Greater palatine foramen
| Greater palatine foramen | |
|---|---|
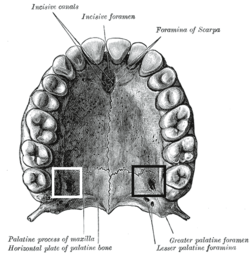 Permanent teeth of upper dental arch, seen from below. (Greater palatine foramen labeled at lower right.) | |
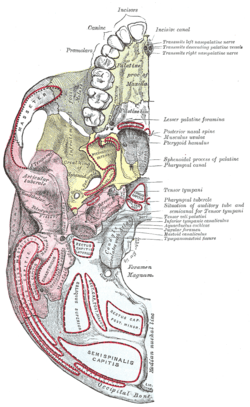 Base of skull. Inferior surface. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen palatinum majus |
| TA | A02.1.00.058 |
| FMA | 53173 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
At either posterior angle of the hard palate is the greater palatine foramen, for the transmission of the descending palatine vessels and greater palatine nerve; and running anteriorly (forward) and medially (towards the center-line) from it is a groove, for the same vessels and nerve.
Variations

Greater palatine foramen
The greater palatine foramen (GPF) is related to the upper 3rd molar tooth in most of the skulls (55%), 2nd molar in (12%), between the 2nd and 3rd molar in (19%) and retromolar in (14%). The shape of the foramen is elongated antero-posteriorly; however, an unusually crescent shaped foramen is rare.[1]
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 180 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ Akram Abood Jaffar. "Anatomical variations – Greater palatine foramen". Archived from the original on 2009-10-25.
External links
- Anatomy photo:22:os-0607 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- "Anatomy diagram: 05287.011-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.