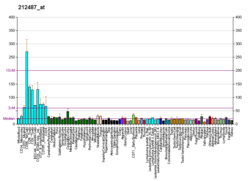
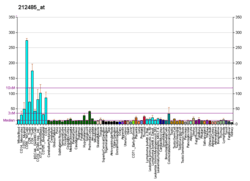
G patch domain-containing protein 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPATCH8 gene.[5][6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000186566 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000034621 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (Aug 1998). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. IX. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 5 (1): 31–9. doi:10.1093/dnares/5.1.31. PMID 9628581.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: GPATCH8 G patch domain containing 8".
- ↑ Kaneko H, Kitoh H, Matsuura T, Masuda A, Ito M, Mottes M, Rauch F, Ishiguro N, Ohno K (Nov 2011). "Hyperuricemia cosegregating with osteogenesis imperfecta is associated with a mutation in GPATCH8". Hum. Genet. 130 (5): 671–83. doi:10.1007/s00439-011-1006-9. PMID 21594610.
Further reading
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, Patel AJ, Szabó G, Rual JF, Fisk CJ, Li N, Smolyar A, Hill DE, Barabási AL, Vidal M, Zoghbi HY (2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell. 125 (4): 801–14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569.
- Nousiainen M, Silljé HH, Sauer G, Nigg EA, Körner R (2006). "Phosphoproteome analysis of the human mitotic spindle". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (14): 5391–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507066103. PMC 1459365. PMID 16565220.
- McKinney JL, Murdoch DJ, Wang J, Robinson J, Biltcliffe C, Khan HM, Walker PM, Savage J, Skerjanc I, Hegele RA (2005). "Venn analysis as part of a bioinformatic approach to prioritize expressed sequence tags from cardiac libraries". Clin. Biochem. 37 (11): 953–60. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2004.07.010. PMID 15498521.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, Elias JE, Villén J, Li J, Cohn MA, Cantley LC, Gygi SP (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Thornton MA, Poncz M, Korostishevsky M, Yakobson E, Usher S, Seligsohn U, Peretz H (1999). "The human platelet alphaIIb gene is not closely linked to its integrin partner beta3". Blood. 94 (6): 2039–47. PMID 10477733.