angles and speeds for different boat speeds for a boat sailing downwind at 135°.
Note that for both the upwind and downwind cases, the apparent crosswind (the component of true wind perpendicular to the heading of a boat) is true wind speed x sin(β), independent of the boat's speed. The maximum speed of a sail boat is a function of how fast it can travel for a given apparent crosswind and the drag from the water (or land or ice) related to the boat's true speed. Since the drag from the water (or land or ice) increases with the boat's true speed, the boat achieves its maximum apparent wind on an upwind tack, where its true speed is the slowest. This is why minimum β for a boat is smaller upwind than it is downwind.
- Vector diagrams and resulting speed of sailing craft
 Upwind course.
Upwind course.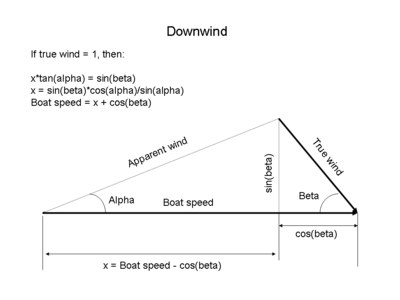 Downwind course of 135°.
Downwind course of 135°.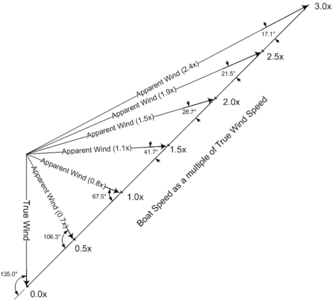 Boat speed as a multiple of true wind speed for various angles of apparent wind.
Boat speed as a multiple of true wind speed for various angles of apparent wind.
Vector operations and calculations to find the speed of a craft sailing on each course shown.
The Beta Theorem and Maximum speed course sailing angle
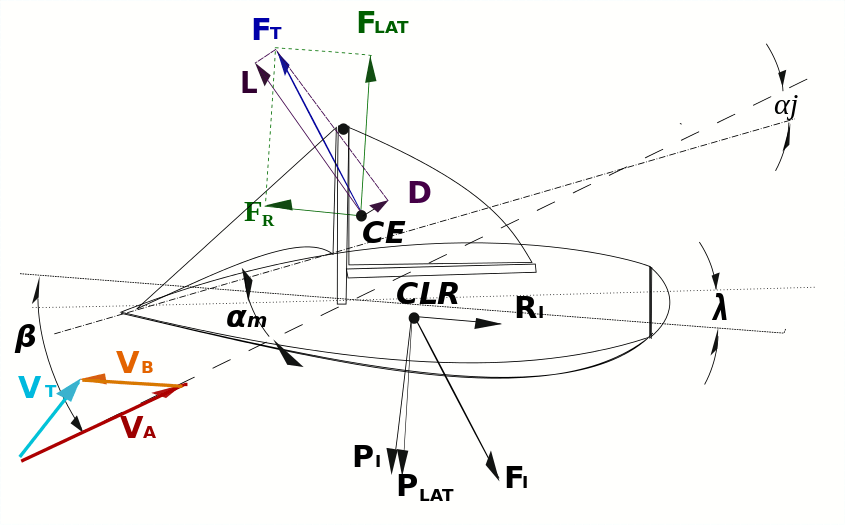
Beta Theorem
Garrett describes the Beta Theorem as the result of the net effect of two counteracting foils, the sail in the air and the keel in the water. When one resolves the ratio of lift to drag for each in its medium, the resulting motion of the sailing vessel resolves to an angle, beta (β), between the apparent wind and the course over the water. The hull (below the water) drag angle and sailing rig (above the water) each have drag angle with respect to the medium flowing past them (water or air). The sum of those two drag angles are equal to the apparent wind angle (the angle between the apparent wind and the course sailed). This theorem applies for every point of sail. A small β denotes high efficiency and a potential for high speed.[30]
Maximum speed course sailing angle
This is stating the potential for efficiency, and is especially applicable to speed sailing efforts, where the craft is tuned (e.g. reefed down or up, or bigger fin used etc.) for the chosen angle of each speed run.
The course sailing angle conclusion for maximum speed is shown to be a corollary of the Beta Theorem, with the assistance of Figures 1-3.
- Beta Theorem
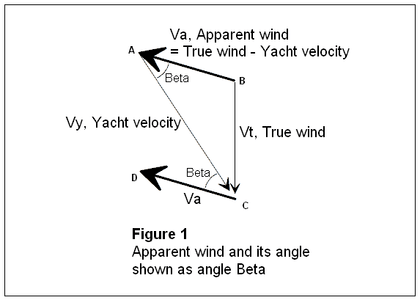 Vectors that determine β.
Vectors that determine β.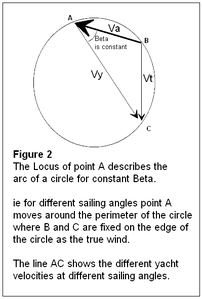 Velocity of craft for arbitrary β.
Velocity of craft for arbitrary β.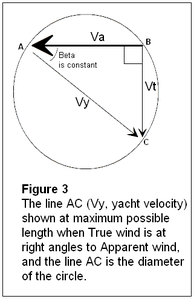 β for greatest velocity.
β for greatest velocity.
Figure 1 shows the relationship of the true wind and apparent wind vectors as differing by the yacht velocity. Also shown is the angle β, which is the "apparent wind angle", i.e., the angle between the yacht heading and the apparent wind on the yacht.
Although β is assumed to be constant, this is not perfectly true in practice. However, in the quest for maximum speed, it could be made to be true -- i.e., by setting the size of the yacht sails and fin or centreboard for each speed run so as to maintain the same (optimal) operating points, and therefore the same lift to drag ratios, and correspondingly a constant β for each heading under test.
Having accepted the constraints for a constant β, then it is simple maths (a constant angle is subtended on the arc of a circle) that we arrive with the locus of a circle for one end of the vector showing yacht velocity, as in Figure 2.
The maximum yacht velocity clearly occurs when the vector Vy lies across the diameter of the circle, as shown in Figure 3. In this figure, the apparent wind and the true wind are at right angles. Also note that the optimum speed sailing angle is equal to the apparent wind angle (β) below a beam reach.
Vt and Va appear equal in figure 3, where Vy is about 1.4x Vt. This is not the general case. The more efficient the yacht, the smaller β is, and the closer to a beam reach is the optimum speed sailing course. The ultimate ratio of yacht speed to wind speed therefore also gives rise to β by inverse cosine, e.g., speed-sailing at twice the wind speed corresponds to a 30° apparent wind angle, i.e., β = 30°.
Speed sailing windsurfers have an apparent wind angle somewhat worse (greater) than 30°, and accordingly their speed sailing courses are set for a broader sailing angle than this. Speed sailing kite boards prefer an even broader course than windsurfers. In contrast, the highly efficient Vestas Sailrocket has a design β of about 20° (the hull is offset this amount from the centreline) and this is how close to a beam reach she may sail.
Velocity made good (VMG)
Most sailing is not done in order to achieve a maximum speed, but in order to go from one point to another. In most sailboat racing the objective is to sail a certain distance directly upwind (to a point called the upwind mark), and then to return downwind, as fast as possible.
Since sailboats cannot sail directly into the wind, they must tack in order to reach the upwind mark (this process is called beating or working to the mark). This lengthens the course, thus the boat takes longer to reach the upwind mark than it would if it could have sailed directly towards it. The component of a sailboat's velocity that is in the direction of the next mark is called the velocity made good.[31]
If a boat sails perpendicular to the wind, it will never reach the upwind mark. So, in racing, speed is not everything. What counts is the velocity made good, that is, the progress towards the upwind mark. Again, simple trigonometry can be used to calculate the velocity made good. The tables below show velocity made good, again as a multiple of windspeed, and again assuming negligible surface resistance. The first column indicates the course as an angle off the true wind; α is the closest angle to the apparent wind at which the boat can sail. The calculation assumes that the boat accelerates until the apparent wind is at angle α off the bow.
|
|
It can be seen that a boat that can sail closer than 20° to the apparent wind can make good upwind faster than the real wind.
Many boats can make good downwind faster by not sailing dead downwind, but instead jibing (also spelled gybing) back and forth.[32] If the boat can accelerate until the apparent wind is at angle α off the bow, then it can be seen from the table above that it can make good downwind faster than the true wind.[33] Such performance is theoretically possible.[34] An easy-to-grasp animation demonstrating the principle of how it can be possible to go faster than the wind can be found at.[35]
However real boats cannot equal the performances shown in the table,[36] although iceboats can come close to them. Indeed, iceboats can make good both upwind and downwind at speeds greater than the wind.[37][38] And so can sand yachts: during the 2009 land speed record, the yacht Greenbird was proceeding at about 3 times the speed of the wind on a course about 120° off the true wind.[15] Thus, its speed made good downwind was about 1.5 times the speed of the wind. During a training run the catamaran Alinghi 5, one of the competitors for the 2010 America's Cup, covered 20 nautical miles (37 km; 23 mi) to windward and back in 2.5 hours in 8–9-knot (15–17 km/h; 9.2–10.4 mph) winds, so its average velocity made good was 16 knots (30 km/h; 18 mph), about 1.9 times wind speed.[39] This is consistent with the yacht being able to sail at about 15° off the apparent wind, see the table above. Indeed, the catamaran sails so fast downwind that the apparent wind it generates is only 5-6° different from that when it is racing upwind; that is, the boat is always sailing upwind with respect to the apparent wind.[40]
During the first race of the 2010 America's Cup, the winning yacht USA 17 sailed 20 nautical miles (37 km; 23 mi) to windward in 1 hour 29 minutes, in winds of 5–10 knots (9.3–18.5 km/h; 5.8–11.5 mph). Thus its velocity made good upwind was about 1.8 times windspeed, consistent with being able to sail about 13° off the apparent wind when sailing upwind. She sailed 20 nautical miles (37 km; 23 mi) downwind in 1 hour 3 minutes, so her velocity made good downwind was about 2.5 times windspeed, consistent with being able to sail about 14° off the apparent wind when sailing downwind.[41][42][43][44] During the second race, winds were 7–8 knots (13–15 km/h; 8.1–9.2 mph). USA 17 reached the windward mark in 59 minutes, so her velocity made good was about 13.2 knots (24.4 km/h; 15.2 mph), about 1.65 times wind speed. The course was a triangle, so the velocity made good downwind was only 11.5 knots (21.3 km/h; 13.2 mph), about 1.4 times wind speed. USA 17 averaged 26.8 knots (49.6 km/h; 30.8 mph), about 3.35 times the wind speed, on the faster first triangular leg.[45][46][47]
Other sailboats (such as the 18ft Skiff) can make good downwind at speeds faster than the wind.[48] Indeed, it can be seen from the polar chart[49] for the 18 ft (5.5 m) Skiff that it can make good about 12 knots (22 km/h; 14 mph) downwind at a windspeed of 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph), by jibing back and forth at about 140° off the true wind.[48][50][51] The polar chart in Figure PS1 of the cited book High Performance Sailing[24] shows that boats that were sailing in 1996 were able to make good downwind at about 1.5 times the speed of the wind.
Rotor-powered vehicles
Related to high-performance sailing craft are vehicles powered by wind turbine rotors, which have wheels that are propelled by the rotor (as seen from a ground-stationary vantage point). These vehicles share a common trait with high-performance sailing craft: As the vehicle increases in speed, the advancing rotor airfoil encounters an increasing apparent wind at an angle of attack that is increasingly smaller. At the same time, such vehicles are subject to forward resistance. As a result, such vehicles are often capable of speeds exceeding that of the wind.
Such vehicles have demonstrated ground speeds that exceed that of the wind, both directly into the wind and directly downwind by transferring power through a drive train between the rotor and the wheels. A rotor-powered land yacht, Blackbird, achieved a dead downwind speed of about 2.8 times the speed of the wind.[52][53][54] In 2011, a streamlined Blackbird reached close to 3 times the speed of wind[55] and in 2012, achieved a dead upwind speed of about 2.1 times the speed of the wind.[52]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Jobson, Gary (1990). Championship Tactics: How Anyone Can Sail Faster, Smarter, and Win Races. New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 323. ISBN 0-312-04278-7.
... as the boat speeds up the apparent wind direct goes further and further forward without stalling the sails and the apparent wind speed also increases - so increasing the boat's speed even further. This particular factor is exploited to the full in sand-yachting in which it is common for a sand yacht to exceed the wind speed as measured by a stationary observer.
- ↑ Bethwaite, Frank (2007). High Performance Sailing. Adlard Coles Nautical. ISBN 978-0-7136-6704-2.
- ↑ How yachts go faster than the wind Gray, R. The Telegraph 26 September 2013
- ↑ "AC34 Multihull Class Rule Concept Document" (PDF). 34th America's Cup. Retrieved 2010-09-14.
- ↑ "New high performance yachts for 34th America's Cup" (PDF). 34th America's Cup. 2 July 2010. Retrieved 2010-09-14.
- ↑ The monohull concept for the 34th America's Cup called for a design that would achieve 1.0 times true wind speed upwind and 1.4 times downwind, see "AC34 Monohull Class Rule Concept Document" (PDF). 34th America's Cup. Retrieved 2010-09-14.
- ↑ "Emirates Team New Zealand gets leg up on ORACLE TEAM USA". 2012-13 America's Cup Event Authority. 7 September 2013. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ↑ "About eXtreme 40". eXtreme40. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ "The Winged World of C Cats". Sail Magazine. Archived from the original on March 14, 2010. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ The 500-meter record was 51.36 knots (95.12 km/h; 59.10 mph), achieved in 30-knot (56 km/h; 35 mph) winds by Hydroptère, a hydrofoil trimaran, see "Hydroptère World Records". World Sailing Speed Record Council. September 23, 2009. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ "Official web site of l'Hydroptère". Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ "500 Metre Records". World Sailing Speed Record Council.
- ↑ See "How fast do these things really go?" in the "Frequently Asked Questions". Four Lakes Ice Yacht Club. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- 1 2 Bob Dill (July 13, 2003). "Frequently Asked Questions". North American Land Sailing Association. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- 1 2 The record was 126 mph (109 kn; 203 km/h) with winds of 30–50 mph (48–80 km/h), see Bob Dill (April 5, 2009). "Measurement report for Speed Record Attempt Made by Richard Jenkins in the Yacht Greenbird on March 26, 2008". North American Land Sailing Association. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ Editors (March 27, 2009). "Wind-powered car breaks record". BBC New, UK. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ The formula for the apparent wind is (using the symbols shown in the vector diagrams) tan(α)=sin(β)/ (Boat speed+cos(β)). The figures shown for the angle of the apparent wind assume a boat speed around 0.3 times windspeed, say 6 knots (11 km/h; 6.9 mph) for a keelboat in 18-knot (33 km/h; 21 mph) winds. The figures for the angle of the true wind are from the main article on sailing.
- ↑ "Russell Coutts Talks About BMW Oracle's Giant Multi-hull". cupinfo.com. April 13, 2009. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ See also p. 204 of the cited book High Performance Sailing
- ↑ Forward means making a smaller angle relative to the bow than the angle that the true wind makes relative to the bow. This phenomenon is explained in most sailing manuals, see for example p. 82 of The New Glénans Sailing Manual. David & Charles. 1978. ISBN 0-7153-7470-2. Or see p. 32 and p. 122 of The New Complete Sailing Manual. Dorling Kindersley. 2005. ISBN 978-1-4053-0255-5.
- ↑ An explanation of how this applies to iceboats can be found at the bottom of the "FAQ published by the Four Lakes Ice Yacht Club". Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ High Performance Sailing, p. 204.
- ↑ The maximum multiple of windspeed is achieved at an angle of 90°+α off the true wind. For α = 45°, the maximum multiple of windspeed is 1.41 at an angle of 135° off the true wind.
- 1 2 Bethwaite, Frank (2007). High Performance Sailing. Adlard Coles Nautical. ISBN 978-0-7136-6704-2. (particularly chapter 16) has a very comprehensive explanation of all aspects of the topic.
- ↑ See the charts at the end of "the official measurement report". Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ See section 16.13 and in particular Figure 16.10 of the cited book High Performance Sailing, and more generally Chapter 24
- ↑ See the bottom of the "FAQ published by the Four Lakes Ice Yacht Club". Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ The values in the table are derived from the formulas shown in the section Vector diagrams and formulas
- ↑ A detailed explanation, with examples, can also be found in Figure 24.2 of the cited book High Performance Sailing
- ↑ Garrett, Ross (1996). The Symmetry of Sailing: The Physics of Sailing for Yachtsmen. Sheridan House, Inc. p. 268. ISBN 9781574090000.
- ↑ If a boat sails at an angle (β) to the true wind, then its velocity made good is cos( (β))*boat_speed.
- ↑ Zack Leonard (November 6, 2003). "Basic Downwind Performance, Part Two". SailNet. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ In such a situation, the boat is jibing with respect to the true wind, but it is tacking with respect to the apparent wind, because of the apparent wind shift.
- ↑ See Marchaj, Czeslaw Anthony (1979). Aero-hydrodynamics of Sailing. Dodd, Mead & Company, New York. See in particular Chapter I (High speed sailing, pp. 84-127) and Chapter H (Land and hard-water sailing craft, pp. 128-152) of Part 1. The latter contains speed polars along with the equations for maximum speeds and states that it can be expected that the maximum ratio of downwind VMG to true wind would be in the order of 2.1-2.6.
- ↑ "Animation demonstrating the principle of how it can be possible to go faster than the wind".
- ↑ "Dans le mille". Hydroptère. Archived from the original on September 21, 2010. Retrieved 2010-08-25. . Its velocity made good downwind was therefore about equal to the speed of the true wind.
- ↑ Bob Dill (November 2004). "Putting Numbers on Iceboat Performance" (PDF). North American Land Sailing Association. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ See in particular pages 3 and 4 of Bob Dill (March 2003). "Sailing Yacht Design for Maximum Speed" (PDF). Scuttlebutt.com. Retrieved 2010-06-21.
- ↑ "Training in Racing Mode". Consorcio Valencia. February 4, 2010. Archived from the original on July 11, 2012. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ "Friday the Third, PT 1?". Consorcio Valencia. February 11, 2010. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ Pierre Nusslé (February 13, 2010). "La démonstration de puissance d'Oracle brise le rêve d'Alinghi". Tribune de Genève. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ "First blood to USA – News – 33rd America's Cup". Consorsio Valencia. 2007-06-25. Archived from the original on 2012-05-31. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ "BMW ORACLE Racing Wins Race One". BMW ORACLE Racing. 2003-09-30. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ "America's Cup, the numbers of a victory". Yacht Online. Archived from the original on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2010-03-09.
- ↑ "USA win 33rd America's Cup Match – News – 33rd America's Cup". Consorcio Valencia. Archived from the original on 2011-07-07. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ "BMW ORACLE Racing crosses the finish line ahead in Race Two". BMW ORACLE Racing. 2003-09-30. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ See minute 30 of podcast interview with USA 17 designer Mike Drummond at "Oracle Racing's USA 17". Omega Tau. 20 July 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2011. ; a clear explanation of how the boat can sail downwind at more than twice the speed of the wind is given at minute 59 of the interview.
- 1 2 Yoav Raz (April 2009). "Sailboat speed Vs. wind speed". Amateur Yacht Research Society (Catalyst, Journal of the Amateur Yacht Research Society). Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ A good discussion of polar charts for sailboats can be found at Stan Honey and Jim Teeters (June 10, 2008). "Get Your Performance on Target". Sailing World. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ According to the polar chart in section 24.1 (Figure 24.1) of the cited book High Performance Sailing the 18ft Skiff can make good 13 knots downwind in 10 knots of wind and 20 knots in 15 knots of wind.
- ↑ Another good explanation of a polar chart, which indicates that a high-performance boat can make good downwind faster than the wind, is found at page 123 of The New Complete Sailing Manual. Dorling Kindersley. 2005. ISBN 978-1-4053-0255-5.
- 1 2 "Direct Downwind Record Attempts". NALSA. August 2, 2010. Retrieved August 6, 2010.
- ↑ Cort, Adam (April 5, 2010). "Running Faster than the Wind". sailmagazine.com. Retrieved April 6, 2010.
- ↑ Barry, Keith (June 2, 2010). "Wind Powered Car Travels Downwind Faster Than The Wind". wired.com. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ↑ Adam Fischer (February 28, 2011). "One Man's Quest to Outrace Wind". Wired.
Further reading
- Bethwaite, Frank (1993). High Performance Sailing. Waterline (1993), Thomas Reed Publications (1996, 1998, and 2001), and Adlard Coles Nautical (2003 and 2007). ISBN 978-0-7136-6704-2.
- This book provides a comprehensive description of technological developments up to 1993 that have permitted the developments of sailboats that can sail faster than the wind. It covers in particular the 18ft Skiff. It also covers in detail boat and sail handling techniques (course to sail, sail trim, handling waves, etc.) required to reach high speeds. Rod Carr, former British Olympic Sailing Team Manager stated: "[This book] represents a breakthrough in the way it related the theoretical aspects of wind, sea state and rig shape to the way a crew would sail and handle a boat during a race."