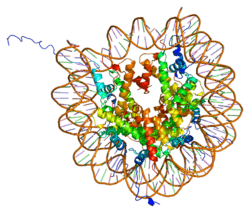
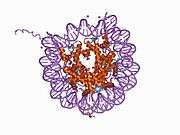
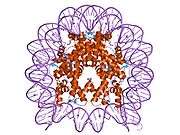
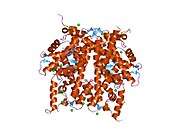
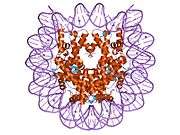
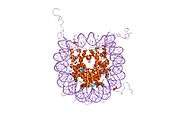
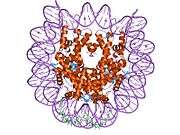
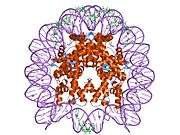
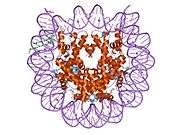
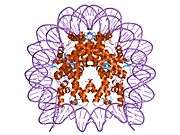
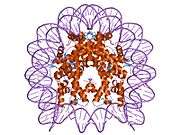
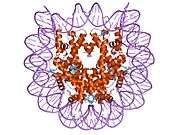
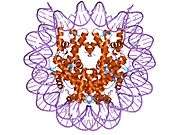
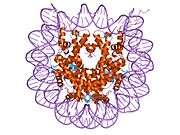
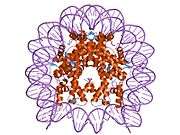
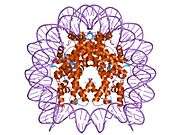
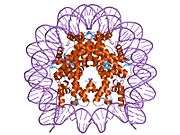
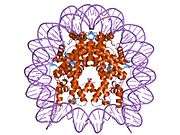
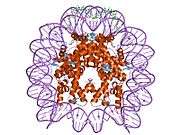
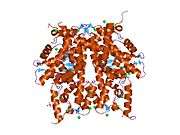
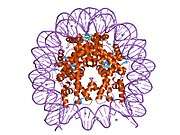
Histone H2B type 2-F is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST2H2BF gene.[5]
Further reading
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Cheung WL, Ajiro K, Samejima K, et al. (2003). "Apoptotic phosphorylation of histone H2B is mediated by mammalian sterile twenty kinase". Cell. 113 (4): 507–17. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00355-6. PMID 12757711.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Golebiowski F, Kasprzak KS (2007). "Inhibition of core histones acetylation by carcinogenic nickel(II)". Mol. Cell. Biochem. 279 (1–2): 133–9. doi:10.1007/s11010-005-8285-1. PMID 16283522.
- Zhu B, Zheng Y, Pham AD, et al. (2006). "Monoubiquitination of human histone H2B: the factors involved and their roles in HOX gene regulation". Mol. Cell. 20 (4): 601–11. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.09.025. PMID 16307923.
- Bonenfant D, Coulot M, Towbin H, et al. (2006). "Characterization of histone H2A and H2B variants and their post-translational modifications by mass spectrometry". Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 5 (3): 541–52. doi:10.1074/mcp.M500288-MCP200. PMID 16319397.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE, et al. (2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature. 441 (7091): 315–21. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
- Pavri R, Zhu B, Li G, et al. (2006). "Histone H2B monoubiquitination functions cooperatively with FACT to regulate elongation by RNA polymerase II". Cell. 125 (4): 703–17. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.029. PMID 16713563.
- Kim SC, Sprung R, Chen Y, et al. (2006). "Substrate and functional diversity of lysine acetylation revealed by a proteomics survey". Mol. Cell. 23 (4): 607–18. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.026. PMID 16916647.
PDB gallery |
|---|
1aoi: COMPLEX BETWEEN NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE (H3,H4,H2A,H2B) AND 146 BP LONG DNA FRAGMENT 1eqz: X-RAY STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE AT 2.5 A RESOLUTION 1f66: 2.6 A CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE CONTAINING THE VARIANT HISTONE H2A.Z 1hq3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HISTONE-CORE-OCTAMER IN KCL/PHOSPHATE 1kx3: X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP146, at 2.0 A Resolution 1kx4: X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP146b, at 2.6 A Resolution 1kx5: X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP147, at 1.9 A Resolution 1m18: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA 1m19: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA 1m1a: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA 1p34: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3a: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3b: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3f: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3g: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3i: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3k: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3l: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3m: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3o: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3p: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1s32: Molecular Recognition of the Nucleosomal 'Supergroove' 1tzy: Crystal Structure of the Core-Histone Octamer to 1.90 Angstrom Resolution 1u35: Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle containing the histone domain of macroH2A 1zbb: Structure of the 4_601_167 Tetranucleosome 1zla: X-ray Structure of a Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus LANA peptide bound to the nucleosomal core 2aro: Crystal Structure Of The Native Histone Octamer To 2.1 Angstrom Resolution, Crystalised In The Presence Of S-Nitrosoglutathione 2cv5: Crystal structure of human nucleosome core particle 2f8n: 2.9 Angstrom X-ray structure of hybrid macroH2A nucleosomes 2fj7: Crystal structure of Nucleosome Core Particle Containing a Poly (dA.dT) Sequence Element 2hio: HISTONE OCTAMER (CHICKEN), CHROMOSOMAL PROTEIN 2nzd: Nucleosome core particle containing 145 bp of DNA |