Hexachlorocyclohexane
Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) is any of several polyhalogenated organic compounds consisting of a six-carbon ring with one chlorine and one hydrogen attached to each carbon. There are many isomers for this structure, differing by the stereochemistry of the individual chlorine substituents on the cyclohexane. It is sometimes erroneously called "benzene hexachloride" (BHC). They have been used as models for analyzing the effects of different geometric positions of the large atoms with dipolar bonds on the stability of the cyclohexane conformation.[1] Some isomers are pesticides.
Common forms are:
- α-HCH (CAS RN: 319-84-6 ), or α-BHC, alpha-hexachlorocyclohexane, the only isomer that is optically active
- β-HCH (CAS RN: 319-85-7 ), or β-BHC, beta-hexachlorocyclohexane
- γ-HCH (CAS RN: 58-89-9 ), or γ-BHC, gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane, or lindane
- δ-HCH (CAS RN: 319-86-8 ), or δ-BHC, delta-hexachlorocyclohexane
- t-HCH (CAS RN: 608-73-1 ), or t-BHC, technical hexachlorocyclohexane
-hexachlorocyclohexane.svg.png)
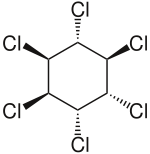
 δ-hexachlorocyclohexane.
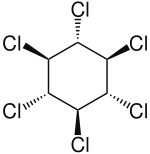
δ-hexachlorocyclohexane.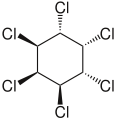 ε-hexachlorocyclohexane.
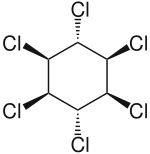
ε-hexachlorocyclohexane.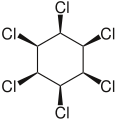 ζ-hexachlorocyclohexane.
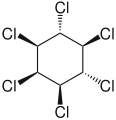
ζ-hexachlorocyclohexane. η-hexachlorocyclohexane.
η-hexachlorocyclohexane.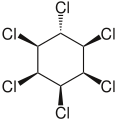 θ-hexachlorocyclohexane.
θ-hexachlorocyclohexane.
References
- ↑ Zdravkovski, Zoran (2004). "Theoretical Study of the Stability of Hexachloro- and Hexafluorocyclohexane Isomers" (PDF). Bulletin of the Chemists and Technologists of Macedonia. 23 (2): 131–137. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2005-12-28. Retrieved 2016-04-17.
External links
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.