Hawrami dialects
| Horami | |
|---|---|
| ھۆرامی | |
| Native to | Iraq and Iran |
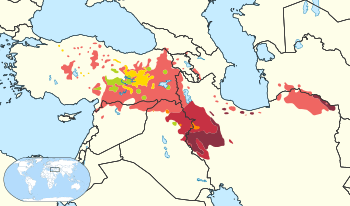
| Region | Hawraman |
Native speakers | 330,000 (2010)[1] |
| Dialects |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
hac (ambiguous with Gorani) |
| Glottolog |
hawr1242 Horaman-I Luhon[2]hawr1243 Horaman-I Taxt[3] |
 | |
Horami (ھۆرامی; Horamî) also known as Avromani, Awromani or Owrami, is one of the main groups of dialects of the Gorani language, a subgroup of Northwestern Iranian languages. Like all other Gorani varieties, it has some phonological features which distinguish it from the Kurdish languages, though it is surrounded by Kurdish dialects and has been affected by them.[4]
Etymology
It is regarded as the most archaic of the Gorani group.[5]
Dialects
The Horami dialects are:
- Lahuni (Lehûnî)
- Tekhti (Textî)
- Basarani (Bêsaranî)
- Halabjayi (Helebceyî)
- Shaykhani (Şeyxanî)
Demographics
According to a survey carried out by the Summer Institute of Linguistics in 1996 there were 200,000 speakers of Horami in the world.[6]
It is mostly spoken in the Hawraman region, a mountainous region located in western Iran (Iranian Kurdistan) and northeastern Iraq (Iraqi Kurdistan). The key cities of this region are Pawe in Iran and Halabja in Iraq. Horami is sometimes called Auramani or Horami by people foreign to the region.
Generally, the majority of Horami speakers can also speak Sorani Kurdish, and Arabic or Persian, in order to communicate with other people in neighboring cities.
Siya Cheman
Both the Zazas and Gorani speakers adhere to a form of Yazdânism or Ali-Illahism. Groups with similar beliefs also exist in all parts of Kurdistan.
Research
The notable professor Zare Yusupova, has carried out a lot of work and research into the Hawarami dialect (as well as many other minority/ancient Kurdish dialects).[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Horami at Ethnologue (16th ed., 2009)
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Horaman-I Luhon". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Horaman-I Taxt". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Hawrami dialects at Encyclopædia Iranica
- ↑ Hawrami dialects at Encyclopædia Iranica
- ↑ "THE KURDISH PEOPLES". Retrieved 2 July 2013.
- ↑ Leezenberg, M. (Jun 15, 2016). Soviet Kurdology and Kurdish Orientalism. researchgate.net. p. 10. Retrieved 24 Nov 2017.