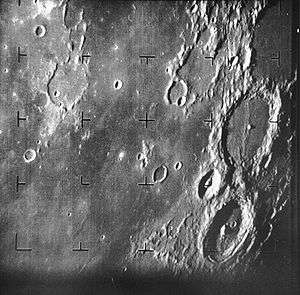
Guericke (crater)
 Apollo 16 mapping camera image | |
| Coordinates | 11°30′S 14°06′W / 11.5°S 14.1°WCoordinates: 11°30′S 14°06′W / 11.5°S 14.1°W |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 60.75 km[1] |
| Depth | 0.7 km |
| Colongitude | 14° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Otto von Guericke |

Guericke is the remnant of a lunar impact crater at the north part of the Mare Nubium and is named after Otto von Guericke. To the north-northwest lies the large Fra Mauro crater, along with the co-joined craters Parry and Bonpland. To the east are the craters Kundt and Davy. West-southwest is Darney, in between is Rimae Opelt which is a rim, the crater itself is nearly to the southwest.
The surviving rim of Guericke has been worn, battered, and partly submerged by the basaltic lava that covers the floor. The wall is now little more than a circular series of ridges that join with rises that flow to the north, northwest, and south. The flooded crater remnant Guericke F is attached to the southwest exterior. The interior flood has a few small rises in the otherwise nearly flat surface. Two craters (Guericke D and H) mark the floor in the southwest quadrant.
Northeast of the main crater are Guericke J and S makes up of the 18-km-long "figure 8" pair of noncircular craters probably was not formed by hypervelocity impacts of bodies from space. It could be a secondary impact feature formed by projectiles from the Imbrium basin 700 km to the north.
Guericke was one of the lunar features in the Ranger 7 image which was the first lunar image by an American spacecraft made on March 24, 1965.
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Guericke.
| Guericke | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 11.1° S | 17.3° W | 5 km |
| B | 14.5° S | 15.3° W | 16 km |
| D | 12.0° S | 14.6° W | 8 km |
| E | 10.0° S | 12.0° W | 4 km |
| F | 12.2° S | 15.3° W | 21 km |
| G | 14.0° S | 15.0° W | 5 km |
| H | 12.4° S | 14.2° W | 6 km |
| J | 10.6° S | 13.4° W | 8 km |
| K | 15.1° S | 13.3° W | 3 km |
| M | 12.9° S | 12.5° W | 2 km |
| N | 12.5° S | 9.9° W | 3 km |
| P | 15.0° S | 14.6° W | 3 km |
| S | 10.3° S | 13.3° W | 11 km |
 Guericke B from Lunar Orbiter 4
Guericke B from Lunar Orbiter 4 Guericke B from Apollo 16
Guericke B from Apollo 16
The following craters have been renamed by the IAU.
- Guericke C — See Kundt.
References
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Guericke (crater). |
Related article
- Wood, Chuck (May 12, 2006). "LPOD is Back Again". Lunar Photo of the Day. Archived from the original on October 8, 2017.