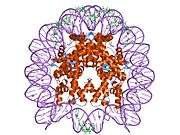
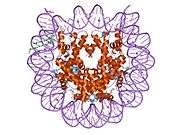
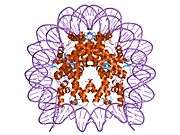
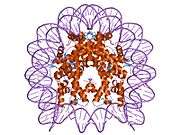
Histone H2A.J is a protein that in humans is encoded by the H2AFJ gene.[5]
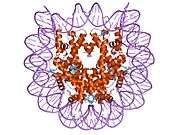
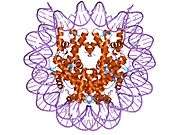
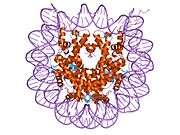
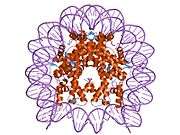
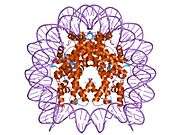
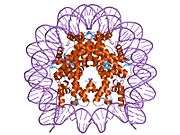
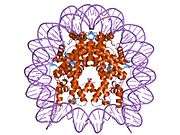
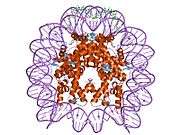
Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is located on chromosome 12 and encodes a variant H2A histone. The protein is divergent at the C-terminus compared to the consensus H2A histone family member.[5]
Further reading
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Lusic M, Marcello A, Cereseto A, Giacca M (2004). "Regulation of HIV-1 gene expression by histone acetylation and factor recruitment at the LTR promoter". EMBO J. 22 (24): 6550–61. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg631. PMC 291826. PMID 14657027.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Deng L, Wang D, de la Fuente C, et al. (2001). "Enhancement of the p300 HAT activity by HIV-1 Tat on chromatin DNA". Virology. 289 (2): 312–26. doi:10.1006/viro.2001.1129. PMID 11689053.
- Chadwick BP, Willard HF (2001). "Histone H2A variants and the inactive X chromosome: identification of a second macroH2A variant". Hum. Mol. Genet. 10 (10): 1101–13. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.10.1101. PMID 11331621.
- Deng L, de la Fuente C, Fu P, et al. (2001). "Acetylation of HIV-1 Tat by CBP/P300 increases transcription of integrated HIV-1 genome and enhances binding to core histones". Virology. 277 (2): 278–95. doi:10.1006/viro.2000.0593. PMID 11080476.
- El Kharroubi A, Piras G, Zensen R, Martin MA (1998). "Transcriptional activation of the integrated chromatin-associated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (5): 2535–44. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.5.2535. PMC 110633. PMID 9566873.
PDB gallery |
|---|
1aoi: COMPLEX BETWEEN NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE (H3,H4,H2A,H2B) AND 146 BP LONG DNA FRAGMENT 1eqz: X-RAY STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE AT 2.5 A RESOLUTION 1hq3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HISTONE-CORE-OCTAMER IN KCL/PHOSPHATE 1kx3: X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP146, at 2.0 A Resolution 1kx4: X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP146b, at 2.6 A Resolution 1kx5: X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP147, at 1.9 A Resolution 1m18: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA 1m19: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA 1m1a: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA 1p34: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3a: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3b: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3f: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3g: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3i: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3k: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3l: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3m: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3o: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1p3p: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants 1s32: Molecular Recognition of the Nucleosomal 'Supergroove' 1tzy: Crystal Structure of the Core-Histone Octamer to 1.90 Angstrom Resolution 1zbb: Structure of the 4_601_167 Tetranucleosome 1zla: X-ray Structure of a Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus LANA peptide bound to the nucleosomal core 2aro: Crystal Structure Of The Native Histone Octamer To 2.1 Angstrom Resolution, Crystalised In The Presence Of S-Nitrosoglutathione 2cv5: Crystal structure of human nucleosome core particle 2f8n: 2.9 Angstrom X-ray structure of hybrid macroH2A nucleosomes 2fj7: Crystal structure of Nucleosome Core Particle Containing a Poly (dA.dT) Sequence Element 2hio: HISTONE OCTAMER (CHICKEN), CHROMOSOMAL PROTEIN 2nzd: Nucleosome core particle containing 145 bp of DNA |