Healthcare in Europe
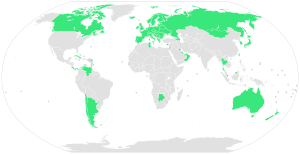
Most European countries have universal health coverage.
>90% health insurance coverage, and
>90% skilled birth attendance.

Healthcare in Europe is provided through a wide range of different systems run at the national level. The systems are primarily publicly funded through taxation (universal health care). Private funding may represent personal contributions towards meeting the non-taxpayer refunded portion of costs or may reflect totally private (non-subsidized) healthcare either paid out of pocket or met by some form of personal or employer funded insurance. Many European countries (and all European Union countries) offer their citizens a European Health Insurance Card which, on a reciprocal basis, provides insurance for emergency medical treatment insurance when visiting other participating European countries.
European Union
The European Union has no major administrative responsibility in the field of healthcare. The European Commission's Directorate-General for Health and Consumers however seeks to align national laws on the safety of food and other products, on consumers' rights and on the protection of people's health, to form new EU wide laws and thus strengthen its internal markets.
Healthcare rankings
| Country | Ranking | Total Score | Patient rights & Information | Accessibility (waiting times) | Outcomes | Range and reach of services provided | Prevention | Pharmaceuticals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 924 | 125 | 200 | 278 | 125 | 107 | 89 | |
| 2 | 898 | 117 | 225 | 278 | 94 | 101 | 83 | |
| 3 | 864 | 117 | 118 | 267 | 120 | 95 | 119 | |
| 4 | 850 | 125 | 125 | 289 | 115 | 119 | 78 | |
| 5 | 850 | 104 | 213 | 244 | 109 | 107 | 72 | |
| 6 | 856 | 108 | 150 | 289 | 120 | 101 | 78 | |
| 7 | 836 | 108 | 188 | 267 | 83 | 101 | 89 | |
| 8 | 832 | 108 | 213 | 233 | 115 | 95 | 72 | |
| 9 | 830 | 117 | 175 | 256 | 115 | 113 | 56 | |
| 10 | 825 | 104 | 188 | 256 | 99 | 95 | 83 | |
| 11 | 816 | 113 | 188 | 233 | 104 | 101 | 78 | |
| 12 | 807 | 113 | 113 | 278 | 125 | 101 | 78 | |
| 13 | 749 | 113 | 225 | 189 | 73 | 83 | 67 | |
| 14 | 747 | 108 | 137 | 233 | 89 | 107 | 72 | |
| 15 | 735 | 113 | 100 | 222 | 109 | 113 | 78 | |
| 16 | 726 | 108 | 163 | 211 | 89 | 83 | 72 | |
| 17 | 726 | 79 | 188 | 222 | 104 | 77 | 56 | |
| 18 | 695 | 88 | 113 | 222 | 94 | 107 | 72 | |
| 19 | 691 | 113 | 163 | 189 | 89 | 77 | 61 | |
| 20 | 673 | 104 | 200 | 167 | 57 | 89 | 56 | |
| 21 | 673 | 88 | 150 | 211 | 73 | 101 | 50 | |
| 22 | 649 | 108 | 200 | 133 | 63 | 89 | 56 | |
| 23 | 642 | 88 | 150 | 167 | 104 | 95 | 39 | |
| 24 | 630 | 75 | 88 | 211 | 78 | 95 | 83 | |
| 25 | 623 | 88 | 200 | 156 | 52 | 77 | 50 | |
| 26 | 620 | 96 | 138 | 178 | 94 | 65 | 50 | |
| 27 | 596 | 88 | 213 | 156 | 42 | 65 | 33 | |
| 28 | 587 | 104 | 138 | 156 | 68 | 77 | 44 | |
| 29 | 584 | 79 | 125 | 167 | 63 | 95 | 56 | |
| 30 | 584 | 79 | 138 | 156 | 78 | 89 | 44 | |
| 31 | 574 | 104 | 138 | 144 | 78 | 65 | 44 | |
| 32 | 569 | 58 | 125 | 200 | 52 | 83 | 50 | |
| 33 | 548 | 67 | 175 | 156 | 47 | 65 | 39 | |
| 34 | 439 | 71 | 113 | 122 | 52 | 48 | 33 | |
| x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Country | Overall ranking | Total score | Patient rights and information score | Accessibility (waiting times for treatment) score | Outcomes score | Range and reach of services score | Prevention score | Pharmaceuticals score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 927 | 122 | 200 | 288 | 125 | 107 | 86 | |
| 2 | 904 | 111 | 225 | 288 | 94 | 101 | 86 | |
| 3 | 865 | 125 | 138 | 288 | 115 | 119 | 81 | |
| 4 | 860 | 104 | 225 | 250 | 109 | 95 | 76 | |
| 5 | 854 | 115 | 163 | 288 | 115 | 113 | 62 | |
| 6 | 851 | 101 | 200 | 263 | 104 | 107 | 76 | |
| 7 | 849 | 104 | 188 | 288 | 83 | 101 | 86 | |
| 8 | 842 | 108 | 150 | 288 | 115 | 101 | 81 | |
| 9 | 827 | 111 | 150 | 275 | 115 | 95 | 81 | |
| 10 | 826 | 108 | 200 | 238 | 99 | 101 | 81 | |
| 11 | 815 | 90 | 188 | 263 | 94 | 95 | 86 | |
| 12 | 786 | 104 | 100 | 275 | 125 | 101 | 81 | |
| 13 | 780 | 87 | 213 | 238 | 104 | 77 | 62 | |
| 14 | 763 | 108 | 150 | 250 | 78 | 101 | 76 | |
| 15 | 761 | 108 | 100 | 250 | 109 | 113 | 81 | |
| 16 | 740 | 104 | 125 | 263 | 89 | 83 | 76 | |
| 17 | 729 | 108 | 163 | 238 | 94 | 65 | 62 | |
| 18 | 709 | 87 | 113 | 238 | 94 | 107 | 71 | |
| 19 | 703 | 108 | 175 | 188 | 104 | 71 | 57 | |
| 20 | 699 | 118 | 225 | 138 | 68 | 89 | 62 | |
| 21 | 689 | 80 | 100 | 250 | 78 | 95 | 86 | |
| 22 | 682 | 83 | 138 | 225 | 78 | 101 | 57 | |
| 23 | 678 | 97 | 163 | 175 | 89 | 83 | 71 | |
| 24 | 670 | 111 | 188 | 163 | 57 | 89 | 62 | |
| 25 | 666 | 80 | 163 | 188 | 94 | 95 | 48 | |
| 26 | 623 | 73 | 125 | 213 | 68 | 83 | 62 | |
| 27 | 620 | 97 | 175 | 163 | 68 | 65 | 52 | |
| 28 | 593 | 63 | 125 | 213 | 52 | 83 | 57 | |
| 29 | 589 | 87 | 113 | 188 | 73 | 77 | 52 | |
| 30 | 575 | 73 | 125 | 163 | 73 | 89 | 52 | |
| 31 | 564 | 66 | 100 | 188 | 63 | 95 | 52 | |
| 32 | 551 | 73 | 163 | 175 | 42 | 65 | 33 | |
| 33 | 526 | 66 | 150 | 150 | 47 | 65 | 48 | |
| 34 | 518 | 63 | 113 | 175 | 57 | 77 | 33 | |
| 35 | 497 | 80 | 150 | 125 | 52 | 48 | 43 | |
See also
References
- ↑ Stuckler, David; Feigl, Andrea B.; Basu, Sanjay; McKee, Martin (November 2010). "The political economy of universal health coverage. Background paper for the First Global Symposium on Health Systems Research, 16–19 November 2010, Montreaux, Switzerland" (PDF). Pacific Health Summit. Seattle: National Bureau of Asian Research. p. 16.
Figure 2. Global Prevalence of Universal Health Care in 2009; 58 countries: Andorra, Antigua, Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Botswana, Brunei Darussalam, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, Costa Rica, Croatia, Cuba, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Kuwait, Luxembourg, Moldova, Mongolia, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Oman, Panama, Portugal, Poland, Romania, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand, Tunisia, UAE, Ukraine, United Kingdom, Venezuela.
- ↑ Arna, Björnberg (2018). "Euro Health Consumer Index 2017" (PDF). Health Consumer Powerhouse. ISBN 978-91-980687-5-7.
- ↑ "Euro Health Consumer Index 2016" (PDF). Health Consumer Powerhouse. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ↑ http://www.who.int/whr/2010/en/index.html The world health report - Health systems financing: the path to universal coverage http://whqlibdoc.who.int/whr/2010/9789241564021_eng.pdf