Haematin
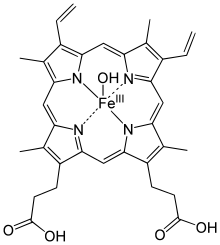
Structure of hematin
Haematin (also known as hematin, ferriheme, hematosin, hydroxyhemin, oxyheme, phenodin, or oxyhemochromogen) is a dark bluish or brownish pigment containing iron in the ferric state, obtained by the oxidation of haem.[1]
Haematin inhibits the synthesis of porphyrin, and stimulates the synthesis of globin. It is a component of cytochromes and peroxidases, and is also used as a reagent.[2]
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.